Abstract
Discriminant validity assessment has become a generally accepted prerequisite for analyzing relationships between latent variables. For variance-based structural equation modeling, such as partial least squares, the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the examination of cross-loadings are the dominant approaches for evaluating discriminant validity. By means of a simulation study, we show that these approaches do not reliably detect the lack of discriminant validity in common research situations. We therefore propose an alternative approach, based on the multitrait-multimethod matrix, to assess discriminant validity: the heterotrait-monotrait ratio of correlations. We demonstrate its superior performance by means of a Monte Carlo simulation study, in which we compare the new approach to the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the assessment of (partial) cross-loadings. Finally, we provide guidelines on how to handle discriminant validity issues in variance-based structural equation modeling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Variance-based structural equation modeling (SEM) is growing in popularity, which the plethora of recent developments and discussions (e.g., Henseler et al. 2014; Hwang et al. 2010; Lu et al. 2011; Rigdon 2014; Tenenhaus and Tenenhaus 2011), as well as its frequent application across different disciplines, demonstrate (e.g., Hair et al. 2012a, b; Lee et al. 2011; Peng and Lai 2012; Ringle et al. 2012). Variance-based SEM methods—such as partial least squares path modeling (PLS; Lohmöller 1989; Wold 1982), generalized structured component analysis (GSCA; Henseler 2012; Hwang and Takane 2004), regularized generalized canonical correlation analysis (Tenenhaus and Tenenhaus 2011), and best fitting proper indices (Dijkstra and Henseler 2011)—have in common that they employ linear composites of observed variables as proxies for latent variables, in order to estimate model relationships. The estimated strength of these relationships, most notably between the latent variables, can only be meaningfully interpreted if construct validity was established (Peter and Churchill 1986). Thereby, researchers ensure that the measurement models in their studies capture what they intend to measure (Campbell and Fiske 1959). Threats to construct validity stem from various sources. Consequently, researchers must employ different construct validity subtypes to evaluate their results (e.g., convergent validity, discriminant validity, criterion validity; Sarstedt and Mooi 2014).
In this paper, we focus on examining discriminant validity as one of the key building blocks of model evaluation (e.g.,Bagozzi and Phillips 1982; Hair et al. 2010). Discriminant validity ensures that a construct measure is empirically unique and represents phenomena of interest that other measures in a structural equation model do not capture (Hair et al. 2010). Technically, discriminant validity requires that “a test not correlate too highly with measures from which it is supposed to differ” (Campbell 1960, p. 548). If discriminant validity is not established, “constructs [have] an influence on the variation of more than just the observed variables to which they are theoretically related” and, as a consequence, “researchers cannot be certain results confirming hypothesized structural paths are real or whether they are a result of statistical discrepancies” (Farrell 2010, p. 324). Against this background, discriminant validity assessment has become common practice in SEM studies (e.g., Shah and Goldstein 2006; Shook et al. 2004).
Despite its obvious importance, researchers using variance-based SEM usually rely on a very limited set of approaches to establish discriminant validity. As shown in Table 1, tutorial articles and introductory books on PLS almost solely recommend using the Fornell and Larcker (1981) criterion and cross-loadings (Chin 1998). Reviews of PLS use suggest that these recommendations have been widely applied in published research in the fields of management information systems (Ringle et al. 2012), marketing (Hair et al. 2012a), and strategic management (Hair et al. 2012b). For example, the marketing studies in Hair et al.'s (2012a) review that engage in some type of discriminant validity assessment use the Fornell-Larcker criterion (72.08%), cross-loadings (7.79%), or both (26.13%). Reviews in other disciplines paint a similar monotonous picture. Very few studies report other means of assessing discriminant validity. These alternatives include testing whether the latent variable correlations are significantly different from one another (Milberg et al. 2000) and running separate confirmatory factor analyses prior to employing variance-based SEM (Cording et al. 2008; Pavlou et al. 2007; Ravichandran and Rai 2000) by using, for example, Anderson and Gerbing's (1988) test as the standard.Footnote 1
While marketing researchers routinely rely on the Fornell-Larcker criterion and cross-loadings (Hair et al. 2012a), there are very few empirical findings on the suitability of these criteria for establishing discriminant validity. Recent research suggests that the Fornell-Larcker criterion is not effective under certain circumstances (Henseler et al. 2014; Rönkkö and Evermann 2013), pointing to a potential weakness in the most commonly used discriminant validity criterion. However, these studies do not provide any systematic assessment of the Fornell-Larcker criterion’s efficacy regarding testing discriminant validity. Furthermore, while researchers frequently note that cross-loadings are more liberal in terms of indicating discriminant validity (i.e., the assessment of cross-loadings will support discriminant validity when the Fornell-Larcker criterion fails to do so; Hair et al. 2012a, b; Henseler et al. 2009), prior research has not yet tested this notion.
In this research, we present three major contributions to variance-based SEM literature on marketing that are relevant for the social sciences disciplines in general. First, we show that neither the Fornell-Larcker criterion nor the assessment of the cross-loadings allows users of variance-based SEM to determine the discriminant validity of their measures. Second, as a solution for this critical issue, we propose the heterotrait-monotrait ratio of correlations (HTMT) as a new approach to assess discriminant validity in variance-based SEM. Third, we demonstrate the efficacy of HTMT by means of a Monte Carlo simulation, in which we compare its performance with that of the Fornell-Larcker criterion and with the assessment of the cross-loadings. Based on our findings, we provide researchers with recommendations on when and how to use the approach. Moreover, we offer guidelines for treating discriminant validity problems. The findings of this research are relevant for both researchers and practitioners in marketing and other social sciences disciplines, since we establish a new standard means of assessing discriminant validity as part of measurement model evaluation in variance-based SEM.
Traditional discriminant validity assessment methods
Comparing average communality and shared variance
In their widely cited article on tests to evaluate structural equation models, Fornell and Larcker (1981) suggest that discriminant validity is established if a latent variable accounts for more variance in its associated indicator variables than it shares with other constructs in the same model. To satisfy this requirement, each construct’s average variance extracted (AVE) must be compared with its squared correlations with other constructs in the model. According to Gefen and Straub (2005, p. 94), “[t]his comparison harkens back to the tests of correlations in multi-trait multi-method matrices [Campbell and Fiske, 1959], and, indeed, the logic is quite similar.”
The AVE represents the average amount of variance that a construct explains in its indicator variables relative to the overall variance of its indicators. The AVE for construct ξ j is defined as follows:
where λ jk is the indicator loading and Θ jk the error variance of the k th indicator (k = 1,…,K j ) of construct ξ j . K j is the number of indicators of construct ξ j . If all the indicators are standardized (i.e., have a mean of 0 and a variance of 1), Eq. 1 simplifies to
The AVE thus equals the average squared standardized loading, and it is equivalent to the mean value of the indicator reliabilities. Now, let r ij be the correlation coefficient between the construct scores of constructs ξ i and ξ j The squared inter-construct correlation r 2 ij indicates the proportion of the variance that constructs ξ i and ξ j share. The Fornell-Larcker criterion then indicates that discriminant validity is established if the following condition holds:
Since it is common to report inter-construct correlations in publications, a different notation can be found in most reports on discriminant validity:
From a conceptual perspective, the application of the Fornell-Larcker criterion is not without limitations. For example, it is well known that variance-based SEM methods tend to overestimate indicator loadings (e.g., Hui and Wold 1982; Lohmöller 1989). The origin of this characteristic lies in the methods’ treatment of constructs. Variance-based SEM methods, such as PLS or GSCA, use composites of indicator variables as substitutes for the underlying constructs (Henseler et al. 2014). The loading of each indicator on the composite represents a relationship between the indicator and the composite of which the indicator is part. As a result, the degree of overlap between each indicator and composite will be high, yielding inflated loading estimates, especially if the number of indicators per construct (composite) is small (Aguirre-Urreta et al. 2013).Footnote 2 Furthermore, each indicator’s error variance is also included in the composite (e.g., Bollen and Lennox 1991), which increases the validity gap between the construct and the composite (Rigdon 2014) and, ultimately, compounds the inflation in the loading estimates. Similar to the loadings, variance-based SEM methods generally underestimate structural model relationships (e.g., Reinartz et al. 2009; Marcoulides, Chin, and Saunders 2012). While these deviations are usually relatively small (i.e., less than 0.05; Reinartz et al. 2009), the interplay between inflated AVE values and deflated structural model relationships in the assessment of discriminant validity has not been systematically examined. Furthermore, the Fornell-Larcker criterion does not rely on inference statistics and, thus, no procedure for statistically testing discriminant validity has been developed to date.
Assessing cross-loadings
Another popular approach for establishing discriminant validity is the assessment of cross-loadings, which is also called “item-level discriminant validity.” According to Gefen and Straub (2005, p. 92), “discriminant validity is shown when each measurement item correlates weakly with all other constructs except for the one to which it is theoretically associated.” This approach can be traced back to exploratory factor analysis, where researchers routinely examine indicator loading patterns to identify indicators that have high loadings on the same factor and those that load highly on multiple factors (i.e., double-loaders; Mulaik 2009).
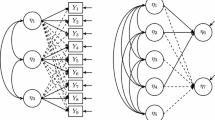
In the case of PLS, Barclay et al. (1995), as well as Chin (1998), were the first to propose that each indicator loading should be greater than all of its cross-loadings.Footnote 3 Otherwise, “the measure in question is unable to discriminate as to whether it belongs to the construct it was intended to measure or to another (i.e., discriminant validity problem)” (Chin 2010, p. 671). The upper part a) of Fig. 1 illustrates this cross-loadings approach.
However, there has been no reflection on this approach’s usefulness in variance-based SEM. Apart from the norm that an item should be highly correlated with its own construct, but have low correlations with other constructs in order to establish discriminant validity at the item level, no additional theoretical arguments or empirical evidence of this approach’s performance have been presented. In contrast, research on covariance-based SEM has critically reflected on the approach’s usefulness for discriminant validity assessment. For example, Bollen (1989) shows that high inter-construct correlations can cause a pronounced spurious correlation between a theoretically unrelated indicator and construct. The paucity of research on the efficacy of cross-loadings in variance-based SEM is problematic, because the methods tend to overestimate indicator loadings due to their reliance on composites. At the same time, the introduction of composites as substitutes for latent variables leaves cross-loadings largely unaffected. The majority of variance-based SEM methods are limited information approaches, estimating model equations separately, so that the inflated loadings are only imperfectly introduced in the cross-loadings. Therefore, the very nature of algorithms, such as PLS, favors the support of discriminant validity as described by Barclay et al. (1995) and Chin (1998).
Another major drawback of the aforementioned approach is that it is a criterion, but not a statistical test. However, it is also possible to conduct a statistical test of other constructs’ influence on an indicator using partial cross-loadings.Footnote 4 The partial cross-loadings determine the effect of a construct on an indicator other than the one the indicator is intended to measure after controlling for the influence of the construct that the indicator should measure. Once the influence of the actual construct has been partialed out, the residual error variance should be pure random error according to the reflective measurement model:
If ε jk is explained by another variable (i.e., the correlation between the error term of an indicator and another construct is significant), we can no longer maintain the assumption that ε jk is pure random error but must acknowledge that part of the measurement error is systematic error. If this systematic error is due to another construct ξ i , we must conclude that the indicator does not indiscriminately measure its focal construct ξ j , but also the other construct ξ i , which implies a lack of discriminant validity. The lower part b) of Fig. 1 illustrates the working principle of the significance test of partial cross-loadings.
While this approach has not been applied in the context of variance-based SEM, its use is common in covariance-based SEM, where it is typically applied in the form of modification indices. Substantial modification indices point analysts to the correlations between indicator error terms and other constructs, which are nothing but partial correlations.
An initial assessment of traditional discriminant validity methods
Although the Fornell-Larcker criterion was established more than 30 years ago, there is virtually no systematic examination of its efficacy for assessing discriminant validity. Rönkkö and Evermann (2013) were the first to point out the Fornell-Larcker criterion’s potential problems. Their simulation study, which originally evaluated the performance of model validation indices in PLS, included a population model with two identical constructs. Despite the lack of discriminant validity, the Fornell-Larcker criterion indicated this problem in only 54 of the 500 cases (10.80%). This result implies that, in the vast majority of situations that lack discriminant validity, empirical researchers would mistakenly be led to believe that discriminant validity has been established. Unfortunately, Rönkkö and Evermann’s (2013) study does not permit drawing definite conclusions about extant approaches’ efficacy for assessing discriminant validity for the following reasons: First, their calculation of the AVE—a major ingredient of the Fornell-Larcker criterion—was inaccurate, because they determined one overall AVE value instead of two separate AVE values; that is, one for each construct (Henseler et al. 2014).Footnote 5 Second, Rönkkö and Evermann (2013) did not examine the performance of the cross-loadings assessment.
In order to shed light on the Fornell-Larcker criterion’s efficacy, as well as on that of the cross-loadings, we conducted a small simulation study. We randomly created 10,000 datasets with 100 observations, each according to the one-factor population model shown in Fig. 2, which Rönkkö and Evermann (2013) and Henseler et al. (2014) also used. The indicators have standardized loadings of 0.60, 0.70, and 0.80, analogous to the loading patterns employed in previous simulation studies on variance-based SEM (e.g., Goodhue et al. 2012; Henseler and Sarstedt 2013; Reinartz et al. 2009).
To assess the performance of traditional methods regarding detecting (a lack of) discriminant validity, we split the construct in Fig. 2 into two separate constructs, which results in a two-factor model as depicted in Fig. 3. We then used the artificially generated datasets from the population model in Fig. 2 to estimate the model shown in Fig. 3 by means of the variance-based SEM techniques GSCA and PLS. We also benchmarked their results against those of regressions with summed scales, which is an alternative method for estimating relationships between composites (Goodhue et al. 2012). No matter which technique is used to estimate the model parameters, the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the assessment of the cross-loadings should reveal that the one-factor model rather than the two-factor model is preferable.
Table 2 shows the results of this initial study. The reported percentage values denote the approaches’ sensitivity, indicating their ability to identify a lack of discriminant validity (Macmillan and Creelman 2004). For example, when using GSCA for model estimation, the Fornell-Larcker criterion points to a lack of discriminant validity in only 10.66% of the simulation runs.
The results of this study render the following main findings: First, we can generally confirm Rönkkö and Evermann’s (2013) report on the Fornell-Larcker criterion’s extremely poor performance in PLS, even though our study’s concrete sensitivity value is somewhat higher (14.59% instead of 10.80%).Footnote 6 In addition, we find that the sensitivity of the cross-loadings regarding assessing discriminant validity is 8.78% in respect of GSCA and, essentially, zero in respect of PLS and regression with summed scales. These results allow us to conclude that both the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the assessment of the cross-loadings are insufficiently sensitive to detect discriminant validity problems. As we will show later in the paper, this finding can be generalized to alternative model settings with different loading patterns, inter-construct correlations, and sample sizes. Second, our results are not due to a certain method’s characteristics, because we used different model estimation techniques. Although the results differ slightly across the three methods (Table 2), we find that the general pattern remains stable. In conclusion, the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the assessment of the cross-loadings fail to reliably uncover discriminant validity problems in variance-based SEM.
The heterotrait-monotrait ratio of the correlations approach to assess discriminant validity
Traditional approaches’ unacceptably low sensitivity regarding assessing discriminant validity calls for an alternative criterion. In the following, we derive such a criterion from the classical multitrait-multimethod (MTMM) matrix (Campbell and Fiske 1959), which permits a systematic discriminant validity assessment to establish construct validity. Surprisingly, the MTMM matrix approach has hardly been applied in variance-based SEM (for a notable exception see Loch et al. 2003).
The application of the MTMM matrix approach requires at least two constructs (“multiple traits”) originating from the same respondents. The MTMM matrix is a particular arrangement of all the construct measures’ correlations. Campbell and Fiske (1959) distinguish between four types of correlations, two of which are relevant for discriminant validity assessment. First, the monotrait-heteromethod correlations quantify the relationships between two measurements of the same construct by means of different methods (i.e., items). Second, the heterotrait-heteromethod correlations quantify the relationships between two measurements of different constructs by means of different methods (i.e., items). Figure 4 visualizes the structuring of these correlations types by means of a small example (Fig. 3) with two constructs (ξ 1 and ξ 2) measured with three items each (x 1 to x 3 and x 4 to x 6). Since the MTMM matrix is symmetric, only the lower triangle needs to be considered. The monotrait-heteromethod correlations subpart includes the correlations of indicators that belong to the same construct. In our example, these are the correlations between the indicators x 1 to x 3 and between the indicators x 4 to x 6, as the two triangles in Fig. 4 indicate. The heterotrait-heteromethod correlations subpart includes the correlations between the different constructs’ indicators. In the example in Fig. 4, the heterotrait-heteromethod correlations subpart consists of the nine correlations between the indicators of the construct ξ 1 (i.e., x 1 to x 3) and those of the construct ξ 2 (i.e., x 4 to x 6), which are indicated by a rectangle.
The MTMM matrix analysis provides evidence of discriminant validity when the monotrait-heteromethod correlations are larger than the heterotrait-heteromethod correlations (Campbell and Fiske 1959; John and Benet-Martínez 2000). That is, the relationships of the indicators within the same construct are stronger than those of the indicators across constructs measuring different phenomena, which implies that a construct is empirically unique and a phenomenon of interest that other measures in the model do not capture.
While this rule is theoretically sound, it is problematic in empirical research practice. First, there is a large potential for ambiguities. What if the order is not as expected in only a few incidents? It cannot be ruled out that some heterotrait-heteromethod correlations exceed monotrait-heteromethod correlations, although the two constructs do in fact differ (Schmitt and Stults 1986). Second, one-by-one comparisons of values in large correlation matrices can quickly become tedious, which may be one reason for the MTMM matrix analysis not being a standard approach to assess discriminant validity in variance-based SEM.
We suggest assessing the heterotrait-monotrait ratio (HTMT) of the correlations, which is the average of the heterotrait-heteromethod correlations (i.e., the correlations of indicators across constructs measuring different phenomena), relative to the average of the monotrait-heteromethod correlations (i.e., the correlations of indicators within the same construct). Since there are two monotrait-heteromethod submatrices, we take the geometric mean of their average correlations. Consequently, the HTMT of the constructs ξ i and ξ j with, respectively, K i and K j indicators can be formulated as follows:
In essence, as suggested by Nunnally (1978) and Netemeyer et al. (2003), the HTMT approach is an estimate of the correlation between the constructs ξ i and ξ j (see the Appendix for the derivation), which parallels the disattenuated construct score correlation. Technically, the HTMT provides two advantages over the disattenuated construct score correlation: The HTMT does not require a factor analysis to obtain factor loadings, nor does it require the calculation of construct scores. This allows for determining the HTMT even if the raw data is not available, but the correlation matrix is. Furthermore, HTMT builds on the available measures and data and—contrary to the standard MTMM approach—does not require simultaneous surveying of the same theoretical concept with alternative measurement approaches. Therefore, this approach does not suffer from the standard MTMM approach’s well-known issues regarding data requirements and parallel measures (Schmitt 1978; Schmitt and Stults 1986).
Because the HTMT is an estimate of the correlation between the constructs ξ i and ξ j , its interpretation is straightforward: if the indicators of two constructs ξ i and ξ j exhibit an HTMT value that is clearly smaller than one, the true correlation between the two constructs is most likely different from one, and they should differ. There are two ways of using the HTMT to assess discriminant validity: (1) as a criterion or (2) as a statistical test. First, using the HTMT as a criterion involves comparing it to a predefined threshold. If the value of the HTMT is higher than this threshold, one can conclude that there is a lack of discriminant validity. The exact threshold level of the HTMT is debatable; after all, “when is a correlation close to one”? Some authors suggest a threshold of 0.85 (Clark and Watson 1995; Kline 2011), whereas others propose a value of 0.90 (Gold et al. 2001; Teo et al. 2008). In the remainder of this paper, we use the notations HTMT.85 and HTMT.90 in order distinguish between these two absolute thresholds for the HTMT. Second, the HTMT can serve as the basis of a statistical discriminant validity test (which we will refer to as HTMTinference). The bootstrapping procedure allows for constructing confidence intervals for the HTMT, as defined in Eq. 6, in order to test the null hypothesis (H0: HTMT ≥ 1) against the alternative hypothesis (H1: HTMT < 1).Footnote 7 A confidence interval containing the value one (i.e., H0 holds) indicates a lack of discriminant validity. Conversely, if the value one falls outside the interval’s range, this suggests that the two constructs are empirically distinct. As Shaffer (1995, p. 575) notes, “[t]esting with confidence intervals has the advantage that they give more information by indicating the direction and something about the magnitude of the difference or, if the hypothesis is not rejected, the power of the procedure can be gauged by the width of the interval.”
In real research situations with multiple constructs, the HTMTinference analysis involves the multiple testing problem (Miller 1981). Thus, researchers must control for an inflation of Type I errors resulting from applying multiple tests to pairs of constructs. That is, discriminant validity assessment using HTMTinference needs to adjust the upper and lower bounds of the confidence interval in each test to maintain the familywise error rate at a predefined α level (Anderson and Gerbing 1988). We use the Bonferroni adjustment to assure that the familywise error rate of HTMTinference does not exceed the predefined α level in all the (J–1) J/2 (J = number of latent variables) tests. The Bonferroni approach does not rely on any distributional assumptions about the data, making it particularly suitable in the context of variance-based SEM techniques such as PLS (Gudergan et al. 2008). Furthermore, Bonferroni is a rather conservative approach to maintain the familywise error rate at a predefined level (Hochberg 1988; Holm 1979). Its implementation therefore also renders HTMTinference more conservative in terms of its sensitivity assessment (compared to other multiple testing approaches), which seems warranted given the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the cross-loadings’ poor performance in the previous simulation study.
Comparing the approaches by means of a computational experiment
Objectives
To examine the different approaches’ efficacy for establishing discriminant validity, we conduct a second Monte Carlo simulation study. The aims of this study are (1) to shed further light on the performance of the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the cross-loadings in alternative model settings and (2) to evaluate the newly proposed HTMT criteria’s efficacy for assessing discriminant validity vis-à-vis traditional approaches. We measure the approaches’ performance by means of their sensitivity and specificity (Macmillan and Creelman 2004). The sensitivity, as introduced before, quantifies each approach’s ability to detect a lack of discriminant validity if two constructs are identical. The specificity indicates how frequently an approach will signal discriminant validity if the two constructs are empirically distinct. Both sensitivity and specificity are desirable characteristics and, optimally, an approach should yield high values in both measures. In real research situations, however, it is virtually impossible to achieve perfect sensitivity and perfect specificity simultaneously due to, for example, measurement or sampling errors. Instead, approaches with a higher sensitivity will usually have a lower specificity and vice versa. Researchers thus face a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, and need to find a find a balance between the two (Macmillan and Creelman 2004).
Experimental design and analysis
The design of the Monte Carlo simulation was motivated by the objective to define models that (1) allow for the assessment of approaches’ sensitivity and specificity with regard to detecting a lack of discriminant validity and (2) resemble set-ups commonly encountered in applied research (Paxton et al. 2001). In line with Rönkkö and Evermann (2013), as well as Henseler et al. (2014), the simulation study’s population model builds on a two-construct model, as shown in Fig. 3. Drawing on the results of prior PLS reviews (e.g., Hair et al. 2012a; Ringle et al. 2012), we vary the indicator loading patterns to allow for (1) different levels of the AVE and (2) varying degrees of heterogeneity between the loadings. Specifically, we consider four loading patterns for each of the two constructs:
-
1.
A homogenous pattern of loadings with higher AVE:
$$ {\lambda}_{11}={\lambda}_{12}={\lambda}_{13}={\lambda}_{21}={\lambda}_{22}={\lambda}_{23}=.90; $$ -
2.
A homogenous pattern of loadings with lower AVE:
$$ {\lambda}_{11}={\lambda}_{12}={\lambda}_{13}={\lambda}_{21}={\lambda}_{22}={\lambda}_{23}=.70; $$ -
3.
A more heterogeneous pattern of loadings with lower AVE:
$$ {\lambda}_{11}={\lambda}_{21}=.60,{\lambda}_{12}={\lambda}_{22}=.70,{\lambda}_{13}={\lambda}_{23}=.80; $$ -
4.
A more heterogeneous pattern of loadings with lower AVE:
$$ {\lambda}_{11}={\lambda}_{21}=.50,{\lambda}_{12}={\lambda}_{22}=.70,{\lambda}_{13}={\lambda}_{23}=.90. $$
Next, we examine how different sample sizes—as routinely assumed in simulation studies in SEM in general (Paxton et al. 2001) and in variance-based SEM in particular (e.g., Reinartz et al. 2009; Vilares and Coelho 2013)—would influence the approaches’ efficacy. We consider sample sizes of 100, 250, 500, and 1,000.
Finally, in order to examine the sensitivity and specificity of the approaches, we vary the inter-construct correlations. First, to examine their sensitivity, we consider a situation in which the two constructs are perfectly correlated (φ = 1.0). This condition mirrors a situation in which an analyst mistakenly models two constructs, although they actually form a single construct. Optimally, all the approaches should indicate a lack of discriminant validity under this condition. Second, to examine the approaches’ specificity, we decrease the inter-construct correlations in 50 steps of 0.02 from φ = 1.00 to φ = 0.00, covering the full range of absolute correlations. The smaller the true inter-construct correlation φ, the less an approach is expected to indicate a lack of discriminant validity; that is, we anticipate that the approaches’ specificity will increase with lower levels of φ.
In line with Vilares et al. (2010), as well as Vilares and Coelho (2013), we generate 1,000 datasets for each combination of design factors. Hence, the simulation study draws on a total number of 816,000 simulation runs: 4 levels of loading patterns times 4 levels of sample sizes times 51 levels of inter-construct correlations times 1,000 datasets per condition. In each simulation run, we apply the following approaches to assess the discriminant validity:
-
1.
The Fornell-Larcker criterion: Is the squared correlation between the two constructs greater than any of the two constructs’ AVE?
-
2.
The cross-loadings: Does any indicator correlate more strongly with the other constructs than with its own construct?
-
3.
The partial cross-loadings: Is an indicator significantly explained by a construct that it is not intended to measure when the actual construct’s influence is partialed out?
-
4.
The HTMT.85 criterion: Is the HTMT criterion greater than 0.85?
-
5.
The HTMT.90 criterion: Is the HTMT criterion greater than 0.90?
-
6.
The statistical HTMTinference test: Does the 90% normal bootstrap confidence interval of the HTMT criterion with a Bonferroni adjustment include the value one?Footnote 8
In the simulation study, we focus on PLS, which is regarded as the “most fully developed and general system” (McDonald 1996, p. 240) of the variance-based SEM techniques. Furthermore, the initial simulation study showed that PLS is the variance-based SEM technique with the highest sensitivity (i.e., 14.59% in respect of the Fornell-Larcker criterion; Table 2). All calculations were carried out with R 3.1.0 (R Core Team 2014) and we applied PLS as implemented in the semPLS package (Monecke and Leisch 2012).
Sensitivity results
With respect to each sensitivity analysis situation, we report each approach’s relative frequency to indicate the lack of discriminant validity if the true correlation between the constructs is equal to one (Table 3). This frequency should be 100%, or at least very close to this percentage.
Extending our previous findings, the results clearly show that traditional approaches used to assess discriminant validity perform very poorly; this is also true in alternative model settings with different loading patterns and sample sizes. The most commonly used approach, the Fornell-Larcker criterion, fails to identify discriminant validity issues in the vast majority of cases (Table 3). It only detects a lack of discriminant validity in more than 50% of simulation runs in situations with very heterogeneous loading patterns (i.e., 0.50 /0.70 /0.90) and sample sizes of 500 or less. With respect to more homogeneous loading patterns, the Fornell-Larcker criterion yields much lower sensitivity rates, particularly when the AVE is low.
The analysis of the cross-loadings fails to identify any discriminant validity problems, as this approach yields sensitivity values of 0% across all the factor level combinations (Table 3). Hence, the comparison of cross-loadings does not provide a basis for identifying discriminant validity issues. However, the picture is somewhat different regarding the partial cross-loadings. The sensitivity remains unacceptably low in respect of homogeneous loadings patterns, no matter what the sample size is. However, the sensitivity improves substantially in respect of heterogeneous loadings patterns. The sample size clearly matters for the partial cross-loadings approach. The larger the sample size, the more sensitive the partial cross-loadings are regarding detecting a lack of discriminant validity.
In contrast to the other approaches, the two absolute HTMT.85 and HTMT.90 criteria, as well as HTMTinference, yield sensitivity levels of 95% or higher under all simulation conditions (Table 3). Because of its lower threshold, HTMT.85 slightly outperforms the other two approaches with an average sensitivity rate of 99.90% compared to the 99.45% of HTMT.90 and the 97.01% of HTMTinference. In general, all three HTMT approaches detect discriminant validity issues reliably.
Specificity results
The specificity results are depicted in Fig. 5 (for homogeneous loading patterns) and Fig. 6 (for heterogeneous loadings patterns). The graphs visualize the frequency with which each approach indicates that the two constructs are distinct regarding varying levels of inter-construct correlations, loading patterns, and sample sizes. The discussion focuses on the three HTMT-based approaches, as the sensitivity analysis has already rendered the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the assessment of the (partial) cross-loadings ineffective (we nevertheless plotted their specificity rates for completeness sake).
All HTMT approaches show consistent patterns of decreasing specificity rates at higher levels of inter-construct correlations. As the correlations increase, the constructs’ distinctiveness decreases, making it less likely that the approaches will indicate discriminant validity. Furthermore, the three approaches show similar results patterns for different loadings, sample sizes, and inter-construct correlations, albeit at different levels. For example, ceteris paribus, when loading patterns are heterogeneous, specificity rates decrease at lower levels of inter-construct correlations compared to conditions with homogeneous loading patterns. A more detailed analysis of the results shows that all three HTMT approaches have specificity rates of well above 50% with regard to inter-construct correlations of 0.80 or less, regardless of the loading patterns and sample sizes. At inter-construct correlations of 0.70, the specificity rates are close to 100% in all instances. Thus, neither approach mistakenly indicates discriminant validity issues at levels of inter-construct correlations, which most researchers are likely to consider indicative of discriminant validity.
Comparing the approaches shows that HTMT.85 always exhibits higher or equal sensitivity, but lower or equal specificity values compared to HTMT.90. That is, HTMT.85 is more likely to indicate a lack of discriminant validity, an expected finding considering the criterion’s lower threshold value. The difference between these two approaches becomes more pronounced with respect to larger sample sizes and stronger loadings, but it remains largely unaffected by the degree of heterogeneity between the loadings.
Compared to the two threshold-based HTMT approaches, HTMTinference generally yields much higher specificity values, thus constituting a rather liberal approach to assessing discriminant validity, as it is more likely to indicate two constructs as distinct, even at high levels of inter-construct correlations. This finding holds especially in conditions where loadings are homogeneous and high (Fig. 5). Here, HTMTinference yields specificity rates of 80% or higher in terms of inter-construct correlations as high as 0.95, which many researchers are likely to view as indicative of a lack of discriminant validity. Exceptions occur in sample sizes of 100 and with lower AVE values. Here, HTMT.90 achieves higher sensitivity rates compared to HTMTinference. However, the differences in specificity between the two criteria are marginal in these settings.
Empirical example
To illustrate the approaches, we draw on the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) model (Anderson and Fornell 2000; Fornell et al. 1996), using empirical data from the first quarter of 1999 with N = 10,417 observations after excluding cases with missing data from the indicators used for model estimation (case wise deletion). In line with prior studies (Ringle et al. 2010, 2014) that used this dataset in their ACSI model examples, we rely on a modified version of the ACSI model without the constructs complaints (dummy-coded indicator) and loyalty (more than 80% of the cases for this construct measurement are missing). Figure 7 shows the reduced ACSI model and the PLS results.
The reduced ACSI model consists of the four reflectively measured constructs: customer satisfaction (ACSI), customer expectations (CUEX), perceived quality (PERQ), and perceived value (PERV). The evaluation of the PLS results meets the relevant criteria (Chin 1998, 2010; Götz et al. 2010; Hair et al. 2012a), which Ringle et al. (2010), using this example, presented in detail. According to the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the cross-loadings (Table 4), the constructs’ discriminant validity has been established: (1) the square root of each construct’s AVE is higher than its correlation with another construct, and (2) each item loads highest on its associated construct. Table 4 also lists the significant (p < 0.05) partial cross-loadings. Two thirds of them are significant. This relatively high percentage is not surprising, considering that even marginal correlations (e.g., an absolute value of 0.028) become significant as a result of the high sample size. Hence, and in line with the approach’s sensitivity results (Table 3), the multitude of significant partial cross-loadings seems to suggest serious problems with respect to discriminant validity.
Next, we compute the HTMT criteria for each pair of constructs on the basis of the item correlations (Table 5) as defined in Eq. 6.Footnote 9 The computation yields values between 0.53 in respect of HTMT(CUEX,PERV) and 0.95 in respect of HTMT(ACSI,PERQ) (Table 6). Comparing these results with the threshold values as defined in HTMT.85 gives rise to concern, because two of the six comparisons (ACSI and PERQ; ACSI and PERV) violate the 0.85 threshold. However, in the light of the conceptual similarity of the ACSI model’s constructs, the use of a more liberal criterion for specificity seems warranted. Nevertheless, even when using HTMT.90 as the standard, one comparison (ACSI and PERQ) violates this criterion. Only the use of HTMTinference suggests that discriminant validity has been established.
This empirical example of the ACSI model and the use of original data illustrate a situation in which the classical criteria do not indicate any discriminant validity issues, whereas the two more conservative HTMT criteria do. While it is beyond this study’s scope to discuss the implications of the results for model design, they give rise to concern regarding the empirical distinctiveness of the ACSI and PERQ constructs.
Summary and discussion
Key findings and recommendations
Our results clearly show that the two standard approaches to assessing the discriminant validity in variance-based SEM—the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the assessment of cross-loadings—have an unacceptably low sensitivity, which means that they are largely unable to detect a lack of discriminant validity. In particular, the assessment of the cross-loadings completely fails to detect discriminant validity issues. Similarly, the assessment of partial cross-loadings—an approach which has not been used in variance-based SEM—proves inefficient in many settings commonly encountered in applied research. More precisely, the criterion only works well in situations with heterogeneous loading patterns and high sample sizes.
As a solution to this critical issue, we present a new set of criteria for discriminant validity assessment in variance-based SEM. The new HTMT criteria, which are based on a comparison of the heterotrait-heteromethod correlations and the monotrait-heteromethod correlations, identify a lack of discriminant validity effectively, as evidenced by their high sensitivity rates.
The main difference between the HTMT criteria lies in their specificity. Of the three approaches, HTMT.85 is the most conservative criterion, as it achieves the lowest specificity rates of all the simulation conditions. This means that HTMT.85 can pint to discriminant validity problems in research situations in which HTMT.90 and HTMTinference indicate that discriminant validity has been established. In contrast, HTMTinference is the most liberal of the three newly proposed approaches. Even if two constructs are highly, but not perfectly, correlated with values close to 1.0, the criterion is unlikely to indicate a lack of discriminant validity, particularly when (1) the loadings are homogeneous and high or (2) the sample size is large. Owing to its higher threshold, HTMT.90 always has higher specificity rates than HTMT.85. Compared to HTMTinference, the HTMT.90 criterion yields much lower specificity rates in the vast majority of conditions. We find that none of the HTMT criteria indicates discriminant validity issues for inter-construct correlations of 0.70 or less. This outcome of our specificity analysis is important, as it shows that neither approach points to discriminant validity problems at comparably low levels of inter-construct correlations.
Based on our findings, we strongly recommend drawing on the HTMT criteria for discriminant validity assessment in variance-based SEM. The actual choice of criterion depends on the model set-up and on how conservative the researcher is in his or her assessment of discriminant validity. Take, for example, the technology acceptance model and its variations (Davis 1989; Venkatesh et al. 2003), which include the constructs intention to use and the actual use. Although these constructs are conceptually different, they may be difficult to distinguish empirically in all research settings. Therefore, the choice of a more liberal HTMT criterion in terms of specificity (i.e., HTMT.90 or HTMTinference, depending on the sample size) seems warranted. Conversely, if the strictest standards are followed, this requires HTMT.85 to assess discriminant validity.
Guidelines for treating discriminant validity problems
To handle discriminant validity problems, researchers may follow different routes, which we illustrate in Fig. 8. The first approach retains the constructs that cause discriminant validity problems in the model and aims at increasing the average monotrait-heteromethod correlations and/or decreasing the average heteromethod-heterotrait correlations of the constructs measures. When researchers seek to decrease the HTMT by increasing a construct’s average monotrait-heteromethod correlations, they may eliminate items that have low correlations with other items measuring the same construct. Likewise, heterogeneous sub-dimensions in the construct’s set of items could also deflate the average monotrait-heteromethod correlations. In this case, researchers may consider splitting the construct into homogenous sub-constructs, if the measurement theory supports this step. These sub-constructs then replace the more general construct in the model. However, researchers need to re-evaluate the newly generated constructs’ discriminant validity with all the opposing constructs in the model. When researchers seek to decrease the average heteromethod-heterotrait correlations, they may consider (1) eliminating items that are strongly correlated with items in the opposing construct or (2) reassigning these indicators to the opposing construct, if theoretically plausible.
It is important to note that the elimination of items purely on statistical grounds can have adverse consequences for the construct measures’ content validity (e.g., Hair et al. 2014). Therefore, researchers should carefully scrutinize the scales (either based on prior research results, or on those from a pretest in case of the newly developed measures) and determine whether all the construct domain facets have been captured. At least two expert coders should conduct this judgment independently to ensure a high degree of objectivity (Diamantopoulos et al. 2012).
The second approach to treat discriminant validity problems aims at merging the constructs that cause the problems into a more general construct. Again, measurement theory must support this step. In this case, the more general construct replaces the problematic constructs in the model and researchers need to re-evaluate the newly generated construct’s discriminant validity with all the opposing constructs. This step may entail modifications to increase a construct’s average monotrait-heteromethod correlations and/or to decrease the average heteromethod-heterotrait correlations (Fig. 8).
Further research and concluding remarks
Our research offers several promising avenues for future research. To begin with, many researchers view variance-based SEM as the natural approach when the model includes formatively measured constructs (Chin 1998; Fornell and Bookstein 1982; Hair et al. 2012a). Obviously, the discriminant validity concept is independent of a construct’s concrete operationalization. Constructs that are conceptually different should also be empirically different, no matter how they have been measured, and no matter the types of epistemic relationships between a construct and its indicators. However, just like the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the (partial) cross-loadings, the HTMT-based criteria assume reflectively measured constructs. Applying them to formatively measured constructs is problematic, because neither the monotrait-heteromethod nor the heterotrait-heteromethod correlations of formative indicators are indicative of discriminant validity. As Diamantopoulos and Winklhofer (2001, p. 271) point out, “there is no reason that a specific pattern of signs (i.e., positive versus negative) or magnitude (i.e., high versus moderate versus low) should characterize the correlations among formative indicators.”
Prior literature gives practically no recommendations on how to assess the discriminant validity of formatively measured constructs. One of the few exceptions is the research by Klein and Rai (2009), who suggest examining the cross-loadings of formative indicators. Analogous to their reflective counterparts, formative indicators should correlate more highly with their composite construct score than with the composite score of other constructs. However, considering the poor performance of cross-loadings in our study, its use in formative measurement models appears questionable. Against this background, future research should seek alternative means to consider formatively measured constructs when assessing discriminant validity.
Apart from continuously refining, extending, and testing the HTMT-based validity assessment criteria for variance-based SEM (e.g., by evaluating their sensitivity to different base response scales, inducing variance basis differences and differential response biases), future research should also assess whether this study’s findings can be generalized to covariance-based SEM techniques, or the recently proposed consistent PLS (Dijkstra 2014; Dijkstra and Henseler 2014a, b), which mimics covariance-based SEM. Specifically, the Fornell-Larcker criterion is a standard approach to assess discriminant validity in covariance-based SEM (Shah and Goldstein 2006; Shook et al. 2004). Thus, it is necessary to evaluate whether this criterion suffers from the same limitations in a factor model setting.
In the light of the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the cross-loadings’ poor performance, researchers should carefully reconsider the results of prior variance-based SEM analyses. Failure to properly disclose discriminant validity problems may result in biased estimations of structural parameters and inappropriate conclusions about the hypothesized relationships between constructs. Revisiting the analysis results of prominent models estimated by means of variance-based SEM, such as the ACSI and the TAM, seems warranted. In doing so, researchers should analyze the different sources of discriminant validity problems and apply adequate procedures to treat them (Fig. 8).
It is important to note, however, that discriminant validity is not exclusively an empirical means to validate a model. Theoretical foundations and arguments should provide reasons for constructs correlating or not (Bollen and Lennox 1991). According to the holistic construal process (Bagozzi and Phillips 1982; Bagozzi 1984), perhaps the most influential psychometric framework for measurement development and validation (Rigdon 2012), constructs are not necessarily equivalent to the theoretical concepts at the center of scientific research: a construct should rather be viewed as “something created from the empirical data which is intended to enable empirical testing of propositions regarding the concept” (Rigdon 2014, pp. 43–344). Consequently, any derivation of HTMT thresholds is subjective. On the other hand, concepts are partly defined by their relationships with other concepts within a nomological network, a system of law-like relationships discovered over time and which anchor each concept. Therefore, hindsight failure to establish discriminant validity between two constructs does not necessarily imply that the underlying concepts are identical, especially when follow-up research provides continued support for differing relationships with the antecedent and the resultant concepts (Bagozzi and Phillips 1982). Nevertheless, our research clearly shows that future research should pay greater attention to the empirical validation of discriminant validity to ensure the rigor of theories’ empirical testing and validation.
Notes
It is important to note that studies may have used different ways to assess discriminant validity assessment, but did not include these in the main texts or appendices (e.g., due to page restrictions). We would like to thank an anonymous reviewer for this remark.
Nunnally (1978) offers an extreme example with five mutually uncorrelated indicators, implying zero loadings if all were measures of a construct. However, each indicator’s correlation (i.e., loading) with an unweighted composite of all five items is 0.45.
Chin (2010) suggests examining the squared loadings and cross-loadings instead of the loadings and cross-loadings. He argues that, for instance, compared to a cross-loading of 0.70, a standardized loading of 0.80 may raise concerns, whereas the comparison of a shared variance of 0.64 with a shared variance of 0.49 puts matters into perspective.
We thank an anonymous reviewer for proposing this approach.
We thank Mikko Rönkkö and Joerg Evermann for providing us with the code of their simulation study (Rönkkö and Evermann 2013), which helped us localize this error in their analysis.
Strictly speaking, one should assess the absolute value of the HTMT, because a correlation of −1 implies a lack of discriminant validity, too.
Since HTMTinference relies on one-tailed tests, we use the 90% bootstrap confidence interval in order to warrant an error probability of five percent.
An Excel sheet illustrating the computation of the HTMT values can be downloaded from http://www.pls-sem.com/jams/htmt_acsi.xlsx .
References
Aguirre-Urreta, M. I., Marakas, G. M., & Ellis, M. E. (2013). Measurement of composite reliability in research using partial least squares: some issues and an alternative approach. SIGMIS Database, 44(4), 11–43.
Anderson, E. W., & Fornell, C. G. (2000). Foundations of the American customer satisfaction index. Total Quality Management, 11(7), 869–882.
Anderson, J. C., & Gerbing, D. W. (1988). Structural equation modeling in practice: a review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin, 103(3), 411–423.
Bagozzi, R. P. (1984). A prospectus for theory construction in marketing. Journal of Marketing, 48(1), 11–29.
Bagozzi, R. P., & Phillips, L. W. (1982). Representing and testing organizational theories: a holistic construal. Administrative Science Quarterly, 27(3), 459–489.
Barclay, D. W., Higgins, C. A., & Thompson, R. (1995). The partial least squares approach to causal modeling: personal computer adoption and use as illustration. Technology Studies, 2(2), 285–309.
Bollen, K. A. (1989). Structural equations with latent variables. New York, NY: Wiley.
Bollen, K. A., & Lennox, R. (1991). Conventional wisdom on measurement: a structural equation perspective. Psychological Bulletin, 110(2), 305–314.
Campbell, D. T. (1960). Recommendations for APA test standards regarding construct, trait, or discriminant validity. American Psychologist, 15(8), 546–553.
Campbell, D. T., & Fiske, D. W. (1959). Convergent and discriminant validation by the multitrait-multimethod matrix. Psychological Bulletin, 56(2), 81–105.
Chin, W. W. (1998). The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. In G. A. Marcoulides (Ed.), Modern methods for business research (pp. 295–358). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Chin, W. W. (2010). How to write up and report PLS analyses. In V. Esposito Vinzi, W. W. Chin, J. Henseler, & H. Wang (Eds.), Handbook of partial least squares: concepts, methods and applications in marketing and related fields (pp. 655–690). Berlin: Springer.
Clark, L. A., & Watson, D. (1995). Constructing validity: basic issues in objective scale development. Psychological Assessment, 7(3), 309–319.
Cording, M., Christmann, P., & King, D. R. (2008). Reducing causal ambiguity in acquisition integration: intermediate goals as mediators of integration decisions and acquisition performance. Academy of Management Journal, 51(4), 744–767.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319–340.
Diamantopoulos, A., & Winklhofer, H. M. (2001). Index construction with formative indicators: an alternative to scale development. Journal of Marketing Research, 38(2), 269–277.
Diamantopoulos, A., Sarstedt, M., Fuchs, C.,Wilczynski, P., & Kaiser, S. (2012). Guidelines for choosing between multi-item and single-item scales for construct measurement: a predictive validity perspective. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 40(3), 434–449.
Dijkstra, T. K. (2014). PLS’ Janus face – response to professor Rigdon’s ‘rethinking partial least squares modeling: in praise of simple methods’. Long Range Planning, 47(3), 146–153.
Dijkstra, T. K., & Henseler, J. (2011). Linear indices in nonlinear structural equation models: best fitting proper indices and other composites. Quality and Quantity, 45(6), 1505–1518.
Dijkstra, T. K. and Henseler, J. (2014a). Consistent partial least squares path modeling. MIS Quarterly, forthcoming.
Dijkstra, T. K. and Henseler, J. (2014b). Consistent and asymptotically normal PLS estimators for linear structural equations. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, forthcoming.
Falk, R. F., & Miller, N. B. (1992). A primer for soft modeling. Akron: University of Akron Press.
Farrell, A. M. (2010). Insufficient discriminant validity: a comment on Bove, Pervan, Beatty, and Shiu (2009). Journal of Business Research, 63(3), 324–327.
Fornell, C. G., & Bookstein, F. L. (1982). Two structural equation models: LISREL and PLS applied to consumer exit-voice theory. Journal of Marketing Research, 19(4), 440–452.
Fornell, C. G., & Cha, J. (1994). Partial least squares. In R. P. Bagozzi (Ed.), Advanced methods of marketing research (pp. 52–78). Oxford: Blackwell.
Fornell, C. G., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39–50.
Fornell, C. G., Johnson, M. D., Anderson, E. W., Cha, J., & Bryant, B. E. (1996). The American Customer Satisfaction Index: nature, purpose, and findings. Journal of Marketing, 60(4), 7–18.
Gefen, D., & Straub, D. W. (2005). A practical guide to factorial validity using PLS-Graph: tutorial and annotated example. Communications of the AIS, 16, 91–109.
Gefen, D., Straub, D. W., & Boudreau, M.-C. (2000). Structural equation modeling techniques and regression: guidelines for research practice. Communications of the AIS, 4, 1–78.
Gold, A. H., Malhotra, A., & Segars, A. H. (2001). Knowledge management: an organizational capabilities perspective. Journal of Management Information Systems, 18(1), 185–214.
Goodhue, D. L., Lewis, W., & Thompson, R. (2012). Does PLS have advantages for small sample size or non-normal data? MIS Quarterly, 36(3), 891–1001.
Götz, O., Liehr-Gobbers, K., & Krafft, M. (2010). Evaluation of structural equation models using the partial least squares (PLS) approach. In V. Esposito Vinzi, W. W. Chin, J. Henseler, & H. Wang (Eds.), Handbook of partial least squares: concepts, methods and applications (pp. 691–711). Berlin: Springer.
Gudergan, S. P., Ringle, C. M., Wende, S., & Will, S. (2008). Confirmatory tetrad analysis in PLS path modeling. Journal of Business Research, 61(12), 1238–1249.
Haenlein, M., & Kaplan, A. M. (2004). A beginner’s guide to partial least squares analysis. Understanding Statistics, 3(4), 283–297.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis (7th ed.). Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2011). PLS-SEM: indeed a silver bullet. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 19(2), 139–151.
Hair, J. F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., & Mena, J. A. (2012a). An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 40(3), 414–433.
Hair, J. F., Sarstedt, M., Pieper, T. M., & Ringle, C. M. (2012b). The use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in strategic management research: a review of past practices and recommendations for future applications. Long Range Planning, 45(5–6), 320–340.
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2014). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Henseler, J. (2012). Why generalized structured component analysis is not universally preferable to structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 40(3), 402–413.
Henseler, J., & Sarstedt, M. (2013). Goodness-of-fit indices for partial least squares path modeling. Computational Statistics, 28(2), 565–580.
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sinkovics, R. R. (2009). The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing. Advances in International Marketing, 20, 277–320.
Henseler, J., Dijkstra, T. K., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., Diamantopoulos, A., Straub, D. W., Ketchen, D. J., Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., & Calantone, R. J. (2014). Common beliefs and reality about partial least squares: comments on Rönkkö & Evermann (2013). Organizational Research Methods, 17(2), 182–209.
Hochberg, Y. (1988). A sharper Bonferroni procedure for multiple significance testing. Biometrika, 75(4), 800–802.
Holm, S. (1979). A simple sequentially rejective Bonferroni test procedure. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 6(1), 65–70.
Hui, B. S., & Wold, H. (1982). Consistency and consistency at large of partial least squares estimates. In K. G. Jöreskog, & H. Wold (Eds.), Systems under indirect observation, part II (pp. 119–130). Amsterdam: North Holland.
Hulland, J. (1999). Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: a review of four recent studies. Strategic Management Journal, 20(2), 195–204.
Hwang, H., & Takane, Y. (2004). Generalized structured component analysis. Psychometrika, 69(1), 81–99.
Hwang, H., Malhotra, N. K., Kim, Y., Tomiuk, M. A., & Hong, S. (2010). A comparative study on parameter recovery of three approaches to structural equation modeling. Journal of Marketing Research, 47(4), 699–712.
John, O. P., & Benet-Martínez, V. (2000). Measurement: reliability, construct validation, and scale construction. In H. T. Reis & C. M. Judd (Eds.), Handbook of research methods in social and personality psychology (pp. 339–369). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Klein, R., & Rai, A. (2009). Interfirm strategic information flows in logistics supply chain relationships. MIS Quarterly, 33(4), 735–762.
Kline, R. B. (2011). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. New York: Guilford Press.
Lee, L., Petter, S., Fayard, D., & Robinson, S. (2011). On the use of partial least squares path modeling in accounting research. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 12(4), 305–328.
Loch, K. D., Straub, D. W., & Kamel, S. (2003). Diffusing the Internet in the Arab world: The role of social norms and technological culturation. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 50(1), 45–63.
Lohmöller, J.-B. (1989). Latent variable path modeling with partial least squares. Heidelberg: Physica.
Lu, I. R. R., Kwan, E., Thomas, D. R., & Cedzynski, M. (2011). Two new methods for estimating structural equation models: an illustration and a comparison with two established methods. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 28(3), 258–268.
Macmillan, N. A., & Creelman, C. D. (2004). Detection theory: a user’s guide. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Marcoulides, G. A., Chin, W. W., & Saunders, C. (2012). When imprecise statistical statements become problematic: a response to Goodhue, Lewis, and Thompson. MIS Quarterly, 36(3), 717-728.
McDonald, R. P. (1996). Path analysis with composite variables. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 31(2), 239–270.
Milberg, S. J., Smith, H. J., & Burke, S. J. (2000). Information privacy: corporate management and national regulation. Organization Science, 11(1), 35–57.
Miller, R. G. (1981). Simultaneous statistical inference. New York: Wiley.
Monecke, A., & Leisch, F. (2012). semPLS: structural equation modeling using partial least squares. Journal of Statistical Software, 48(3), 1–32.
Mulaik, S. A. (2009). Foundations of factor analysis. New York: Chapman & Hall/CRC.
Netemeyer, R. G., Bearden, W. O., & Sharma, S. (2003). Scaling procedures: issues and applications. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Nunnally, J. (1978). Psychometric theory (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Pavlou, P. A., Liang, H., & Xue, Y. (2007). Understanding and mitigating uncertainty in online exchange relationships: a principal-agent perspective. MIS Quarterly, 31(1), 105–136.
Paxton, P., Curran, P. J., Bollen, K. A., Kirby, J., & Chen, F. (2001). Monte Carlo experiments: design and implementation. Structural Equation Modeling, 8(2), 287–312.
Peng, D. X., & Lai, F. (2012). Using partial least squares in operations management research: a practical guideline and summary of past research. Journal of Operations Management, 30(6), 467–480.
Peter, J. P., & Churchill, G. A. (1986). Relationships among research design choices and psychometric properties of rating scales: a meta-analysis. Journal of Marketing Research, 23(1), 1–10.
R Core Team (2014). R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Ravichandran, T., & Rai, A. (2000). Quality management in systems development: an organizational system perspective. MIS Quarterly, 24(3), 381–415.
Reinartz, W. J., Haenlein, M., & Henseler, J. (2009). An empirical comparison of the efficacy of covariance-based and variance-based SEM. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 26(4), 332–344.
Rigdon, E. E. (2012). Rethinking partial least squares path modeling: In praise of simple methods. Long Range Planning, 45(5–6), 341–358.
Rigdon, E. E. (2014). Rethinking partial least squares path modeling: breaking chains and forging ahead. Long Range Planning, 47(3), 161–167.
Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., & Mooi, E. A. (2010). Response-based segmentation using finite mixture partial least squares: theoretical foundations and an application to American Customer Satisfaction Index data. Annals of Information Systems, 8, 19–49.
Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., & Straub, D. W. (2012). A critical look at the use of PLS-SEM in MIS Quarterly. MIS Quarterly, 36(1), iii–xiv.
Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., & Schlittgen, R. (2014). Genetic algorithm segmentation in partial least squares structural equation modeling. OR Spectrum, 36(1), 251–276.
Roldán, J. L., & Sánchez-Franco, M. J. (2012). Variance-based structural equation modeling: guidelines for using partial least squares in information systems research. In M. Mora, O. Gelman, A. Steenkamp, & M. Raisinghani (Eds.), Research methodologies, innovations and philosophies in software systems engineering and information systems (pp. 193–221). Hershey: IGI Global.
Rönkkö, M., & Evermann, J. (2013). A critical examination of common beliefs about partial least squares path modeling. Organizational Research Methods, 16(3), 425–448.Sarstedt, M. & Mooi, E. A. (2014). A concise guide to market research. The process, data, and methods using IBM SPSS Statistics. Berlin: Springer.
Sarstedt, M. & Mooi, E. A. (2014). A concise guide to market research. The process, data, and methods using IBM SPSS Statistics. Berlin: Springer.
Schmitt, N. (1978). Path analysis of multitrait-multimethod matrices. Applied Psychological Measurement, 2(2), 157–173.
Schmitt, N., & Stults, D. M. (1986). Methodology review: analysis of multitrait-multimethod matrices. Applied Psychological Measurement, 10(1), 1–22.
Shaffer, J. P. (1995). Multiple hypothesis testing. Annual Review of Psychology, 46, 561–584.
Shah, R., & Goldstein, S. M. (2006). Use of structural equation modeling in operations management research: looking back and forward. Journal of Operations Management, 24(2), 148–169.
Shook, C. L., Ketchen, D. J., Hult, G. T. M., & Kacmar, K. M. (2004). An assessment of the use of structural equation modeling in strategic management research. Strategic Management Journal, 25(4), 397–404.
Sosik, J. J., Kahai, S. S., & Piovoso, M. J. (2009). Silver bullet or voodoo statistics? A primer for using the partial least squares data analytic technique in group and organization research. Group Organization Management, 34(1), 5–36.
Tenenhaus, A., & Tenenhaus, M. (2011). Regularized generalized canonical correlation analysis. Psychometrika, 76(2), 257–284.
Tenenhaus, M., Esposito Vinzi, V., Chatelin, Y.-M., & Lauro, C. (2005). PLS path modeling. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 48(1), 159–205.
Teo, T. S. H., Srivastava, S. C., & Jiang, L. (2008). Trust and electronic government success: an empirical study. Journal of Management Information Systems, 25(3), 99–132.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27(3), 425–478.
Vilares, M. J., & Coelho, P. S. (2013). Likelihood and PLS estimators for structural equation modeling: an assessment of sample size, skewness and model misspecification effects. In J. Lita da Dilva, F. Caeiro, I. Natário, & C. A. Braumann (Eds.), Advances in regression, survival analysis, extreme values, Markov processes and other statistical applications (pp. 11–33). Berlin: Springer.
Vilares, M. J., Almeida, M. H., & Coelho, P. S. (2010). Comparison of likelihood and PLS estimators for structural equation modeling: a simulation with customer satisfaction data. In V. Esposito Vinzi, W. W. Chin, J. Henseler, & H. Wang (Eds.), Handbook of partial least squares: concepts, methods and applications (pp. 289–305). Berlin: Springer.
Wold, H. (1982). Soft modeling: the basic design and some extensions. In K. G. Jöreskog & H. Wold (Eds.), Systems under indirect observations: part II (pp. 1–54). Amsterdam: North-Holland.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Theo Dijkstra, Rijksuniversiteit Groningen, The Netherlands, for his helpful comments to improve earlier versions of the manuscript. The authors contributed equally and are listed in alphabetical order. The manuscript was written when the first author was an associate professor of marketing at the Institute for Management Research, Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
In this Appendix we demonstrate that the heterotrait-monotrait ratio of correlations (HTMT) as presented in the main manuscript is an estimator of the inter-construct correlation φ.
Let x i 1,…,x iK i be the K i reflective indicators of construct ξ i , and x j 1,…,x jK j the K j reflective indicators of construct ξ j . The empirical correlation matrix R is then
If the reflective measurement model (i.e., a common factor model) holds true for both constructs, the implied correlation matrix Σ is then
We depart from the notion that Cronbach’s alpha is
Moreover, the composite reliability ρ c , is:
If a construct’s indicators are tau-equivalent, Cronbach’s alpha is a consistent estimate of a set of indicators just like the composite reliability ρ c , which implies that:
The HTMT ij of constructs ξ i and ξ j as introduced in the manuscript is then:
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Henseler, J., Ringle, C.M. & Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. of the Acad. Mark. Sci. 43, 115–135 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8