Abstract
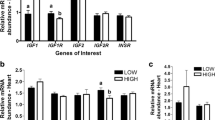
The main objective was to evaluate if different planes of maternal nutrition during late gestation and weaning age alter microRNA (miRNA) and target gene expression in offspring longissimus muscle (LM). Early (EW) and normal weaned (NW) Angus × Simmental calves (n = 30) born to cows that were grazing endophyte-infected tall fescue and red clover pastures with no supplement [low plane of nutrition (LPN)], or supplemented with 2.3 and 9.1 kg of dried distiller’s grains with solubles and soy hulls [medium and high plane of nutrition (MPN, HPN), respectively] during the last 105 ± 11 days of gestation were used. Biopsies of LM were harvested at 78 (early weaning), 187 (normal weaning) and 354 days of age. Results indicate a role of pro-adipogenic miRNA in the control of adipogenesis in LM of NW-MPN steers between 78 and 187 days of age through upregulation of (1) miR-103 which inhibits CAV1, a protein that destabilizes INSR and leads to insulin resistance; (2) miR-143 which inhibits DLK1, a protein that inhibits adipocyte differentiation; and (3) miR-21 which impairs TGFBR2-induced inhibition of adipocyte differentiation. Among the studied anti-adipogenic miRNA, cow plane of nutrition resulted in downregulation of miR-34a expression in MPN steers compared with HPN and LPN at 78 days of age. Data for miR-34a provided a potential sign of epigenetic regulation of LM in beef offspring due to the cow plane of nutrition during late gestation.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADIPOQ:
-
Adiponectin
- ADG:
-
Average daily gain
- CAV1:
-
Caveolin 1
- C/EBPA:
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), alpha
- C/EBPB:
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), beta
- C/EBPD:
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), delta
- CREB:
-
cAMP response element binding protein
- DLK1:
-
Delta-like 1 homolog
- DM:
-
Dry matter
- DMI:
-
Dry matter intake
- ERK1/2:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3
- EW:
-
Early wean(ed)
- FABP4:
-
Fatty acid binding protein 4
- G0S2:
-
G0/G1 switch 2
- hASC:
-
Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- HPN:
-
High plane of nutrition
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- INSR:
-
Insulin receptor
- KLF5:
-
Kruppel-like factor 5
- LM:
-
Longissimus muscle
- LPN:
-
Low plane of nutrition
- MAPK1:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- miR-16b:
-
MicroRNA 16a
- miR-let-7a:
-
MicroRNA let7a
- miR-181a:
-
MicroRNA 181a
- miR-103:
-
MicroRNA 103
- miR-143:
-
MicroRNA 143
- miR-21-5p:
-
MicroRNA 21-5p
- miR-378:
-
MicroRNA 378
- miR-27a/b:
-
MicroRNA 27a/b
- miR-130a:
-
MicroRNA 130a
- miR-34a:
-
MicroRNA 34a
- miR-369-5p:
-
MicroRNA 369-5p
- miR-448:
-
MicroRNA 448
- MPN:
-
Medium plane of nutrition
- MSTN:
-
Myostatin
- MTG1:
-
Mitochondrial ribosome-associated GTPase 1
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells
- NW:
-
Normal wean(ed)
- PANK:
-
Pantothenate kinase
- PDCD4:
-
Programmed cell death 4
- PGC-1β:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 beta
- PPARG:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative RT-PCR
- RPS15A:
-
Ribosomal protein S15a
- SIRT1:
-
Sirtuin 1
- SLC2A4:
-
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 4
- SREBP:
-
Sterol responsive element binding protein
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- TGFBR2:
-
Transforming growth factor, beta receptor II
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis alpha
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis alpha
- TP53:
-
Tumor protein p53
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- UXT:
-
Ubiquitously-expressed
References
Wilkins JF (2005) Genomic imprinting and methylation: epigenetic canalization and conflict. Trends Genet 21:356–365
Munshi A, Shafi G, Aliya N, Jyothy A (2009) Histone modifications dictate specific biological readouts. J Genet Genom 36:75–88
McKay JA, Mathers JC (2011) Diet induced epigenetic changes and their implications for health. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 202:103–118
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Jin W, Grant JR, Stothard P, Moore SS, Guan LL (2009) Characterization of bovine miRNAs by sequencing and bioinformatics analysis. BMC Mol Biol 10:90
Basu U, Romao JM, Guan LL (2012) Adipogenic transcriptome profiling using high throughput technologies. J Genom 1:22–28
Erhuma A, Salter AM, Sculley DV, Langley-Evans SC, Bennett AJ (2007) Prenatal exposure to a low-protein diet programs disordered regulation of lipid metabolism in the aging rat. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292:E1702–E1714
Moisa SJ, Shike DW, Shoup L, Rodriguez-Zas SL, Loor JJ (2015) Maternal plane of nutrition during late gestation and weaning age alter Angus × Simmental offspring longissimus muscle transcriptome and intramuscular fat. PLoS One 10:e0131478
Shoup LM, Wilson TB, González-Peña D, Ireland FA, Rodriguez-Zas S, Felix TL, Shike DW (2015) Beef cow prepartum supplement level and age at weaning: II. Effects of developmental programming on performance and carcass composition of steer progeny. J Anim Sci 93(10):4936–4947. doi:10.2527/jas2014-8565
Shoup LM, Kloth AC, Wilson TB, González-Peña D, Ireland FA, Rodriguez-Zas S, Felix TL, Shike DW (2015) Prepartum supplement level and age at weaning: I. Effects on pre- and postpartum beef cow performance and calf performance through weaning. J Anim Sci 93(10):4926-35. doi: 10.2527/jas2014-8564
Raddatz J (2008) Measurement of adiponectin and insulin in lactating and non-lactating Holstein cows in Animal Sciences. North Carolina State University, Raleigh, p 79. http://repository.lib.ncsu.edu/ir/handle/1840.1816/1845
Funston RN, Larson DM, Vonnahme KA (2010) Effects of maternal nutrition on conceptus growth and offspring performance: implications for beef cattle production. J Anim Sci 88:E205–E215
Bohnert DW, Stalker LA, Mills RR, Nyman A, Falck SJ, Cooke RF (2013) Late gestation supplementation of beef cows differing in body condition score: effects on cow and calf performance. J Anim Sci 91:5485–5491
Moisa SJ, Shike DW, Faulkner DB, Meteer WT, Keisler D, Loor JJ (2014) Central role of the PPARgamma gene network in coordinating beef cattle intramuscular adipogenesis in response to weaning age and nutrition. Gene Regul Syst Bio 8:17–32
Hoffstedt J, Arvidsson E, Sjolin E, Wahlen K, Arner P (2004) Adipose tissue adiponectin production and adiponectin serum concentration in human obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:1391–1396
Smith J, Al-Amri M, Sniderman A, Cianflone K (2006) Leptin and adiponectin in relation to body fat percentage, waist to hip ratio and the apoB/apoA1 ratio in Asian Indian and Caucasian men and women. Nutr Metab (Lond) 3:18
Kabara E, Sordillo LM, Holcombe S, Contreras GA (2014) Adiponectin links adipose tissue function and monocyte inflammatory responses during bovine metabolic stress. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 37:49–58
Ji P, Drackley JK, Khan MJ, Loor JJ (2014) Overfeeding energy upregulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)gamma-controlled adipogenic and lipolytic gene networks but does not affect proinflammatory markers in visceral and subcutaneous adipose depots of Holstein cows. J Dairy Sci 97:3431–3440
Ji P, Drackley JK, Khan MJ, Loor JJ (2014) Inflammation- and lipid metabolism-related gene network expression in visceral and subcutaneous adipose depots of Holstein cows. J Dairy Sci 97:3441–3448
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, Hotta K, Shimomura I, Nakamura T, Miyaoka K, Kuriyama H, Nishida M, Yamashita S, Okubo K, Matsubara K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2012) Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. 1999. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 425:560–564
Ohtani Y, Takahashi T, Sato K, Ardiyanti A, Song SH, Sato R, Onda K, Wada Y, Obara Y, Suzuki K, Hagino A, Roh SG, Katoh K (2012) Changes in circulating adiponectin and metabolic hormone concentrations during periparturient and lactation periods in Holstein dairy cows. Anim Sci J 83:788–795
Xie H, Lim B, Lodish HF (2009) MicroRNAs induced during adipogenesis that accelerate fat cell development are downregulated in obesity. Diabetes 58:1050–1057
Sarr O, Thompson JA, Zhao L, Lee TY, Regnault TR (2014) Low birth weight male guinea pig offspring display increased visceral adiposity in early adulthood. PLoS One 9:e98433
Polster BJ, Westaway SK, Nguyen TM, Yoon MY, Hayflick SJ (2010) Discordant expression of miR-103/7 and pantothenate kinase host genes in mouse. Mol Genet Metab 101:292–295
Wilfred BR, Wang WX, Nelson PT (2007) Energizing miRNA research: a review of the role of miRNAs in lipid metabolism, with a prediction that miR-103/107 regulates human metabolic pathways. Mol Genet Metab 91:209–217
Ragaller V, Lebzien P, Sudekum KH, Huther L, Flachowsky G (2011) Pantothenic acid in ruminant nutrition: a review. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 95:6–16
Rottiers V, Naar AM (2012) MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:239–250
Trajkovski M, Hausser J, Soutschek J, Bhat B, Akin A, Zavolan M, Heim MH, Stoffel M (2011) MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity. Nature 474:649–653
Wang H, Xiao S, Wang M, Kim NH, Li H, Wang G (2015) In silico identification of conserved microRNAs and their targets in bovine fat tissue. Gene 559(2):119–128
Li H, Zhang Z, Zhou X, Wang Z, Wang G, Han Z (2011) Effects of microRNA-143 in the differentiation and proliferation of bovine intramuscular preadipocytes. Mol Biol Rep 38:4273–4280
Zhu L, Shi C, Ji C, Xu G, Chen L, Yang L, Fu Z, Cui X, Lu Y, Guo X (2013) FFAs and adipokine-mediated regulation of hsa-miR-143 expression in human adipocytes. Mol Biol Rep 40:5669–5675
Kim YJ, Min TS, Seo KS, Kim SH (2015) Expression of pref-1/dlk-1 is regulated by microRNA-143 in 3T3-L1 cells. Mol Biol Rep 42:617–624
Kavalkova P, Touskova V, Roubicek T, Trachta P, Urbanova M, Drapalova J, Haluzikova D, Mraz M, Novak D, Matoulek M, Lacinova Z, Haluzik M (2013) Serum preadipocyte factor-1 concentrations in females with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: the influence of very low calorie diet, acute hyperinsulinemia, and fenofibrate treatment. Horm Metab Res 45:820–826
Keller P, Gburcik V, Petrovic N, Gallagher IJ, Nedergaard J, Cannon B, Timmons JA (2011) Gene-chip studies of adipogenesis-regulated microRNAs in mouse primary adipocytes and human obesity. BMC Endocr Disord 11:7
Kim YJ, Hwang SJ, Bae YC, Jung JS (2009) MiR-21 regulates adipogenic differentiation through the modulation of TGF-beta signaling in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissue. Stem Cells 27:3093–3102
Kim YJ, Hwang SH, Cho HH, Shin KK, Bae YC, Jung JS (2012) MicroRNA 21 regulates the proliferation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells and high-fat diet-induced obesity alters microRNA 21 expression in white adipose tissues. J Cell Physiol 227:183–193
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH (2008) Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283:1026–1033
Subedi A, Kim MJ, Nepal S, Lee ES, Kim JA, Sohn DH, Song K, Lee SH, Park WS, Jeong BS, Park PH (2013) Globular adiponectin modulates expression of programmed cell death 4 and miR-21 in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway. FEBS Lett 587:1556–1561
Kang M, Yan LM, Zhang WY, Li YM, Tang AZ, Ou HS (2013) Role of microRNA-21 in regulating 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation and adiponectin expression. Mol Biol Rep 40:5027–5034
Eichner LJ, Perry MC, Dufour CR, Bertos N, Park M, St-Pierre J, Giguere V (2010) miR-378(*) mediates metabolic shift in breast cancer cells via the PGC-1beta/ERRgamma transcriptional pathway. Cell Metab 12:352–361
Romao JM, Jin W, He M, McAllister T, le Guan L (2014) MicroRNAs in bovine adipogenesis: genomic context, expression and function. BMC Genom 15:137
Jin W, Dodson MV, Moore SS, Basarab JA, Guan LL (2010) Characterization of microRNA expression in bovine adipose tissues: a potential regulatory mechanism of subcutaneous adipose tissue development. BMC Mol Biol 11:29
Ganesan J, Ramanujam D, Sassi Y, Ahles A, Jentzsch C, Werfel S, Leierseder S, Loyer X, Giacca M, Zentilin L, Thum T, Laggerbauer B, Engelhardt S (2013) MiR-378 controls cardiac hypertrophy by combined repression of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway factors. Circulation 127:2097–2106
Liu SY, Zhang YY, Gao Y, Zhang LJ, Chen HY, Zhou Q, Chai ML, Li QY, Jiang H, Yuan B, Dai LS, Zhang JB (2015) MiR-378 Plays an Important Role in the Differentiation of Bovine Preadipocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 36:1552–1562
Ishida M, Shimabukuro M, Yagi S, Nishimoto S, Kozuka C, Fukuda D, Soeki T, Masuzaki H, Tsutsui M, Sata M (2014) MicroRNA-378 regulates adiponectin expression in adipose tissue: a new plausible mechanism. PLoS One 9:e111537
Gerin I, Bommer GT, McCoin CS, Sousa KM, Krishnan V, MacDougald OA (2010) Roles for miRNA-378/378* in adipocyte gene expression and lipogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 299:E198–E206
Jiang X, Xue M, Fu Z, Ji C, Guo X, Zhu L, Xu L, Pang L, Xu M, Qu H (2014) Insight into the effects of adipose tissue inflammation factors on miR-378 expression and the underlying mechanism. Cell Physiol Biochem 33:1778–1788
Zhu Y, Zhang X, Ding X, Wang H, Chen X, Zhao H, Jia Y, Liu S, Liu Y (2014) miR-27 inhibits adipocyte differentiation via suppressing CREB expression. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 46:590–596
Qin L, Chen Y, Niu Y, Chen W, Wang Q, Xiao S, Li A, Xie Y, Li J, Zhao X, He Z, Mo D (2010) A deep investigation into the adipogenesis mechanism: profile of microRNAs regulating adipogenesis by modulating the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. BMC Genom 11:320
Zhao JX, Hu J, Zhu MJ, Du M (2011) Trenbolone enhances myogenic differentiation by enhancing beta-catenin signaling in muscle-derived stem cells of cattle. Domest Anim Endocrinol 40:222–229
Miretti S, Martignani E, Accornero P, Baratta M (2013) Functional effect of mir-27b on myostatin expression: a relationship in Piedmontese cattle with double-muscled phenotype. BMC Genom 14:194
McFarlane C, Vajjala A, Arigela H, Lokireddy S, Ge X, Bonala S, Manickam R, Kambadur R, Sharma M (2014) Negative auto-regulation of myostatin expression is mediated by Smad3 and microRNA-27. PLoS One 9:e87687
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V, Czech MP (2008) Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:367–377
Kim C, Lee H, Cho YM, Kwon OJ, Kim W, Lee EK (2013) TNFalpha-induced miR-130 resulted in adipocyte dysfunction during obesity-related inflammation. FEBS Lett 587:3853–3858
Ortega FJ, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Pardo G, Sabater M, Hummel M, Ferrer A, Rodriguez-Hermosa JI, Ruiz B, Ricart W, Peral B, Fernandez-Real JM (2010) MiRNA expression profile of human subcutaneous adipose and during adipocyte differentiation. PLoS One 5:e9022
Chen F, Hu SJ (2012) Effect of microRNA-34a in cell cycle, differentiation, and apoptosis: a review. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 26:79–86
Yamakuchi M, Lowenstein CJ (2009) MiR-34, SIRT1 and p53: the feedback loop. Cell Cycle 8:712–715
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M, Lowenstein CJ (2008) miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13421–13426
Bork S, Horn P, Castoldi M, Hellwig I, Ho AD, Wagner W (2011) Adipogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells is down-regulated by microRNA-369-5p and up-regulated by microRNA-371. J Cell Physiol 226:2226–2234
Oishi Y, Manabe I, Tobe K, Tsushima K, Shindo T, Fujiu K, Nishimura G, Maemura K, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Suzuki R, Kitamura T, Akira S, Kadowaki T, Nagai R (2005) Kruppel-like transcription factor KLF5 is a key regulator of adipocyte differentiation. Cell Metab 1:27–39
Kinoshita M, Ono K, Horie T, Nagao K, Nishi H, Kuwabara Y, Takanabe-Mori R, Hasegawa K, Kita T, Kimura T (2010) Regulation of adipocyte differentiation by activation of serotonin (5-HT) receptors 5-HT2AR and 5-HT2CR and involvement of microRNA-448-mediated repression of KLF5. Mol Endocrinol 24:1978–1987
Farmer SR (2006) Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab 4:263–273
Pratt SL, Burns TA, Curry E, Duckett SK (2010) Expression of microRNA during bovine adipogenesis. J Nucleic Acids Investig 1:12
Hulsmans M, De Keyzer D, Holvoet P (2011) MicroRNAs regulating oxidative stress and inflammation in relation to obesity and atherosclerosis. FASEB J 25:2515–2527
Kang M, Yan LM, Li YM, Zhang WY, Wang H, Tang AZ, Ou HS (2013) Inhibitory effect of microRNA-24 on fatty acid-binding protein expression on 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation. Genet Mol Res 12:5267–5277
McGregor RA, Choi MS (2011) microRNAs in the regulation of adipogenesis and obesity. Curr Mol Med 11:304–316
Romao JM, Jin W, Dodson MV, Hausman GJ, Moore SS, le Guan L (2011) MicroRNA regulation in mammalian adipogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 236:997–1004
Lin Q, Gao Z, Alarcon RM, Ye J, Yun Z (2009) A role of miR-27 in the regulation of adipogenesis. FEBS J 276:2348–2358
Sacco J, Adeli K (2012) MicroRNAs: emerging roles in lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol 23:220–225
Lee J, Kemper JK (2010) Controlling SIRT1 expression by microRNAs in health and metabolic disease. Aging (Albany NY) 2:527–534
John E, Wienecke-Baldacchino A, Liivrand M, Heinaniemi M, Carlberg C, Sinkkonen L (2012) Dataset integration identifies transcriptional regulation of microRNA genes by PPARgamma in differentiating mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Nucleic Acids Res 40:4446–4460
Esau C, Kang X, Peralta E, Hanson E, Marcusson EG, Ravichandran LV, Sun Y, Koo S, Perera RJ, Jain R, Dean NM, Freier SM, Bennett CF, Lollo B, Griffey R (2004) MicroRNA-143 regulates adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 279:52361–52365
Kajimoto K, Naraba H, Iwai N (2006) MicroRNA and 3T3-L1 pre-adipocyte differentiation. RNA 12:1626–1632
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the help from J. Segers, T. B. Wilson and L. Shoup at the time of collecting tissue samples, as well as the rest of the staff at the University of Illinois Beef and Sheep Field Laboratory for animal handling and care. Supported in part by a competitive grant from the “Division of Nutritional Sciences: Vision 20/20’’ (University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign) interdisciplinary nutrition-related research program. Project # ILLU-971-352 (National Institute of Food and Agriculture, USA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Author(s) disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Moisá, S.J., Shike, D.W., Shoup, L. et al. Maternal Plane of Nutrition During Late-Gestation and Weaning Age Alter Steer Calf Longissimus Muscle Adipogenic MicroRNA and Target Gene Expression. Lipids 51, 123–138 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-4092-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-4092-y