Abstract
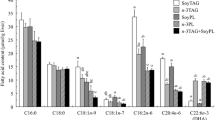
Although several works have reported absorption rate differences of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) bound to different lipid forms, such as ethyl ester, triacylglycerol (TAG), and phospholipids, no studies have investigated the effect of n-3 PUFA from glycolipids (GL). The present study compared the fatty acid contents of tissue and serum lipids from normal C57BL/6J mice fed two types of α-linolenic acid (ALA)-rich lipids, spinach lipid (SPL), and linseed oil (LO). ALA was primarily present as the GL form in SPL, while it existed as TAG in LO. Supplementation of both lipids increased ALA and its n-3 metabolites, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), and docosahexaenoic acid, and decreased n-6 PUFA, linoleic acid and arachidonic acid, in the livers, small intestines, and sera of the treated mice compared with those of the control group. When the comparison between the SPL and LO diets containing the same amount of ALA was conducted, the EPA and DPA levels in the liver lipids from mice fed the SPL diet were significantly higher than those fed the LO diet. Additionally, the total contents of n-3 PUFA of lipids from the livers, small intestines, and sera of the SPL group were higher than those of the LO group.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALA:
-
α-Linolenic acid
- ARA:
-
Arachidonic acid
- DGDG:
-
Digalactosyl diacylglycerol
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- DPA:
-
Docosapentaenoic acid
- EE:
-
Ethyl esters
- EPA:
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid
- FFA:
-
Free fatty acid
- GC:
-
Gas chromatography
- GL:
-
Galactolipids
- LA:
-
Linoleic acid
- LO:
-
Linseed oil
- MGDG:
-
Monogalactosyl diacylglycerol
- PC:
-
Phosphatidyl choline
- PL:
-
Phospholipids
- SPL:
-
Spinach lipids
- SQDG:
-
Sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- TL:
-
Total lipids
- TLC:
-
Thin layer chromatography
References
Harwood JL (1979) The synthesis of acyl lipids in plant tissues. Prog Lipid Res 18:55–86
Kamogawa H, Hosokawa M, Abe M, Miyashita K (2012) Carotenoid contents in Chlorella pyrenoidosa and concentration by saponification. Bull Fish Sci Hokkaido Univ 62:83–88 (Japanese)
Harwood JL (1980) Plant acyl lipids: structure, distribution and analysis. In: Stump PK, Conn EE (eds) Biochemistry of plants, vol 4. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–55
Block MA, Dorne AJ, Joyard J, Douce R (1983) Preparation and characterization of membrane fractions enriched in outer and inner envelope membranes from spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem 258:13281–13286
Whitaker BD (1986) Fatty-acid composition of polar lipids in fruit and leaf chloroplasts of “16:3”—and “18:3”—plant species. Planta 169:313–319
O’Brien JS, Benson AA (1964) Isolation and fatty acid composition of the plant sulfolipid and galactolipids. J Lipid Res 5:432–436
Bahl J, Francke B, Monéger R (1976) Lipid composition of envelopes, prolamellar bodies and other plastid membranes in etiolated, green and greening wheat leaves. Planta 129:193–201
Nichols BW (1965) The lipids of moss (Hypnum cupressiforme) and of the leaves of green holly (Ilex aquifolium). Phytochemistry 4:769–772
Kim K-B, Nam YA, Kim HS, Hayes AW, Lee B-M (2014) α-Linolenic acid: nutraceutical, pharmacological and toxicological evaluation. Food Chem Toxicol 70:163–178
Allayee H, Roth N, Hodis HN (2009) Polyunsaturated fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: implications for nutrigenetics. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics 2:140–148
Harris WS, Miller M, Tighe AP, Davidson MH, Schaefer EJ (2008) Omega-3 fatty acids and coronary heart disease risk: clinical and mechanistic perspectives. Atherosclerosis 197:12–24
Mori TA (2014) Dietary n-3 PUFA and CVD: a review of the evidence. Proc Nutr Soc 73:57–64
Superko HR, Superko AR, Lundberg GP, Margolis B, Garrett BC, Nasir K, Agatston AS (2014) Omega-3 fatty acid blood levels clinical significance update. Curr Cardiovasc Risk Rep 8:407
Wachira JK, Larson MK, Harris WS (2014) n-3 Fatty acids affect haemostasis but do not increase the risk of bleeding: clinical observations and mechanistic insights. Br J Nutr 111:1652–1662
Carnielli VP, Simonato M, Verlato G, Luijendijk I, De Curtis M, Sauer PJJ, Cogo PE (2007) Synthesis of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in preterm newborns fed formula with long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Am J Clin Nutr 86:1323–1330
Williams CM, Burdge G (2006) Long-chain n-3 PUFA: plant v. marine sources. Proc Nutr Soc 65:42–50
Brenna JT, Salem N Jr, Sinclair AJ, Cunnane SC (2009) α-Linolenic acid supplementation and conversion to n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in humans. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 80:85–91
Domenichiello AF, Chen CT, Trepanier M-T, Stavro PM, Bazinet RP (2014) Whole body synthesis rates of DHA from α-linolenic acid are greater than brain DHA accretion and uptake rates in adult rats. J Lipid Res 55:62–74
Barceló-Coblijn G, Murphy EJ (2009) Alpha-linolenic acid and its conversion to longer chain n-3 fatty acids: benefits for human health and a role in maintaining tissue n-3 fatty acid levels. Prog Lipid Res 48:355–374
Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS, Appel LJ (2002) Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 106:2747–2757
Andersson L, Bratt C, Arnoldsson KC, Herslöf B, Olsson NU, Sternby B, Nilsson Å (1995) Hydrolysis of galactolipids by human pancreatic lipolytic enzymes and duodenal contents. J Lipid Res 36:1392–1400
Sugawara T, Miyazawa T (2000) Digestion of plant monogalactosyldiacylglycerol and digalactosyldiacylglycerol in rat alimentary canal. J Nutr Biochem 11:147–152
Dyerberg J, Madsen P, Møller JM, Aardestrup I, Schmidt EB (2010) Bioavailability of marine n-3 fatty acid formulations. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 83:137–141
Schuchardt JP, Schneider I, Meyer H, Neubronner J, von Schacky C, Hahn A (2011) Incorporation of EPA and DHA into plasma phospholipids in response to different omega-3 fatty acid formulations—a comparative bioavailability study of fish oil vs. krill oil. Lipids Health Dis 10:145
Ramíreza M, Amatea L, Gil A (2001) Absorption and distribution of dietary fatty acids from different sources. Early Hum Dev 65:S95–S101
Tanaka Y, Ohkubo T, Fukuda N, Hibino H (2003) Effect of molecular forms on distribution of docosahexaenoic acid into organs in mice. J Oleo Sci 52:89–97
Tang X, Li Z-J, Xu J, Xue Y, Li J-Z, Wang J-F, Yanagita T, Xue C-H, Wang Y-M (2012) Short term effects of different omega-3 fatty acid formulation on lipid metabolism in mice fed high or low fat diet. Lipids Health Dis 11:70
Ulven SM, Kirkhus B, Lamglait A, Basu S, Elind E, Haider T, Berge K, Vik H, Pedersen JI (2011) Metabolic effects of krill oil are essentially similar to those of fish oil but at lower dose of EPA and DHA, in healthy volunteers. Lipids 46:37–46
Prevot AF, Mordret FX (1976) Utilisation des colonnes capillaries de verre pour l’analyse des corps gras par chromotographie en phase gazeuse. Rev Fse Corps Gras 23:409–423
Folch J, Lees M, Stanley GHS (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Blanchard H, Pédrono F, Boulier-Monthéan N, Catheline D, Rioux V, Legrand P (2013) Comparative effects of well-balanced diets enriched in α-linolenic or linoleic acids on LC-PUFA metabolism in rat tissues. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 88:383–389
Delplanque B, Du Q, Agnani G, LeRuyet P, Martin JC (2013) A dairy fat matrix providing alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is better than a vegetable fat mixture to increase brain DHA accretion in young rats. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 88:115–120
Poudyal H, Panchal SK, Ward LC, Brown L (2013) Effects of ALA, EPA and DHA in high-carbohydrate, high-fat diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. J Nutr Biochem 24:1041–1052
Yamaguchi T, Sugimura R, Shimajiri J, Suda M, Abe M, Hosokawa M, Miyashita K (2012) Oxidative stability of glyceroglycolipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Oleo Sci 61:505–513
Burri L, Hoem N, Banni S, Berge K (2012) Marine omega-3 phospholipids: metabolism and biological activities. Int J Mol Sci 13:15401–15419
Mun S, Decker EA, McClements DJ (2007) Influence of emulsifier type on in vitro digestibility of lipid droplets by pancreatic lipase. Food Res Int 40:770–781
Salem NM, Lin YH, Moriguchi T, Lim SY, Salem N Jr, Hibbeln JR (2015) Distribution of omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the whole rat body and 25 compartments. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 100:13–20
Ghasemifard S, Hermon K, Turchini GM, Sinclair AJ (2014) Metabolic fate (absorption, β-oxidation and deposition) of long-chain n-3 fatty acids is affected by sex and by the oil source (krill oil or fish oil) in the rat. Br J Nutr 114:684–692
Ghasemifard S, Turchini GM, Sinclair AJ (2014) Omega-3 long chain fatty acid “bioavailability”: a review of evidence and methodological considerations. Prog Lipid Res 56:92–108
Domenichiello AF, Kitson AP, Bazinet RP (2015) Is docosahexaenoic acid synthesis from α-linolenic acid sufficient to supply the adult brain? Prog Lipid Res 59:54–66
Guichardant M, Calzada C, Bernoud-Hubac N, Lagarde M, Véricel E (2015) Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and oxygenated metabolism in atherothrombosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1851:485–495
Bruno A, Rossi C, Marcolongo G, Di Lena A, Venzo A, Berrie CP, Corda D (2005) Selective in vivo anti-inflammatory action of the galactolipid monogalactosyldiacylglycerol. Eur J Pharmacol 524:159–168
Maeda N, Hada T, Yoshida H, Mizushina Y (2007) Inhibitory effect on replicative DNA polymerases, human cancer cell proliferation, and in vivo anti-tumor activity by glycolipids from spinach. Curr Med Chem 14:955–967
Maeda N, Kokai Y, Ohtani S, Sahara H, Kumamoto-Yonezawa Y, Kuriyama I, Hada T, Sato N, Yoshida H, Mizushina Y (2008) Anti-tumor effect of orally administered spinach glycolipid fraction on implanted cancer cells, colon-26, in mice. Lipids 43:741–748
Ma L, Lin X-M (2010) Effects of lutein and zeaxanthin on aspects of eye health. J Sci Food Agric 90:2–12
Ruban AV, Johnson MP (2010) Xanthophylls as modulators of membrane protein function. Arch Biochem Biophys 504:78–85
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the “Scientific technique research promotion program from agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and food industry” from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries in Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Kuroe, M., Kamogawa, H., Hosokawa, M. et al. Dietary ALA from Spinach Enhances Liver n-3 Fatty Acid Content to Greater Extent than Linseed Oil in Mice Fed Equivalent Amounts of ALA. Lipids 51, 39–48 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-4086-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-4086-9