Abstract
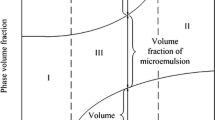
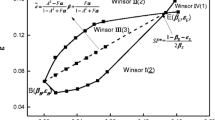
The partition of n-butanol in Winsor type III (W-III) microemulsions was investigated in this work. Three kinds of anionic surfactants (sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), sodium dodecyl sulfonate (DSS), and sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS)) and two kinds of anionic/cationic surfactant mixtures (SDS/octadecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (OTAC) mixtures and DSS/OTAC mixtures) were studied. Internal standard gas chromatography was employed in n-butanol content analysis. The results showed that no water exists in the excess oil (EO) phase and no oil exists in the excess water (EW) phase. For the W-III microemulsions obtained by salinity scanning, relatively constant n-butanol content in the EO (11–12 v%) and EW (1–4 v%) was found under different salinities. Accurate measurement of n-butanol content in each phase is important for those systems having low solubilization ability. For the W-III microemulsions prepared using SDS/OTAC surfactant mixture, the percentage of n-butanol distributed into the interfacial layer decreased while the fraction of n-butanol in the interfacial layer first increased sharply and then tended to be stable with the addition of n-butanol. For the different optimum W-III microemulsion systems tested, most of the surfactant-to-alcohol molar ratio data are near 1:3, but obvious deviation could be observed for some data. On the basis of the accurate measurement of n-butanol content in the EO and EW phases, the standard free energy, ΔG * o→in (T = 298.15 K) of n-butanol transferring from the EO phase to the interfacial region was calculated. The results show negative ΔG * o→in values. For microemulsions with the same components, n-butanol content is an important factor influencing the ΔG * o→in value, and a high absolute value of ΔG * o→in leads to high solubilization ability.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fanun M (2009) Microemulsions: properties and applications. CRC Press, New York
Tanthakit P, Nakrachata-Amorn A, Scamehorn JF, Sabatini DA, Tongcumpou C, Chavadej S (2009) Microemulsion formation and detergency with oily soil: V. effects of water hardness and builder. J Surfact Deterg 12:173–183
Santanna VC, Curbelo FDS, Castro Dantas TN, Dantas Neto AA, Albuquerque HS, Garnica AIC (2009) Microemulsion flooding for enhanced oil recovery. J Petrol Sci Eng 66(3/4):117–120
Cheng HF, Sabatini DA (2002) Phase-behavior-based surfactant-contaminant separation of middle phase microemulsion. Sep Sci Technol 37(1):127–146
Upadhyaya A, Acosta EJ, Scamehorn JF, Sabatini DA (2006) Microemulsion Phase Behavior of Anionic-Cationic Surfactant Mixtures: Effect of Tail Branching. J Surfact Deterg 9(2):169–179
Huh C (1979) Interfacial tensions and solubilizing ability of a microemulsion phase that coexists with oil and brine. J Colloid Interface Sci 71:408–426
Salager JL, Morgan JC, Schechter RS, Wade WH, Vasquez E (1979) Optimum formulation of surfactant/water/oil systems for minimum interfacial tension of phase behavior. Soc Pet Eng J 19:107–115
Bourrel M, Salager JL, Schechter RS, Wade WH (1980) A correlation for phase behavior of nonionic surfactants. J Colloid Interface Sci 75(2):451–461
Anton RE, Salager JL (1990) Effect of the electrolyte anion on the salinity contribution to optimum formulation of anionic surfactant microemulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 140(1):75–81
Liu H, Yuan Y, Ding C, Chen S, Qi X (2015) Effect of electrolytes and correlations for salinities at the optimum formulation of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate microemulsions. J Surfact Deterg 18:569–578
Rakshit AK, Moulik SP (2009) Physicochemistry of W/O Microemulsions: Formation, Stability, and Droplet Clustering, in: Microemulsions: Properties and Applications, ed. by Fanun M. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group
Hirasaki GJ (1982) Interpretation of the Change in Optimal Salinity with Overall Surfactant Concentration. Society of Petroleum, Engineering Journal Dec, pp 339–354
Robertson S D (1988) An Empirical Model for Microemulsion Phase Behavior, SPE Reserv Eng Aug 1002–1016
Baviere M, Schechter R, Wade W (1981) The influence of alcohols on microemulsion composition. J Colloid Interface Sci 81:266–279
Li W, Xu P, Zhou H, Yang L, Liu H (2012) Advanced functional nanomaterials with microemulsion phase. Sci China Tech Sci 55(2):387–416
Liu H, Zhang X, Ding C, Chen S, Qi X, Xia X (2014) Phase Behavior of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-n-butanol-kerosene-water Microemulsion System. Chin J Chem Eng 22(6):699–705
Graciaa A, Lachaise J, Cucuphat C, Bourrel M, Salager JL (1993) Improving solubilization in microemulsions with additives. 2. Long chain alcohols as lipophilic linkers. Langmuir 9:3371–3374
Zhou M, Rhue RD (2001) Effect of pentanol partitioning on solubilization of tetrachloroethylene and gasoline by sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles. J Colloid Interface Sci 241:199–204
Salager JL, Anton R, Sabatini DA, Harwell JH, Acosta EJ, Tolosa LI (2005) Enhancing solubilization in microemulsions-state of the art and current trends. J Surfact Deterg 8(1):3–21
Salager JL, Forgiarini AM, Bullón J (2013) How to attain ultralow interfacial tension and three-phase behavior with surfactant formulation for enhanced oil recovery: a review. Part 1. Optimum formulation for simple surfactant–oil–water ternary systems. J Surfact Deterg 16(4): 449–472
Salager J L, Forgiarini A M, Márquez L, Manchego L, Bullon J (2013) How to Attain an Ultralow Interfacial Tension and a Three-Phase Behavior with a Surfactant Formulation for Enhanced Oil Recovery: A Review. Part 2. Performance Improvement Trends from Winsor’s Premise to Currently Proposed Inter-and Intra-Molecular Mixtures. J Surfact Deterg 16(5): 631–663
Tohren CGK, Ramsburg CA, Pennell KD, Hayes KF (2002) Implications of alcohol partitioning behavior for in situ density modification of entrapped dense nonaqueous phase liquids. Environ Sci Technol 36:104–111
Damrongsiri S, Tongcumpou C, Sabatini DA (2013) Partition behavior of surfactants, butanol, and salt during application of density-modified displacement of dense non-aqueous phase liquids, J Hazard. Mater 248–249:261–267
Caponetti E, Lizzio A, Triolo Griffith RWL, Johnson JS Jr (1992) Alcohol partition in a water-in-oil microemulsion from small-angle neutron scattering. Langmuir 8:1554–1562
Yao J, Laurence SR (1994) Arenediazonium Arenediazonium Salts: new probes of the interfacial compositions of association colloids. 3. Distributions of Butanol, Hexanol, and Water in Four-Component Cationic Microemulsions. J Am Chem Soc 116:11779–11786
Chai J, Zhao J, Gao Y, Yang X, Wu C (2007) Studies on the phase behavior of the microemulsions formed by sodium dodecyl sulfonate, sodium dodecyl sulfate and sodium dodecyl benzenesulfonate with a novel fishlike phase diagram, Colloids and Surfaces A. Physicochem Eng. Aspects 302:31–35
Chai J, Wu Y, Li X, Yang B, Lu J (2011) Effect of oil/water ratios on the phase behavior and the solubilization ability of microemulsion systems containing sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Solution Chem 40:1889–1898
Magee JA, Herd AC (1999) Internal standard calculations in chromatography. J Chem Educ 76(2):252
Kuchler T, Bizezinski H (2000) Application of GC-MS/MS for the analysis of PCDD/Fs in sewage effluents. Chemosphere 40(2):213–217
Cheng H, Sabatini DA (2007) Separation of organics compounds from surfactant solutions: a review. Sep Sci Technol 42:453–475
Grob RL (ed) (1995) Modern practice of gas chromatography, 3rd edn. New York, Wiley
Høiland H, Gjerde MI, Mo C, Lie E (2001) Solubilization of alcohols in SDS and TTAB from isentropic partial molar compressibilities and solubilities, Colloids and Surfaces A. Physicochem Eng Aspects 183–185:651–660
Rao IV, Ruckenstein E (1986) Micellization behavior in the presence of alcohols. J Colloid Interface Sci 113(2):375–387
Queste S, Salager JL, Strey R, Aubry JM (2007) The EACN Scale for oil classification revisited thanks to fish diagrams. J Colloid Interface Sci 312:98–107
Reed RL, Healy RN (1977) Some Physico-chemical Aspects of Microemulsion Flooding: A Review, in Improved Oil Recovery by Surfactant and Polymer Flooding, edited by D.O. Shah and R.S. Schechter, Academic Press, New York, 383
Barakat Y, Fortney LN, Schechter RS, Wade WH, Yiv SH (1982) Alpha-olefin sulfonates for enhanced oil recovery. In: Proceedings 2nd European symposium on enhanced oil recovery, Paris, November 1982, Technip, Paris pp 11–20
Zhao Z, Bi Ch, Li Z, Qiao W, Cheng L (2006) Interfacial tension between crude oil and decylmethylnaphthalene sulfonate surfactant alkali-free flooding systems. Colloids Surf A 276:186–191
Stubenrauch C (2009) Microemulsions: Background. Applications, Perspectives, Blackwell Publishing Ltd, New Concepts
Shah D (1971) Significance of the 1:3 molecular ratio in mixed surfactant systems. J Coll Interface Sci 37:744–752
Wang CC, Yu NS, Chen CY (1996) Kinetic study of the mini-emulsion polymerization of styrene. Polymer 37(12):2509–2511
Zhou M, Rhue RD (2000) Effect of interfacial alcohol concentrations on oil solubilization by sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles. J Colloid Interface Sci 228(1):18–23
Guerin G, Bellocq AM (1988) Effect of salt on the phase behavior of the ternary system water-pentanol-sodium dodecylsulfate. J Phys Chem 92(9):2550–2557
Salager J (1977) Physico-chemical properties of surfactant-water-oil mixtures: phase behavior, microemulsion formation and interfacial tension, PhD Dissertation, The University of Texas at Austin
Jones SC, Dreher KD (1976) Co-surfactants in micellar systems used for tertiary oil recovery. Soc Petrol Eng J 16:161
Gerbacia W, Rosano HL (1973) Microemulsions: formation and stabilization. J Colloid Interface Sci 44(2):242–248
Birdi KS (1982) Microemulsions: effect of alkyl chain length of alcohol and alkane. Colloid Polym Sci 260:628–631
He Y, Yang B, Cheng G, Pan H (2004) Influence of the thermodynamic stability of microemulsion on the size of nanoparticles prepared by a coupling route of microemulsion with homogeneous precipitation. Mater Lett 58:2019–2022
Qiu G, Chen Y, Tian Y, Fang L, Xiao L, Sun Y (2004) Study on properties of microemulsion aeo-9/butanol/cyclohexane/salt aqueous solution, J Rare Earths 22:25–28
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21106187), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (14CX05031A), and the project of Huangdao district (2014-1-49) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Wu, Z., Jing, J. et al. Partition of n-Butanol Among Phases and Solubilization Ability of Winsor type III Microemulsions. J Surfact Deterg 19, 713–724 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-016-1818-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-016-1818-7