Abstract
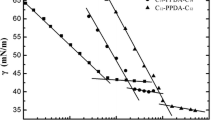
A series of novel cationic gemini surfactants, bis-(N-(3-alkylamido-propyl)-N,N-dimethyl)-p-phenylenediammonium dichloride, were synthesized. The structures of the gemini surfactants were characterized by IR, 1H NMR and 13C NMR. The Krafft temperatures of surfactants were determined through conductivity, the surface active properties in aqueous solution were studied at various temperatures by surface tension and conductivity. The thermodynamic functions of micellization process of the surfactants were also calculated by conductivity. The Krafft temperatures of the surfactants were 12, 13 and 28 °C. The values of CMC and Γ max decreased with increasing the length of hydrophobic chains, but the values of CMC and α increased with increasing temperature. The process of micellization is a spontaneous, exothermic and entropy-driven process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han Y, Wang Y (2011) Aggregation behavior of gemini surfactants and their interaction with macromolecules in aqueous solution. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:1939–1956
Patial P, Shaheen A, Ahmad I (2013) Synthesis of ester based cationic pyridinium gemini surfactants and appraisal of their surface active properties. J Surf Deterg 16:49–56
Zhang Y, Ding M, Zhou L et al (2012) Synthesis and antibacterial characterization of gemini surfactant monomers and copolymers. Polym Chem 3:907–913
Hegazy MA, El-Tabei AS (2013) Synthesis, surface properties, synergism parameter and inhibitive performance of novel cationic gemini surfactant on carbon steel corrosion in 1M HCl solution. J Surf Deterg 16:221–232
Rosen MJ, Mathias JH, Davenport L (1999) Aberrant aggregation behavior in cationic gemini surfactants investigated by surface tension, interfacial tension, and fluorescence methods. Langmuir 15:7340–7346
Xu H, Chen D, Cui Z (2011) Study on the synthesis and surface active properties of a novel surfactant with triple quaternary ammonium groups and triple dodecyl chains derived from glycerin. J Surf Deterg 14:167–172
Han Y, He C, Cao M, Huang X et al (2010) Facile disassembly of amyloid fibrils using gemini surfactant micelles. Langmuir 26:1583–1587
Caillier L, Givenchy ET, Levy R et al (2009) Polymerizable semi-fluorinated gemini surfactants designed for antimicrobial materials. J Colloid Interface Sci 332:201–207
Tehrani-Bagha AR, Holmberg K (2010) Cationic ester-containing gemini surfactants: physical–chemical properties. Langmuir 26:9276–9282
Ao M, Huang P, Xu G et al (2009) Aggregation and thermodynamic properties of ionic liquid-type gemini imidazolium surfactants with different spacer length. Colloid Polym Sci 287:395–402
Zhang Q, Gao Z, Xu F, Tai S (2012) Effect of hydrocarbon structure of the head group on the thermodynamic properties of micellization of cationic gemini surfactants: an electrical conductivity study. J Colloid Interface Sci 371:73–81
Menger FM, Keiper JS (2000) Gemini surfactants. Angew Chem Int Ed 39:1906–1920
Mivehi L, Bordes R, Holmberg K (2011) Adsorption of cationic gemini surfactants at solid surfaces studied by QCM–D and SPR: effect of the rigidity of the spacer. Langmuir 27:7549–7557
Zhang Z, Zheng P, Guo Y et al (2012) The effect of the spacer rigidity on the aggregation behavior of two ester-containing gemini surfactants. J Colloid Interface Sci 379:64–71
Zhang Q, Gao Z, Xu F et al (2012) Surface tension and aggregation properties of novel cationic gemini surfactants with diethylammonium head groups and a diamido spacer. Langmuir 28:11979–11987
Song LD, Rosen MJ (1996) Surface properties, micellization, and premicellar aggregation of gemini surfactants with rigid and flexible spacers. Langmuir 12:1149–1153
Menger FM, Keiper JS, Azov V (2000) Gemini surfactants with acetylenic spacers. Langmuir 16:2062–2067
Zhu D, Cheng F, Chen Y, Jiang S (2012) Preparation, characterization and properties of anionic gemini surfactants with long rigid or semi–rigid spacers. Colloids Surf A 397:1–7
Pires PAR, Seoud OA El (2006) Benzyl (3-acylaminopropyl) dimethylammonium chloride surfactants: structure and some properties of the micellar aggregates. Progr Colloid Polym Sci 133: 131–141
Zhao J, Christian SD, Fung BM (1998) Mixtures of monomeric and dimeric cationic surfactants. J Phys Chem B 102:7613–7618
Hirata H, Ohira A, Iimura N (1996) Measurements of the Krafft point of surfactant molecular complexes: insights into the intricacies of “solubilization”. Langmuir 12:6044–6052
Wang X, Wang J, Wang Y, Yan H (2004) Effect of the nature of the spacer on the aggregation properties of gemini surfactants in an aqueous solution. Langmuir 20:53–56
Chen ML, Penfold J, Thomas RK, Smyth TJP et al (2010) Mixing behavior of the biosurfactant, rhamnolipid, with a conventional anionic surfactant, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate. Langmuir 26:17958–17968
Mata J, Varade D, Bahadur P (2005) Aggregation behavior of quaternary salt based cationic surfactants. Thermo chim Acta 428:147–155
Alami E, Beinert G, Marie P, Zana R (1993) Alkanediyl–α, ω–bis(dimethylalkylammonium bromide) surfactants. 3. Behavior at the air–water interface. Langmuir 9:1465–1467
Rodriguez A, Graciani M del M, Robina I et al (2006) Effects of ethylene glycol addition on the aggregation and micellar growth of gemini surfactants. Langmuir 22: 9519–9525
Lu T, Lan Y, Liu C, Huang J, Wang Y (2012) Surface properties, aggregation behavior and micellization thermodynamics of a class of gemini surfactants with ethyl ammonium head groups. J Colloid Interface Sci 377:222–230
Zhou L, Jiang X, Li Y, Chen Z, Hu X (2007) Synthesis and properties of a novel class of gemini pyridinium surfactants. Langmuir 23:11404–11408
Angayarkanny S, Vijay R, Baskar G, Mandal AB (2012) Formation of self–aggregated structures of different types in water of chiral polymerizable amphiphiles from l-tyrosine and l-phenylalanine. Langmuir 28:9378–9386
Perez L, Pinazo A, Rosen MJ, Infante MR (1998) Surface activity properties at equilibrium of novel gemini cationic amphiphilic compounds from arginine, bis(args). Langmuir 14:2307–2315
Tsubone K, Arakawa Y, Rosen MJ (2003) Structural effects on surface and micellar properties of alkanediyl–α, ω–bis(sodium N–acyl–β–alaninate) gemini surfactants. J Colloid Interface Sci 262:516–524
Yoshimura T, Esumi K (2004) Synthesis and surface properties of anionic gemini surfactants with amide groups. J Colloid Interface Sci 276:231–238
Li PF, Chen QH, Zhao JL et al. (2012) Synthesis and properties of X–type alkyl sulfonate Gemini surfactants derived from cyanuric chloride. J Surf Deterg 15:449–456
Geng F, Liu J, Zheng L et al. (2010) Micelle formation of long-chain imidazolium ionic liquids in aqueous solution measured by isothermal titration micro calorimetry. J Chem Eng Data 55:147–151
Pires PAR, Seoud OAE (2006) Benzyl (3-acylaminopropyl) dimethylammonium chloride surfactants: structure and some properties of the micellar aggregates. Prog Colloid Polym Sci 133:131–141
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (B201114, GC04A408-2), and the Science Research Project of the Ministry of Education of Heilongjiang Province of China (2012TD012, 12511Z030, 12521594).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, D., Guo, X. & Jia, L. Synthesis, Surface Active Properties of Novel Gemini Surfactants with Amide Groups and Rigid Spacers. J Surfact Deterg 16, 913–919 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-013-1502-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-013-1502-0