Abstract
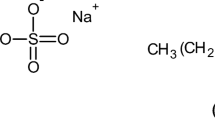
A mixture of anionic and amphoteric surfactants is composed of three components at intermediate pH levels: anionic, cationic (protonated amphoteric), and zwitterionic (unprotonated amphoteric). Knowledge of the composition of each surfactant in both monomer and micellar forms (monomer–micelle equilibrium) is important in applications using this mixture. Hydrogen ion titration of the mixed surfactant solution as a function of surfactant composition is combined with the pseudophase separation model and regular solution theory for the three-surfactant mixture to calculate the concentration of each surfactant in monomer and in micelle forms at different pH levels. The specific systems studied here contain sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and dimethyldodecylamine oxide (DDAO), which are used in a wide range of consumer products. The degree of protonation of monomeric DDAO is not affected by the presence of SDS, indicating an insignificant formation of ion pairs between these monomers. However, the presence of SDS in micelles shifts the micellar pK a of DDAO protonation significantly and the method used here allows the quantification of partial fugacities of each individual surfactant in micelle form. The composition in the monomer phase at each pH will aid in understanding and predicting solution compositions corresponding to anionic/amphoteric surfactant precipitation boundaries, which is the focus of the subsequent paper in this series.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Porter MR (1994) Handbook of surfactants, 2nd edn. Blackie, London, p 258
Rosen MJ (2004) Surfactants and interfacial phenomena, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken, p 1
Herrmann KW (1962) Non-ionic-cationic micellar properties of dimethyl dodecylamine oxide. J Phys Chem 66:295–300
Tokiwa F, Ohki K (1966) Potentiometric titration of a nonionic-cationic surfactant in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem 70:3437–3441
Ikeda S, Tsunoda M, Maeda H (1978) The application of the Gibbs adsorption isotherm to aqueous solutions of a nonionic-cationic surfactant. J Colloid Interface Sci 67:336–348
Ikeda S, Tsunoda M, Maeda H (1979) The effects of ionization of micelle size of dimethyldodecylamine oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 70:448–455
Imae T, Ikeda S (1985) Formation of rodlike micelles of dimethyloleylamine oxide in aqueous solutions: effects of addition of hydrochloric acid and sodium chloride on the micelle size and the intermicellar interaction. J Colloid Polym Sci 263:756–766
Chang DL, Rosano HL, Woodward AE (1985) Carbon–13 NMR study of the effects of pH on dodecyldimethylamine oxide solutions. Langmuir 1:669–672
Rathman JF, Christian SD (1990) Determination of surfactant activities in micellar solutions of dimethyldodecylamine oxide. Langmuir 6:391–395
Zimmerman JA, Schnaare RL (1999) Determination of amine oxide micellar activities in nonswamping electrolytes solutions. Langmuir 15:384–390
Mille M (1981) Effect of nearest-neighbor interactions on surface titrations. J Colloid Interface Sci 81:169–179
Maeda H (1988) Electric and nonelectric free energy of nonionic-ionic micelles. J Phys Chem 92:4490–4498
Maeda H (1995) A simple thermodynamic analysis of the stability of ionic/nonionic mixed micelles. J Colloid Interface Sci 172:98–105
Maeda H (2003) A thermodynamic analysis of the hydrogen ion titration of micelles. J Colloid Interface Sci 263:277–287
Lair V, Bouguerra S, Turmine M, Letellier P (2004) Thermodynamic study of the protonation of dimethyldodecylamine N-oxide micelles in aqueous solution at 298 K. Establishment of a theoretical relationship linking critical micelle concentrations and pH. Langmuir 20:8490–8495
Goldsipe A, Blankschtein D (2006) Molecular-thermodynamic theory of micellization of pH-sensitive surfactants. Langmuir 22:3547–3559
Kolp DG, Laughlin RG, Krause FP, Zimmerer RE (1963) Interaction of dimethyldodecylamine oxide with sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate in dilute solution. J Phys Chem 67:51–55
Rosen MJ, Friedman D, Gross M (1964) A surface tension study of the interaction of dimethyldodecylamine oxide with potassium dodecane sulfonate in dilute aqueous solution. J Phys Chem 68:3219–3225
Chang DL, Rosano HL (1984) Structure/performance relationships in surfactants. In: Rosen MJ (ed) ACS symposium series 253. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, p 129
Imae T, Araki H, Ikeda S (1986) The anomalous behavior or surface tension of aqueous solutions of dimethyloleylamine oxide and its multimolecular adsorption on aqueous surfaces. Colloids Surf 17:207–219
Imae T, Araki H, Ikeda S (1986) The absorption spectra and the micelle species of dimethyloleylamine oxide in aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf 17:221–228
Abe M, Kato K, Ogino K (1989) Effects of inorganic electrolytes and of pH on micelle formation of amphoteric-anionic mixed surfactant systems. J Colloid Interface Sci 127:328–335
Weers JG, Rathman JF, Scheuing DR (1990) Structure/performance relationships in long chain dimethylamine oxide/sodium dodecylsulfate surfactant mixtures. Colloid Polym Sci 268:832–846
Imae T, Kakitani M (1996) Electrokinetic properties of mixed solutions of dodecyldimethylamine oxide and sodium dodecyl sulfate: specific adsorption effects of small ions. Colloid Polym Sci 274:1170–1175
Goldsipe A, Blankschtein D (2006) Titration of mixed micelles containing a pH-sensitive surfactant and conventional (pH-insensitive) surfactants: a regular solution theory modeling approach. Langmuir 22:9894–9904
Tokiwa F, Ohki K (1968) Effects of small ions and long-chain alkyl ions on the potentiometric behavior of micelles of dimethyldodecylamine oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 27:247–252
Soontravanich S, Scamehorn JF, Harwell JH, Sabatini DA (2007) Interaction between an anionic and an amphoteric surfactant. Part II. Precipitation. J Surfact Deterg (submitted)
Davies CW (1962) Ion association. Butterworths, London, p 41
Kanicky JR, Shah DO (2003) Effect of premicellar aggregation on the pK a of fatty acid soap solutions. Langmuir 19:2034–2038
Maeda H, Kakehashi R (2000) Effects of protonation on the thermodynamic properties of alkyl dimethylamine oxides. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 88:275–293
Maeda H, Muroi S, Ishii M, Kakehashi R, Kaimoto H, Nakahara T, Motomura K (1995) Effects of ionization on the critical micelle concentration and the surface excess of dodecyldimethylamine oxide in salt solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 175:497–505
Holland PM, Rubingh DN (1983) Nonideal multicomponent mixed micelle model. J Phys Chem 87:1984–1990
Rubingh DN (1979) Mixed micelle solutions. In: Mittal KL (ed) Solution chemistry of surfactants. Plenum Press, New York, pp 337–354
Rosen MJ (2004) Surfactants and interfacial phenomena, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken, p 379
Goloub TP, Pugh RJ, Zhmud BV (2000) Micellar interactions in nonionic/ionic mixed surfactant systems. J Colloid Interface Sci 229:72–81
Tajima K, Nakamura A, Tsutsui T (1979) Surface activity of complex in mixed surfactant solution. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 52:2060–2063
Stellner KL, Amante JC, Scamehorn JF, Harwell JH (1987) Precipitation phenomena in mixtures of anionic and cationic surfactants in aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 123:186–200
da Silva FLB, Bogren D, Soderman O, Akesson T, Jonsson B (2002) Titration of fatty acids solubilized in cationic, nonionic, and anionic micelles. Theory and experiment. J Phys Chem B 106:3515–3522
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Edwin E. Tucker for valuable discussions. Financial support for this work was provided by the industrial sponsors of the Institute for Applied Surfactant Research at the University of Oklahoma including Akzo Nobel, Clorox, Conoco/Phillips, Church and Dwight, Dow, Ecolab, Haliburton, Huntsman, Oxiteno, Proctor & Gamble, Sasol, Shell, and Unilever. Dr. Scamehorn holds the Asahi Glass Chair and Dr. Harwell holds the Conoco/Dupont Professorship in the School of Chemical, Biological, and Materials Engineering at the University of Oklahoma. Dr. Sabatini holds the Sun Oil Company Chair in the School of Civil Engineering and Environmental Science at the University of Oklahoma.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Soontravanich, S., Munoz, J.A., Scamehorn, J.F. et al. Interaction Between an Anionic and an Amphoteric Surfactant. Part I: Monomer–Micelle Equilibrium. J Surfact Deterg 11, 251–261 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-008-1080-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-008-1080-8