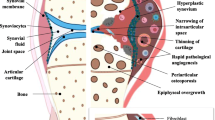
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has become one of the most studied autoimmune chronic inflammatory diseases (ACIDs), either from the pathogenetic or from the therapeutic point of view. It is recognized that synovial fibroblasts, TH1 and TH17 cells likely play along with the B cells the most relevant role. The disease has a polygenic background that characterizes the seropositive and the seronegative subsets. Over the years, we realized that no more than 15–20% of long-standing RA (LSRA) treated with conventional drugs can reach full remission, whereas the most recent data in early RA (ERA) have demonstrated that 40–60% can be put into clinical and biological remission. This of course is of crucial importance to avoid any progression of the structural damage that leads to functional disability. If we consider that a disability index score (Health Assessment Questionnaire 0–3) of a severe arthritis can cost up to 21,000 EUs, while a mild disease will cost not more than 5,500 EUs per year, it appears very clear that a low disease activity (LDA) or a remission state (Rem) should be the aim in each single patient, in order to keep the workability and maintain the productivity. This is and should be the major aim in each RA patient.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plenge RM (2009) Rheumatoid arthritis genetics: 2009 update. Curr Rheumatol Rep 11:351–356
Tolusso B, Frezza D, Mattioli C, Fedele AL, Bosello S, Faustini F, Peluso G, Giambra V, Pietrapertosa D, Morelli A, Gremese E, De Santis M, Ferraccioli GF (2009) Allele *2 of the HS1, 2 A enhancer of the Ig regulatory region associates with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:416–419
Orozco G, Eyre S, Hinks A, Bowes J, Morgan AW, Wilson AG, Wordsworth P, Steer S, Hocking L, UKRAG consortium, Worthington J, Barton A (2011) Study of the common genetic background for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 70:463–468
Ria F, Penitente R, De Santis M, Nicolo’ C, Di Sante G, Orsini M, Arzani D, Fattorossi A, Battaglia A, Ferraccioli GF (2008) Collagen-specific T cell repertoire in blood and synovial fluid varies with disease activity in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Therapy 10:R135
De Rosa MC, Giardina B, Bianchi C, Carelli Alinovi C, Pirolli D, Ferraccioli GF, De Santis M, Di Sante G, Ria F (2010) Modeling the ternary complex TCR-Vbeta/Collagen II (261–273)/HLA-DR4 associated with rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 5(7):e11550
Ria F et al. Unpublished
Ferraccioli GF, Bracci-Laudiero L, Alivernini S, Gremese E, Tolusso B, De Benedetti F (2010) Interleukin 1 β and interleukin 6 in arthritis animal models: roles in the early phase of transition from acute to chronic inflammation and relevance for human rheumatoid arthritis. M O L M E D 1 6:552–557
Ferraccioli GF, Zizzo G (2011) The potential role of TH17 in mediating the transition from acute to chronic autoimmune inflammation: rheumatoid arthritis as a model. Discovery Medicine 11:413–424
Zizzo G, De Santis M, Bosello SL, Fedele AL, Peluso G, Gremese E, Tolusso B, Ferraccioli GF (2011) Synovial fluid-derived T helper 17 cells correlate with inflammatory activity in arthritis, irrespectively of diagnosis. Clin Immunol 138:107–116
Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Kalden JR, Antoni C, Smolen JS, Leeb B, Breedveld FC, McFarlane JD (1994) Randomized double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha(cA2) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 344:1105–1110
Tanimoto K, Iwabuchi Y, Tanne Y, Kamiya T, Inubushi T, Mitsuyoshi T, Tanne K (2011) Interleukin 1 beta affects cyclooxygenase 2 expression and cartilage metabolism in mandibular condyle. Arch Oral Biol [Epub ahead of print]
Koshy PJ, Henderson N, Logan C, Life PF, Cawston TE, Rowan AD (2002) Interleukin 17 induces cartilage collagen breakdown: novel synergistic effects in combination with proinflammatory cytokines. Ann Rheum Dis 61:704–713
Mihara M, Moriya Y, Kishimoto T, Ohsugi Y (1995) Interleukin 6 induces the proliferation of synovial fibroblastic cells in the presence of soluble IL6 receptors. Br J Rheumatol 34:321–325
Kotake S, Sato K, Kim KJ, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Nakamura I, Yamaguchi A, Kishimoto T, Suda T, Kashiwazaki S (1996) Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin 6 receptors in the synovial fluids from rheumatoid arthritis patients are responsible for osteoclast-like cell formation. J Bone Miner Res 11:88–95
Trebec-Reynolds DP, Voronov I, Heersche JN, Manolson MF (2010) IL1 alpha and IL1beta have different effects on formation and activity of large osteoclasts. J Cell Biochem 109:975–982
Rutella S, De Cristofaro R, Ferraccioli GF (2009) Function and dysfunction of dendritic cells in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Human Immunol 70:360–373
Bosello S, Pers JO, Rochas C, Devauchelle V, De Santis M, Daridon C, Saraux A, Ferraccioli GF, Youinou P (2007) BAFF and rheumatic autoimmune disorders: implications for disease management and therapy. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 20:1–8
Bosello S, Youinou P, Daridon C, Tolusso B, Bendaoud B, Pietrapertosa D, Morelli A, Ferraccioli GF (2008) Concentrations of BAFF correlate with autoantibody levels, clinical disease activity and response to treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 35:1256–1264
Tolusso B, De Santis M, Bosello S, Gremese E, Gobessi S, Cuoghi I, Rumi C, Efremov DG, Ferraccioli GF (2009) Synovial B cells of rheumatoid arthritis express Zap-70 which increases the survival and correlates with the inflammatory and autoimmune phenotypes. Clin Immunol 131:98–108
Michelutti A, Gremese E, Morassi F, Petricca L, Arena V, Tolusso B, Alivernini S, Peluso G, Bosello SL, Ferraccioli GF (2011) B cell subsets in the joint compartments of seropositive and seronegative RA and non-RA arthritides express memory markers and Zap-70 and characterize the aggregate pattern irrespectively of the autoantibody status. Mol Med [Epub ahead of print]
Pietrapertosa D, Tolusso B, Gremese E, Papalia MC, Bosello S, Peluso G, Petricca L, Michelutti A, Faustini F, Fedele AL, Ferraccioli GF (2010) Diagnostic performance of anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: the relevance of the likelihood ratios. Clin Chem Lab Med 48:829–834
Neogi T et al (2010) The 2010 American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Phase 2 methodological report. Arthritis Rheum 62:2582–2591
Maini RN, StClair EW, Breedveld F, Furst D, Kalden J, Weisman M, Smolen J, Emery P, Feldmann M, Lipsky P (1999) Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomized phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet 354:1932–1939
Maini RN, Taylor PC, Szechinski J, Pavelka K, Broll J, Balint G, Emery P, Raemen F, Petersen J, Smolen J, Thomson D, Kishimoto T, the CHARISMA Study Group (2006) Double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial of the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, tocilizumab, in European patients with rheumatoid arthritis who had an incomplete response to methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum 54:2817–2829
Van der Linden MPM, Le Cessie S, Raza K, Van der Woude D, Knevel R, Huizinga TW, Van der Helm-Van Mil AH (2010) Long-term impact of delay in assessment of patients with early arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 62:3537–3546
Vermeer M, Kuper HH, Hoekstra M, Haagsma CJ, Posthumus MD, Brus HL, Van Riel PL, Vam de Laar MA (2011) Implementation of a treat to target strategy in very early rheumatoid arthritis: results of the DREAM remission induction cohort. Arthritis Rheum 63 [Epub ahead of print]
Bosello S, Fedele AL, Peluso G, Gremese E, Tolusso B, Ferraccioli GF (2011) Very early rheumatoid arthritis is the major predictor of major outcomes: clinical ACR remission and radiographic non- progression. Ann Rheum Dis 70:1292–1295
Peluso G, Michelutti A, Bosello S, Gremese E, Tolusso B, Ferraccioli GF (2011) Clinical and ultrasonographic remission determines different chances of relapse in early and long standing rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 70:172–175
Kobelt G (2006) Health economic issues in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 35:415–425
Emery P, Breedvel FC, Hall S, Durez P, Chang DJ, Robertson D, Singh A, Pedersen MD, Koenig AS, Freundlich B (2008) Comparison of methotrexate monotherapy with a combination of methotrexate and etanercept in active, early, moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (COMET): a randomised, double-blind, parallel treatment trial. Lancet 372:375–382
Wolfe F, Michaud K, Choi HK, Williams R (2005) Household income and earnings losses among 6,396 persons with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 32:1875–1883
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferraccioli, G., Gremese, E. Pathogenetic, clinical and pharmaco-economic assessment in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Intern Emerg Med 6 (Suppl 1), 11 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-011-0668-6
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-011-0668-6