Abstract
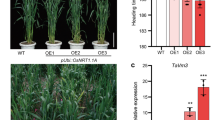
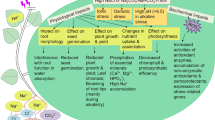
The plasma membrane is critical in sensing, interpreting, and transducing environmental signals. In the present study, we characterized an Oryza sativa salt-responsive little protein 1 (OsSRLP1) in rice, which encodes a plasma membrane localized protein containing 54 amino acid residues. Expression of OsSRLP1 was detected in various rice tissues and was significantly induced by low temperature, drought, and salt. Overexpression of OsSRLP1 in rice improved free proline content and modulated ion balance under salt stress, which resulted in enhanced salt tolerance. Compared to wild-type rice, overexpression of OsSRLP1 inhibited seed germination under normal conditions. Interestingly, OsSRLP1 expression was up-regulated in ABL5-Like1 deficiency mutant abl1 compared to wild-type rice under salt treatment. Moreover, it was observed that overexpression of OsSRLP1 led to the dwarfism phenotype, which was correlated to the OsSRLP1 expression level in transgenic rice. In conclusion, OsSRLP1 is a little membrane protein conferring salt tolerance by modulating the ion balance and proline accumulation in rice.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brunetti SC, Arseneault MKM, Gulick PJ (2018) Characterization of the Esi3/RCI2/PMP3 gene family in the Triticeae. BMC Genomics 19(1):898
Cao P, Jung KH, Choi D, Hwang D, Zhu J, Ronald PC (2012) The rice oligonucleotide array database: an atlas of rice gene expression. Rice 5(1):17–17
Capel J, Jarillo JA, Salinas J, Martinez-Zapater JM (1997) Two homologous low-temperature-inducible genes from Arabidopsis encode highly hydrophobic proteins. Plant Physiol 115(2):569–576
Fedoroff NV, Battisti DS, Beachy RN, Cooper PJ, Fischhoff DA, Hodges CN, Knauf VC, Lobell D, Mazur BJ, Molden D, Reynolds MP, Ronald PC, Rosegrant MW, SanchezPA VA, Zhu JK (2010) Radically rethinking agriculture for the 21st century. Science 327(5967):833–834
Feng D, Liu B, Li W, He Y, Qi K, Wang H, Wang J (2009) Over-expression of cold-induced plasma membrane protein gene (MpRCI) from plantain enhances low temperature-resistance in transgenic tobacco. Environ Exp Bot 65:395–402
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 6(2):271–282
Hu CA, Delauney AJ, Verma DP (1992) A bifunctional enzyme (delta 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase) catalyzes the first two steps in proline biosynthesis in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89(19):9354–9358
Huang J, Yang X, Wang MM, Tang HJ, Ding LY, Shen Y, Zhang HS (2007) A novel rice C2H2-type zinc finger protein lacking DLN-box/EAR-motif plays a role in salt tolerance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1769(4):220–227
Huang J, Sun SJ, Xu DQ, Lan HX, Sun H, Wang ZF, Bao YM, Wang JF, Tang HJ, Zhang HS (2012) A TFIIIA-type zinc finger protein confers multiple abiotic stress tolerances in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 80(3):337–350
Jain M, Nijhawan A, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP (2006) Validation of housekeeping genes as internal control for studying gene expression in rice by quantitative real-time PCR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345(2):646–651
Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: application to complete genomes 1. J Mol Biol 305(3):567–580
Kumar K, Mosa KA, Chhikara S, Musante C, White JC, Dhankher OP (2014) Two rice plasma membrane intrinsic proteins, OsPIP2;4 and OsPIP2;7, are involved in transport and providing tolerance to boron toxicity. Planta 239(1):187–198
Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30(1):325–327
Li HS (2000) Principles and techniques of plant physiology and biochemistry experiments. Higher education press, Beijing, pp 258–260
Li L, Li N, Song SF, Li YX, Xia XJ, Fu XQ, Chen GH, Deng HF (2014) Cloning and characterization of the drought-resistance OsRCI2–5 gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genet Mol Res 13(2):4022–4035
Mansour MM (2014) The plasma membrane transport systems and adaptation to salinity. J Plant Physiol 171(18):1787–1800
Maurel C, Verdoucq L, Luu DT, Santoni V (2008) Plant aquaporins: membrane channels with multiple integrated functions. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59(59):595
Medina J, Ballesteros ML, Salinas J (2007) Phylogenetic and functional analysis of Arabidopsis RCI2 genes. J Exp Bot 58(15–16):4333–4346
Mitsuya S, Taniguchi M, Miyake H, Takabe T (2006) Overexpression of RCI2A decreases Na+ uptake and mitigates salinity-induced damages in Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Physiol Plant 128:95–102
Moulick D, Ghosh D, Chandra Santra S (2016) Evaluation of effectiveness of seed priming with selenium in rice during germination under arsenic stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 109:571
Ren HY, Wei Q (2015) Isolation and Functional Analysis of Phosphate-Responsive Gene OsRCI2-9 in Oryza sativa. Sci Agric Sin 48:831–840
Rocha PS (2016) Plant abiotic stress-related RCI2/PMP3s: multigenes for multiple roles. Planta 243(1):1–12
Udawat P, Jha RK, Sinha D, Mishra A, Jha B (2016) Overexpression of a cytosolic abiotic stress responsive universal stress protein (SbUSP) mitigates salt and osmotic stress in transgenic tobacco plants. Front Plant Sci 7:518
Waadt R, Schmidt LK, Lohse M, Hashimoto K, Rock R, Kudla J (2008) Multicolor bimolecular fluorescence complementation (mcbifc) reveals simultaneous formation of alternative cbl/cipk complexes in planta. Plant J 56(3):505–516
Wang ZF, Wang JF, Bao YM, Wang FH, Zhang HS (2010) Quantitative trait loci analysis for rice seed vigor during the germination stage. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 11(12):958–964
Yang X, Yang YN, Xue LJ, Zou MJ, Liu JY, Chen F, Xue HW (2011) Rice ABI5-Like1 regulates abscisic acid and auxin responses by affecting the expression of ABRE-containing genes. Plant Physiol 156(3):1397–1409
Yuan X, Sun H, Tang ZB, Tang HJ, Zhang HS, Huang J (2015) A Novel little membrane protein confers salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 34(2):524–532
Zhao F, McGrath SP, Crosland AR (1994) Comparison of three wet digestion methods for the determination of plant sulphur by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES). Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 25(3–4):407–418
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Plant Biol 53(53):247–273
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31571627), Cyrus Tang Seed Innovation Center, Nanjing Agricultural University, and Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Modern Crop Production.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.H. planned the project, Y.C., Q.S.,F.L., X.L., H.L., X.H., L.Q.,Z.T., S.D., and H.T. performed the experiments. Y.C., Q.S., and H.Z. analyzed the data. Y.C. and J.H. wrote the article.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by E. Schleiff.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Shao, Q., Li, F. et al. A little membrane protein with 54 amino acids confers salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Physiol Plant 42, 87 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03073-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03073-5