Abstract
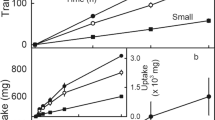
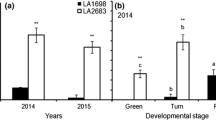
Cracking is caused by physiological stress during the development of jujube fruit, and this causes considerable economic losses to fruit producers. The aim of this study was to clarify the mechanisms of water entry into the fruit and the events that lead to cracking. Differences in water absorption by fruit stalks and surfaces were observed in a cracking-sensitive variety (Ziziphus jujuba Mill. ‘Hupingzao’) and a cracking-resistant variety (Ziziphus jujuba Mill. ‘Yuanlingzao’). The response of the fruit surface to water absorption was studied, and the relationship between stomatal characteristics and cracking was analyzed. The cracking rate of ‘Hupingzao’ was higher during the coloring period. The relative amount of water absorbed through the fruit stalk of ‘Yuanlingzao’ after 10 h was 1.22 times higher than that of ‘Hupingzao’ during the coloring period. The rate of water absorption through the fruit surface of ‘Hupingzao’ was higher than that of ‘Yuanlingzao’ during the coloring period (3.73 and 3.04, respectively). Water was transported by the vascular bundle after entering the fruit through the fruit stalk, but was mainly distributed around the stomata of the epidermis and near-surface cells following entry through the fruit surface. After water was absorbed by the fruit surface, surface and stomatal cracks in ‘Hupingzao’ were apparent, and the degree of cracking of the stomata worsened with increasing water absorption time. The surface of ‘Yuanlingzao’ appeared cracked with increasing immersion time, but stomatal changes were not obvious. The stomatal size and aperture in the cracking-resistant variety of jujube fruit were lower than those in the cracking-sensitive variety. Stomatal size was positively correlated with the rate of fruit cracking. Water absorption through the surface was the main factor that induced fruit cracking. Stomatal characteristics, as well as the increased and deepened fruit surface microcracks caused by stomatal water absorption, were the primary factors related to cracking.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beyer M, Knoche M (2002) Studies on water transport through the sweet cherry fruit surface: V. Conductance for water uptake. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 127:325–332
Cao YB, Sun F, Liu YJ, Zhang LY (2013) Effects of anatomical structure and mineral contents in pericarp on fruit cracking in jujube fruit. J Fruit Sci 30:621–626
Cao YB, Li CJ, Sun F, Zhang LY (2014) Comparison of the endogenous hormone content and the activities of enzymes related to cell-wall metabolism between jujube cultivars susceptible and resistant to fruit cracking. Acta Hortic Sin 41:139–148
Chen HH, Li JG, Shi R, Du Y, Nuernisa T, Niu ZZ, Wang HR (2013) A study on relationships of jun jujube water absorption law and cracking fruit in Akesu Region. J Xinjiang Agric Univ 36:304–309
Christensen JV (1972) Cracking in cherries. IV. Physiological studies of the mechanism of cracking. Acta Agr Scand 22:153–162
Demirsoy L (2004) The epidermal characteristics of fruit skin of some sweet cherry cultivars in relation to fruit cracking. Pak J Bot 36:725–731
Ding Q (2004) A study on the relationship between nectarine, Prunus persica var. nectarina maxim. fruit development and dehiscence of nectarine fruit. Dissertation, North West Agriculture and Forestry University
Ding GX, Wang BM, Wang XY, Cang GY, Chen XB, Niu XY, Ji W, Zhang PF, Wen PF (2014) Changes of anatomical structure of xylem vessels in stalk during Huping jujube fruit development and its relation of fruit cracking. Sci Agric Sin 47:4886–4894
Du W, Li XG, Wang CZ, Gao WH, Wang YQ (2012) Mechanism of fruit cracking in Zizyphus jujuba. J Fruit Sci 29:374–381
Hahn F (2011) Fuzzy controller decreases tomato cracking in greenhouses. Comput Electron Agr 77:21–27
Hao YY, Zhao LQ, Zhang PF, Zhang X, Hao DS, Liu H, Lu GB (2013) Studies on water uptake and apoplastic transport in detached Chinese jujube fruits. Acta Hortic Sin 40:433–440
He RP, Li FL, Xu JR (2011) Investigation and control of cracking in Ziziphus jujube ‘Huping’. Agric Tech Eqpt 2:65–66
Huang LP, Liu H, Chen XD, Li CL, Guo QL (2008a) Observation on stomata characteristics and cracking of different varieties of jujube. Shanxi For Sci Tech 4:8–11
Huang XM, Wang HC, Zhong WL, Yuan WQ, Lu JM, Li JG (2008b) Spraying calcium is not an effective way to increase structural calcium in litchi pericarp. Sci Hortic 117:39–44
Iwasaki N, Fujimoto A, Sagami M (2011) Water uptake and reduced pressure of intercellular space induced by respiration related to sweet cherry fruit cracking. Environ Control Biol 49:149–155
Kasai S, Hayama H, Kashimura Y, Kudo S, Osanai Y (2008) Relationship between fruit cracking and expression of the expansin gene Md EXPA3 in ‘Fuji’ apples, Malus domestica Borkh. Sci Hortic 116:194–198
Khadivi-Khub A (2015) Physiological and genetic factors influencing fruit cracking. Acta Physiol Plant 37:1718
Khanal BP, Grimm E, Knoche M (2011) Fruit growth, cuticle deposition, water uptake, and fruit cracking in jostaberry, gooseberry, and black currant. Sci Hortic 128:289–296
Knoche M (2015) Water uptake through the surface of fleshy soft fruit: barriers, mechanism, factors, and potential role in cracking. Abiotic stress biology in horticultural plants. Springer, Japan, pp 147–166
Li YL, Yang AH, Wang XQ, Shi GG, Wang YN (2015) Effect of abscisic acid spraying on stomatal and cracking on different varieties of jujube leaf and fruit skin. North Hortic 16:22–26
Li N, Song YQ, Li J, Chen YY, Xue XX, Li LL (2018) Development of the cuticular membrane and biomechanical properties in Hupingzao (Ziziphus jujuba Mill. ‘Hupingzao’). Sci Hortic 229:25–32
Liu MJ (2018) The challenges and countermeasures of jujube industry during transition period. China Fruits 1:1–4
Liu TZ, Xu JZ, Wang LR, Chen HJ, Fu YL (2004) Progress on the study of fruit cracking. Hebei J For Orch Res 03:282–287
Liu ZG, Lu YQ, Zhao J, Liu MJ (2015) The effects of water absorbing dynamics and pericarp structure on fruit cracking in Chinese jujube. J Plant Genet Resour 16:192–198
Liu SP, Wen X, Liu S (2017) Correlation of fruit crack and anatomical structure in jujube fruit. North Hortic 04:20–24
Marco B, Steffen L, Knoche M (2005) Studies on water transport through the sweet cherry fruit surface: IX. Comparing permeability in water uptake and transpiration. Planta 220:474–485
Matas A, Lopez-Casado G, Cuartero J, Heredia A (2005) Relative humidity and temperature modify the mechanical properties of isolated tomato fruit cuticles. Am J Bot 92:462–468
Meheriuk M, Neilsen GH, Mckenzie DL (1991) Incidence of rain splitting in sweet cherries treated with calcium or coating materials. Can J Plant Sci 71:231–234
Peschel S, Beyer M, Knoche M (2003) Surface characteristics of sweet cherry fruit: stomata-number, distribution, functionality and surface wetting. Sci Hortic 97:265–278
Sekse L (1965) Fruit cracking in sweet cherries (Prunus avium L). Some physiological aspects—a mini review. Sci Hortic 63:135–141
Sharma SB, Dhillon BS (1988) Endogenous level of abscisic acid in relation to fruit cracking in litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.). Agri Sci Dig 8:55–58
Song YQ, Li J, Fu LJ, Li N, Li LL (2018) Change of fruit surface characteristics and its relationship with water absorption and fruit cracking in Ziziphus jujube ‘Huping’. Sci Silv Sin 54:52–59
Symons GM, Chua YJ, Ross JJ, Quittenden LJ, Davies NW, Reid JB (2012) Hormonal changes during non-climacteric ripening in strawberry. J Exp Bot 63:4741–4750
Wang CZ, Gao JC, Gao H (1998) Identification of crack resistance of main cultivars of Chinese jujube. Acta Agric Bor-Occid Sin 02:81–84
Wang BM, Ding GX, Wang XY, Fu CB, Qin GJ, Yang JQ, Cang GY, Wen PF (2013a) Changes of histological structure and water potential of Huping Jujube fruit cracking. Sci Agric Sin 46:4558–4568
Wang JJ, Mo WP, Jia WS, Liu GJ (2013b) The relationship of grape leaf stomatal conductance and water potential with leaf position under drought conditions. Sci Agric Sin 46:2151–2158
Yang SJ, Zheng GQ, Zhang YC, Zhang YY (2011) Ultracytochemical localization of Ca2+ in the normal fruits and cracking ones of Lingwu Long-jujube. Acta Bot Bor-Occid Sin 31:84–88
Yang SS, Lu XY, Wang QF, Ma BG, Ru SB, Wang C, Fan XM, Zhao BL (2014) Influence of fruit soaked by CaCl2 on fruit cracking rate and Ca, K, Mg content of jujube in Xinjiang. Acta Bot Bor-Occid Sin 34:761–768
Zhang JG, He F (2004) Reason and control technology of jujube fruit cracking. Shanxi Fruits 4:25–27
Zhang Z, Huang J, Li XG (2018) Transcript analyses of ethylene pathway genes during ripening of Chinese jujube fruit. J Plant Physiol 224–225:1–10
Zoffoli JP, Latorre BA, Naranjo P (2008) Hairline, a postharvest cracking disorder in table grapes induced by sulfur dioxide. Postharvest Biol Tec 47:90–97
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Shanxi Province Science and Technology Key Research Projects (Grant number: 2015-TN-4) and Shanxi Province Key Research and Development Projects (Grant numbers: 201703D221015-1 and 201703D221015-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. K. Nagar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Fu, L., Song, Y. et al. Water entry in jujube fruit and its relationship with cracking. Acta Physiol Plant 41, 162 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2954-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2954-2