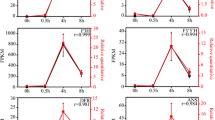
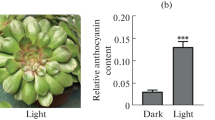
Abstract
Short-wavelength lights (280–400 nm), such as blue and ultraviolet light, play crucial roles in anthocyanin biosynthesis in plants. Previous works have demonstrated that both blue and ultraviolet light can induce anthocyanin pigmentation in the hypocotyls of turnip seedlings. However, in this work we found that anthocyanin biosynthesis is induced either by UV-A or co-irradiation of blue and UV-B, but not by monochromatic blue or UV-B light in the peels of the swollen root of turnip (Brassica rapa L. subsp. rapa). To gain insight into regulation signaling of anthocyanin accumulation and the global transcriptional regulation induced by short-wavelength light, we investigated gene expression profiles in peels of turnip swollen root exposed to UV-A and blue + UV-B using RNA-seq. Among 41,991 genes identified by RNA-seq, 754 genes were specifically modulated by UV-A; three of these genes were anthocyanin biosynthetic structural genes: chalcone synthase, dihydroflavonol 4-reductase, and anthocyanidin synthase. By contrast, PAL, CHI and F3H, the early structural genes of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway were modulated by both UV-A and blue + UV-B. Gene ontology analysis manifested that non-specific signaling pathway ROS and cysteine biosynthetic process pathway were co-regulated with anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway under UV-A. This study provides a valuable overview of the transcriptome changes and gives insight into the genetic background that responsible for UV-A and blue + UV-B-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in turnip.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PAL:
-
Phenylalanine
- C4H:
-
Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase
- 4CL:
-
4-Coumarate CoA ligase
- CHS:
-
Chalone synthase
- CHI:
-
Chalcone isomerase
- F3H:
-
Flavanone 3-hydroxylase
- DFR:
-
Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase
- UF3GT:
-
UDP-glucosyltransferase
- TT8:
-
Transparent Testa 8
- PAP1 (MYB75):
-
Production of anthocyanin pigment 1
- PAP2 (MYB90):
-
Production of anthocyanin pigment 2
- COP1:
-
Constitutively photomorphogenic1
- EGL3:
-
Enhancer of Glabre 3
- HY5:
-
Elongated hypocotyl 5
- LOX2:
-
Lipoxygenase 2
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet irradiation
- UVR8:
-
UV resistance locus 8
- GST26:
-
Glutathione transferases 26
References
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141701
Begara-Morales JC, Sanchez-Calvo B, Luque F, Leyva-Perez MO, Leterrier M, Corpas FJ, Barroso JB (2014) Differential transcriptomic analysis by RNA-Seq of GSNO-responsive genes between Arabidopsis roots and leaves. Plant Cell Physiol 55:1080–1095. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcu044
Brenneisen P, Wlaschek M, Schwamborn E, Schneider L-A, Ma W, Sies H, Scharffetter-konchanek K (2002) Activation of protein kinase CK2 is an early step in the ultraviolet B-mediated increase in interstitial collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase-1;MMP-1) and stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) protein levels in human dermal fibroblast. Biochem J 365:31–40. doi:10.1042/BJ20020110
Carey CC, Strahle JT, Selinger DA, Chandler VL (2004) Mutations in the pale aleurone color1 regulatory gene of the Zea mays anthocyanin pathway have distinct phenotypes relative to the functionally similar TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA1 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 16:450–464. doi:10.1105/tpc.018796
Casati P, Walbot V (2004) Crosslinking of ribosomal proteins to RNA in maize ribosomes by UV-B and its effects on translation. Plant Physiol 136:3319–3332. doi:10.1104/pp.104.047043
Christie JM, Jenkins GI (1996) Distinct UV-B and UV-A/blue light signal transduction pathways induce chalcone synthase gene expression in Arabidopsis cells. Plant Cell 8:1555–1567. doi:10.1105/tpc.8.9.1555
Christie PJ, Alfenito MR, Walbot V (1994) Impact of low-temperature stress on general phenylpropanoid and anthocyanin pathways: enhancement of transcript abundance and anthocyanin pigmentation in maize seedlings. Planta 194:541–549. doi:10.1007/BF00714468
de Vetten N, Quattrocchio F, Mol J, Koes R (1997) The an11 locus controlling flower pigmentation in petunia encodes a novel WD-repeat protein conserved in yeast, plants, and animals. Gene Dev 11:1422–1434. doi:10.1101/gad.11.11.1422
Haas BJ et al (2013) De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat Protoc 8:1494–1512. doi:10.1038/nprot.2013.084
Hartmann U, Valentine WJ, Christie JM, Hays J, Jenkins GI, Weisshaar B (1998) Identification of UV/blue light-response elements in the Arabidopsis thaliana chalcone synthase promoter using a homologous protoplast transient expression system. Plant Mol Biol 36:741–754. doi:10.1023/A:1005921914384
Hideg E, Jansen MA, Strid A (2013) UV-B exposure, ROS, and stress: inseparable companions or loosely linked associates? Trends Plant Sci 18:107–115. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2012.09.003
Hirner AA, Veit S, Seitz HU (2001) Regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in UV-A-irradiated cell cultures of carrot and in organs of intact carrot plants. Plant Sci Int J Exp Plant Biol 161:315–322. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00408-3
Honsel A, Kojima M, Haas R, Frank W, Sakakibara H, Herschbach C, Rennenberg H (2012) Sulphur limitation and early sulphur deficiency responses in poplar: significance of gene expression, metabolites, and plant hormones. J Exp Bot 63:1873–1893. doi:10.1093/jxb/err365
Jenkins GI, Long JC, Wade HK, Shenton MR, Bibikova TN (2001) UV and blue light signalling: pathways regulating chalcone synthase gene expression in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 151:121–131. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2001.00151.x
Jenkins GI, Brown BA (2007) UV-B Perception and Signal Transduction. In: Whitelam G C, Halliday K J (eds) Annual Plant Reviews, vol 30. Light and Plant Development, Wiley, Blackwell, New York, pp 155–182
Kaiser T, Emmler K, Kretsch T, Weisshaar B, ScMfer E, Batschauer A (1995) Promoter elements of the mustard CHS1 gene are sufficient for light regulation in transgenic plants. Plant Mol Biol 28:219–229. doi:10.1007/BF00020242
Kami C, Lorrain S, Hornitschek P, Fankhauser C (2010) Light-regulated plant growth and development. Curr Top Dev Biol 91:29–66. doi:10.1016/s0070-2153(10)91002-8
Li YY et al (2013) Molecular cloning and functional analysis of a blue light receptor gene MdCRY2 from apple (Malus domestica). Plant Cell Rep 32:555–566. doi:10.1007/s00299-013-1387-4
Miyamori T, Nakasone Y, Hitomi K, Christie JM, Getzoff ED, Terazima M (2015) Reaction dynamics of the UV-B photosensor UVR8. Photochem Photobiol Sci 14:995–1004. doi:10.1039/c5pp00012b
Morita Y, Saitoh M, Hoshino A, Nitasaka E, Iida S (2006) Isolation of cDNAs for R2R3-MYB, bHLH and WDR transcriptional regulators and identification of c and ca mutations conferring white flowers in the Japanese morning glory. Plant Cell Physiol 47:457–470. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcj012
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 5:621–628. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1226
Mott KA, Berg DG, Hunt SM, Peak D (2014) Is the signal from the mesophyll to the guard cells a vapour-phase ion? Plant Cell Environ 37:1184–1191. doi:10.1111/pce.12226
Muller-Xing R, Xing Q, Goodrich J (2014) Footprints of the sun: memory of UV and light stress in plants. Front Plant Sci 5:474. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00474
Ordidge M et al (2012) Development of colour and firmness in strawberry crops is UV light sensitive, but colour is not a good predictor of several quality parameters. J Sci Food Agric 92:1597–1604. doi:10.1002/jsfa.4744
Quail MA et al (2008) A large genome center’s improvements to the Illumina sequencing system. Nat Methods 5:1005–1010. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1270
Quattrocchio F, Wing J, van der Woude K, Souer E, de Vetten N, Mol J, Koes R (1999) Molecular analysis of the anthocyanin2 gene of petunia and Its role in the evolution of flower color. Plant Cell 11:1433–1444. doi:10.1105/tpc.11.8.1433
Spelt C, Quattrocchio F, Joseph NMM, Ronald K (2000) anthocyanin1 of petunia encodes a basic helix-loop-helix Protein that directly activates transcription of structural anthocyanin genes. Plant Cell 12:1619–1631. doi:10.1105/tpc.12.9.1619
Su N, Wu Q, Liu Y, Cai J, Shen W, Xia K, Cui J (2014) Hydrogen-rich water reestablishes ROS homeostasis but exerts differential effects on anthocyanin synthesis in two varieties of radish sprouts under UV-A Irradiation. J Agric Food Chem 62:6454–6462. doi:10.1021/jf5019593
Sugano S, Andronis C, Ong MS, Green RM, Tobin EM (1999) The protein kinase CK2 is involved in regulation of circadian rhythms in Arabidopsis. PNAS 96:12362–12366. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.22.12362
Taylor LP, Briggs WR (1990) Genetic regulation and photocontrol of anthocyanin accumulation in maize seedlings. Plant Cell 2:115–127. doi:10.1105/tpc.2.2.115
Trapnell C et al (2012) Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 7:562–578. doi:10.1038/nprot.2012.016
Ubi BE, Honda C, Bessho H, Kondo S, Wada M, Kobayashi S, Moriguchi T (2006) Expression analysis of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in apple skin: effect of UV-B and temperature. Plant Sci 170:571–578. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.10.009
Vidal EA et al (2013) Integrated RNA-seq and sRNA-seq analysis identifies novel nitrate-responsive genes in Arabidopsis thaliana roots. BMC Genom 14:701. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-701
Wade HK, Bibikova TN, Valentine WJ, Jenkins GI (2001) Interactions within a network of phytochrome, cryptochrome and UV-B phototransduction pathways regulate chalcone synthase gene expression in Arabidopsis leaf tissue. Plant J 25:675–685. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01001.x
Walker AR et al (1999) The TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA1 locus, which regulates trichome differentiation and anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis, encodes a WD40 repeat protein. Plant Cell 11:1337–1349. doi:10.1105/tpc.11.7.1337
Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2009) RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 10:57–63. doi:10.1038/nrg2484
Wang Y, Zhou B, Sun M, Li Y, Kawabata S (2012) UV-A light induces anthocyanin biosynthesis in a manner distinct from synergistic blue + UV-B light and UV-A/blue light responses in different parts of the hypocotyls in turnip seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 53:1470–1480. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcs088
Waszczak C, Akter S, Jacques S, Huang J, Messens J, Van Breusegem F (2015) Oxidative post-translational modifications of cysteine residues in plant signal transduction. J Expl Bot 66(10):2923–2934. doi:10.1093/jxb/erv084
Zhang F, Gonzalez A, Zhao M, Payne CT, Lloyd A (2003) A network of redundant bHLH proteins functions in all TTG1-dependent pathways of Arabidopsis. Development 130:4859–4869. doi:10.1242/dev.00681
Zhang X et al (2014) Jasmonate-activated MYC2 represses ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3 activity to antagonize ethylene-promoted apical hook formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26:1105–1117. doi:10.1105/tpc.113.122002
Zhou B, Li Y, Xu Z, Yan H, Homma S, Kawabata S (2007) Ultraviolet A-specific induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in the swollen hypocotyls of turnip (Brassica rapa). J Exp Bot 58:1771–1781. doi:10.1093/jxb/erm036
Acknowledgments
We would like to especially thank the members of Li’s lab and Kawabata’s lab for our discussion and reading of this manuscript. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31272200, 31471911, 31401907, and J1210053), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (2015M581414), and Chinese Scholarship Council (CSC) fellowship to the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Z Miszalski.
Jing Wang and Yu Wang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wang, Y., Chen, B. et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis revealed distinct gene set expression associated with anthocyanin biosynthesis in response to short-wavelength light in turnip. Acta Physiol Plant 38, 134 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2145-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2145-3