Abstract
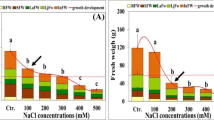
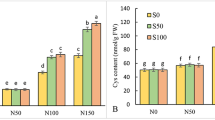
The present study aimed to uncover the interconnected mechanisms underlying salt tolerance of Atriplex nummularia, a potential fodder plant for saline agriculture. The plants were grown in gravel/hydroponic quick check system in the greenhouse and irrigated with various seawater salinities (sws) (0, 25, 50, 100 and 150 %). Raising NaCl salinity stimulated the plant growth, which was highest at 50 % sws. Growth stimulation was mainly due to positive water balance, bestowed by plant ability to adjust osmotically and to minimize water loss via transpiration. Osmotic adjustment was mainly achieved by substantial accumulation of Na+ and Cl−. This was associated concurrently with sharp decrease in K+ and NO3 − concentrations, resulting into ion imbalance. However, the plants were able to maintain adequate ion ratios in their roots and juvenile leaves, where the metabolic activities are expected to be highest. Salt-induced reduction in transpiration rates was coincided with progressive decrease in net photosynthesis (P N). This reduction was proportionally higher than those observed for photosynthesis, leading to improve photosynthetic water use efficiency (PWUE). Reduction in NO3 − concentration may contribute to the overall reduction in total soluble protein (TSP), total N content and hence net photosynthetic rates. However, photosynthetic nitrogen use efficiency (PNUE) and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) were transiently increased, peaked at moderate salinities, indicating that the plants could effectively regulate nitrogen utilization for C-assimilation machinery. Thus, plant’s ability to maintain carbon and nitrogen assimilation in equilibrium through well-coordinated regulatory mechanisms could be considered as a key determinant for salt tolerance in A. nummularia.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C i/C a :
-
Ratio of internal to external CO2 concentration
- E :
-
Transpiration rate
- La:
-
Adult leaves
- Lj:
-
Juvenile leaves
- NUE:
-
Nitrogen-use efficiency
- P N :
-
Net photosynthetic rate
- PNUE:
-
Photosynthetic nitrogen use efficiency
- Pro:
-
Proline
- PWUE:
-
Photosynthetic water use efficiency
- R s :
-
Stomatal resistance
- SAKNa :
-
Selective absorption of K+ over Na+
- STKNa :
-
Selective transport of K+ over Na+
- sws:
-
Seawater salinity
- TAA:
-
Total amino acids
- TSC:
-
Total soluble carbohydrates
- TSP:
-
Total soluble protein
References
Abogadallah GM (2010) Antioxidative defense under salt stress. Plant Signal Behav 5:369–374
Aghaleh M, Niknam V, Ebrahimzadeh H, Razavi K (2009) Salt stress effects on growth, pigments, proteins and lipid peroxidation in Salicornia persica and S. europaea. Biol Plant 53:243–248
Al-Rawahy SA, Stroehlein JL, Pessarakli M (1992) Dry matter yield and nitrogen-15, Na+, Cl− and K+ content of tomatoes under sodium chloride stress. J Plant Nutr 15:341–358
Apse MP, Blumwald E (2007) Na+ transport in plants. FEBS Lett 581:2247–2254
Ashraf M, Foolad MA (2007) Improving plant abiotic-stress resistance by exogenous application of osmoprotectants glycine betaine and proline. Environ Exp Bot 59:206–216
Bajji M, Kinet J, Lutts S (1998) Salt stress effects on roots and leaves of Atriplex halimus L. and their corresponding callus cultures. Plant Sci 137:131–142
Bajji M, Lutts S, Kient JM (2001) Water deficit effects on solute contribution to osmotic adjustment as a function of leaf aging in three durum wheat (Triticum durum Defs.) cultivars performing differently in arid conditions. Plant Sci 160:669–681
Bayuelo-Jimenez JS, Debouck DG, Lynch JP (2003) Growth, gas exchange, water relations and ion composition of Phaseolus species grown under saline conditions. Field Crop Res 80:207–498
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cramer GR, Läuchli A, Polito VS (1985) Displacement of Ca2+ by Na+ from the plasmalemma of root cells: a primary response to stress. Plant Physiol 79:207–211
De Villiers AJ, Von Teichman I, Van Rooyen MW, Theron GK (1996) Salinity induced changes in anatomy, stomatal counts and photosynthetic rate of Atriplex semibaccata. S Afr J Bot 62:270–276
Debez A, Saadaoui D, Ramani B, Ouerghi Z, Koyro H-W, Huchzermeyer B, Abdelly C (2006) Leaf H+-ATPase activity and photosynthetic capacity of Cakile maritima under increasing salinity. Environ Exp Bot 57:285–295
Dunn GM, Neales TF (1993) Are the effect of salinity on growth and leaf gas-exchange related? Photosynthetica 29:33–42
Einarsson S, Josefsson B, Lagerkvist S (1983) Determination of amino acids with 9-fluorenylmethylchloroformate and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 282:609–618
Eisa S, Hussin S, Geissler N, Koyro HW (2012) Effect of NaCl salinity on water relations, photosynthesis and chemical composition of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) as a potential cash crop halophyte. Aust J Crop Sci 6:357–368
El Mourid M, Malki M, Sbeita A, Chiriyaa A, Nefzaoui A, Shideed K, Awawedha F, Hassan SH, Sweidan Y (2001) Crop livestock integration: alternatives to stop desertification in arid regions of WANA. In: Expert meeting: scientific research and its role in combating desertification and stabilizing Sand Dunes. Taghit, Algeria, November 4–6
Epstein E (1972) Mineral nutrition of plants: principles and perspectives. Wiley, New York
Evans JR, Seemann JR (1989) The allocation of protein nitrogen in the photosynthetic apparatus: costs, consequences, and control. In: Briggs WR (ed) Photosynthesis. Alan R Liss Inc., New York, pp 183–205
FAO (2011) Land and plant nutrition management service. http://www.fao.org/ag/agl/agll/spush
Feigin A, Rylski I, Meiri A, Shalhevet J (1987) Response of melon and tomato plants to chloride-nitrate ratios in saline nutrient solutions. J Plant Nutr 10:1787–1794
Feigin A, Pressman E, Imas P, Miltau O (1991) Combined effects of KNO3 and salinity on yield and chemical composition of lettuce and Chinese cabbage. Irrig Sci 12:223–230
Flexas J, Diaz-Espejo A, Galmés J, Kaldenhoff R, Medrano H, Ribas-Carbo M (2007) Rapid variations of mesophyll conductance in response to changes in CO2 concentration around leaves. Plant Cell Environ 30:1284–1298
Flowers TJ (2004) Improving crop salt resistance. J Exp Bot 55:307–319
Flowers TJ, Colmer TD (2008) Salinity resistance in halophytes. New Phytol 179:945–963
Flowers TJ, Troke PF, Yeo AR (1977) Mechanism of salt resistance in halophytes. Ann Rev Plant Physio 28:89–121
Forment J, Naranjo MA, Roldán M, Serrano R, Vicente O (2002) Expression of Arabidopsis SR-like splicing proteins confers salt resistance to yeast and transgenic plants. Plant J 30:511–519
Freitas H, Breckle SW (1992) Importance of bladder hairs for salt resistance of field-grown Atriplex species from a Portuguese salt marsh. Flora 187:283–297
Geissler N, Hussin S, Koyro H-W (2009) Interactive effects of NaCl salinity, elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration on growth, photosynthesis, water relations and chemical composition of the potential cash crop halophyte Aster tripolium L. Environ Exp Bot 65:220–231
Glenn E, Brown JJ, Blumwald E (1999) Salt-tolerant mechanisms and crop potential of halophytes. Crit Rev Plant Sci 18:227–255
Högy P (2002) Wirkungen erhöhter CO2- und/oder Ozonkonzentrationen auf den Ertrag und die Qualität landwirtschaftlicher Nutzpflanzen: dissertation. University of Giessen, Germany
Huang Y, Zhang G, Wu F, Chen J, Zhou M (2006) Differences in physiological traits among salt-stressed barley genotypes. Commun Soil Sci Plan 37:557–570
Huchzermeyer B, Koyro H-W (2005) Salt and drought stress effects on photosynthesis. In: Pessarakli M (ed) Handbook of plant and crop stress, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, pp 751–778
Jeschke WD (1984) K+-Na+ exchange at cellular membranes, intercellular compartmentation of cations, and salt resistance. In: Staples RC, Toeniessen GH (eds) Salinity tolerance in plants strategies for crop improvement. Wiley, New York, pp 37–66
Karimi SH, Ungar IA (1984) The effect of salinity on the ion content and water relations of Atriplex triangularis. In: Tiedemann AR, McArthur ED, Stutz HC, Stevens R, Johnson KL (eds) Proceeding of the symposium on the biology of Atriplex and related Chenopods, pp 124–130
Kelley DB, Goodin JR, Miller DR (1982) Biology of Atriplex. In: Sen DN, Rajpurohit KST (eds) Contribution to the ecology of halophytes. Task Veg Sci 2. Dr. W. Junk Publishers, Hague, pp 79–107
Khan MA, Ungar IA, Showalter AM (2000) Effects of salinity on growth, water relations and ion accumulation of the subtropical perennial halophytes Atriplex griffithii var. stocksii. Ann Bot Lond 85:225–232
Koyro H-W (2000) Effect of high NaCl-salinity on plant growth, leaf morphology, and ion composition in leaf tissues of Beta vulgaris ssp. maritima. J Appl Bot Angew Bot 74:67–73
Koyro H-W (2002) Mechanisms of adaptation to high NaCl-salinity in halophytes: a review. In: Lieth H (ed) Sustainable use of halophytes. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Koyro H-W (2003) Study of potential cash crop halophytes in a quick check system. Task Veg Sci 38:5–17
Koyro H-W, Huchzermeyer B (1999) Influence of high NaCl-salinity on growth, water and osmotic relations of the halophyte Beta vulgaris ssp. maritima: development of a quick check. In: Hamdy A, Lieth H, Todorovic M, Moschenko M (eds) Halophytes uses in different climates I. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, pp 89–103
Koyro H-W, Geissler N, Hussin S, Huchzermeyer B (2006) Mechanisms of cash crop halophytes to maintain yield and reclaim soils in arid areas. In: Khan MA, Weber DJ (eds) Task Veg Sci 40: ecophysiology of high salinity tolerant plants. Springer, Berlin, pp 345–366
Koyro H-W, Geissler N, Hussin S, Debez A, Huchzermeyer B (2008) Strategies of halophytes to survive in a salty environment. In: Khan NA, Singh S (eds) Abiotic stress and plant responses. I.K. International Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 83–104
Koyro H-W, Geissler N, Seenivasan R, Huchzermeyer B (2011) Plant stress physiology; physiological and biochemical strategies allowing to thrive under ionic stress. In: Pessarakli M (ed) Handbook of plant and crop stress, 3rd edn. CRC press, Taylor & Francis Group, West Palm Beach, pp 1051–1094
Koyro H-W, Ahmed P, Geissler N (2012) Abiotic stress response in plants: an overview. In: Ahmed P, Prasad MNV (eds) Environmental adaptation and stress tolerance of plants in the era of climate change. Springer, Dordrecht
Läuchli A, Grattan SR (2007) Plant growth and development under salinity stress. In: Jenks MA, Hasegawa PM, Jain SM (eds) Advances in molecular breeding toward drought and salt tolerant crops. Springer, Dordrecht
Le Houérou HN (1995) Forage halophytes in the Mediterranean basin. In: Chouker-Allah R, Malcolm CV, Hamdy A (eds) Halophytes and biosaline agriculture. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 115–136
Lieth H, Mochtschenko M (2002) Halophyte uses in different climates IV: cashcrop halophytes for future halophytes growers. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden
Lieth H, Moschenkom M, Lohmann M, Koyro H-W, Hamdy A (1999) Halophytes uses in different climates I: ecological and physiological studies. In: Lieth H (ed) Progress in biometeorology, vol 3. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden
Liu F, Stützel H (2002) Leaf expansion, stomatal conductance and transpiration of vegetable amaranth (Amaranthus spp.) in response to soil drying. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 127:878–883
Liu X, Duan D, Li W, Tadano T, Khan A (2006) A comparative study on responses of growth and solute composition in halophytes Suaeda salsa and Limonium bicolor to salinity. In: Khan MA, Weber DJ (eds) Ecophysiology of high salinity tolerant plants. Springer, Netherlands, pp 135–143
Makino A, Osmond B (1991) Effect of nitrogen nutrition on nitrogen partitioning between chloroplast and mitochondria in pea and wheat. Plant Physiol 96:335–362
Mansour MMF (2000) Nitrogen containing compounds and adaptation of plants to salinity stress. Biol Plantarum 43:491–500
Marcum KB (2006) Saline tolerance physiology in grasses. In: Khan MA, Weber DJ (eds) Ecophysiology of high salinity tolerant plants. Task Veg Sci 40. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 157–172
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, New York
Martínez JP, Kinet JM, Bajji M, Lutts S (2005) NaCl alleviates polyethylene glycol-induced water stress in the halophyte species Atriplex halimus L. J Exp Bot 56:2421–2431
Masuko T, Minami A, Iwasaki N, Majima, Nishimura S-I, Lee YC (2005) Carbohydrate analysis by a phenol–sulfuric acid method in microplate format. Anal Biochem 339:69–72
Misra N, Gupta AK (2005) Effect of salt stress on proline metabolism in two high yielding genotypes of green gram. Plant Sci 169:331–339
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:239–250
Munns R (2005) Genes and salt tolerance: bringing them together. New Phytol 167:645–663
Munns R, Termaat A (1986) Whole plant responses to salinity. Aust J Plant Physiol 13:143–160
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Murakeozy EP, Nagy Z, Duhaze C, Bouchereau A, Tuba Z (2003) Seasonal changes in the levels of compatible osmolytes in three halophytic species of inland saline vegetation in Hungary. J Plant Physiol 160:395–401
Naidoo G, Mundree SG (1993) Relationship between morphological and physiological responses to water logging and salinity in Sporobolus virginicus (L.) Kunth. Oecologia 93:360–366
Naidoo G, Jhanke J, Von Willert DJ (1995) Gas exchange responses of the C4 grass, Sporobolus virginicus (Poaceae) to salinity stress. In: Khan MA, Ungar IA (eds) Biology of salt tolerant plants. Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi, pp 121–130
Navarro A, Banón S, Conejero W, Sánchez-Blanco MJ (2008) Ornamental characters, ion accumulation and water status in Arbutus unedo seedlings irrigated with saline water and subsequent relief and transplanting. Environ Exp Bot 62:364–370
Nerd A, Pasternak D (1992) Growth, ion accumulation, and nitrogen fractioning in Atriplex barclayana grown at various salinities. J Range Manage 45:164–166
Osman AE, Ghassaeli F (1997) Effects of storage conditions and presence of fruiting bracts on the germination of Atriplex halimus and Salsola Vermiculata. Exp Agric 33:149–155
Pace GH, Volk RJ, Jackson WA (1990) Nitrate reduction in response to CO2-limited photosynthesis: relationship to carbohydrate supply and nitrate reductase activity in maize seedlings. Plant Physiol 92:286–292
Pessarakli M, Marcum KB, Kopec DM (2005) Growth responses and nitrogen-15 absorption of desert saltgrass under salt stress. J Plant Nutr 28:1441–1452
Pitman MG (1965) Transpiration and the selective uptake of potassium by barley seedlings (Hordeum vulgare cv. Bolivia). Aust J Biol Sci 18:987–999
Popp M, Smirnoff N (1995) Polyol accumulation and metabolism during water deficit. In: Smirnoff N (ed) Environment and plant metabolism: flexibility and acclimation. BIOS Scientific Publishers, Oxford, pp 199–215
Qiu N, Lu Q, Lu C (2003) Photosynthesis, photosystem II efficiency and the xanthophylls cycle in the salt-adapted halophyte Atriplex centralasiatica. New Phytol 159:479–486
Ramos J, Lopez MJ, Benlloch M (2004) Effect of NaCl and KCl salts on the growth and solute accumulation of the halophyte Atriplex nummularia. Plant Soil 259:163–168
Rathert G (1982) Influence of extreme K:Na ratios and high substrate salinity on plant metabolism of crops differing in salt tolerance. V: ion-specific salinity effects on invertase in leaves of bush bean and sugar beet plants. J Plant Nutr 5:97–110
Rivelli AR, Lovelli S, Perniola M (2002) Effect of salinity on gas exchange, water relations growth of sunflower (Helianthus annuus). Funct Plant Biol 29:1405–1415
Rozema J, Flowers TJ (2008) Crops for a salinized world. Science 322:1478–1480
Schirmer U, Breckle SW (1982) The role of bladders for salt removal in some Chenopodiaceae (mainly Atriplex species). In: Sen DN, Rajpurohit KS (eds) Contribution to the ecology of halophytes. Dr. W. Junk publisher, Hauge, pp 215–231
Shannon MC, Grieve CM (1999) Tolerance of vegetable crops to salinity. Sci Hortic 78:5–38
Silveira JAG, Araújo SAM, Lima JPMS, Viegas RA (2009) Roots and leaves display contrasting osmotic adjustment mechanisms in response to NaCl-salinity in Atriplex nummularia. Environ Exp Bot 66:1–8
Singh AK, Chakravarthy D, Singh TPK, Singh HN (1996) Evidence for a role of l-proline as a salinity protectant in the cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum. Plant Cell Environ 19:490–494
Slama I, Ghnaya T, Messedi D, Hessini K, Labidi N, Savoure A, Abdelly C (2007) Effect of sodium chloride on the response of the halophyte species Sesuvium portulacastrum grown in mannitol-induced water stress. J Plant Res 120:291–299
Sobrado MA (2005) Leaf characteristics and gas exchange of the mangrove Laguncularia racemosa as affected by salinity. Photosynthetica 43:217–221
Steubing L, Fangmeier A (1992) Pflanzenökologisches Praktikum. Eugen Ulmer-Verlag, Stuttgart
Storey R, Wyn Jones RG (1979) Responses of Atriplex spongiosa and Suaeda monoica to salinity. Plant Physiol 63:156–162
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot Lond 91:503–527
Vinocur B, Altman A (2005) Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress: achievements and limitations. Curr Opin Biotech 16:1–10
Wang L-W, Showalter AM (2004) Cloning and salt-induced, ABA-independent expression of choline mono-oxygenase in Atriplex prostrata. Physiol Plantarum 120:405–412
Wang SM, Zhu XY (1994) Studies on the characteristics of ion absorption and distribution in Puccinellia tenuiflora. Acta Pratacul Sin 3:39–43
Wang L, Showalter A, Ungar A (1997) Effect of salinity on growth, ion content, and cell wall chemistry in Atriplex prostrata (Chenopodiaceae). Am J Bot 84:1247–1255
Wang S, Wan C, Wang Y, Chen H, Zhou Z, Fu H, Sosebee RE (2004) The characteristics of Na, K and free proline distribution in several drought-resistant plants of the Alxa Desert, China. J Arid Environ 56:525–539
Wyn Jones RG, Gorham J (2002) Intra- and intercellular compartmentation of ions: a study in specificity and plasticity. In: Läuchli A, Lüttge U (eds) Salinity: environment–plants–molecules. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 159–180
Yeo AR, Flowers TJ (1986) Salinity resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and a pyramiding approach to breeding varieties for saline soils. In: Turner NC, Passioura JB (eds) Effect of drought on plant growth. Salts in soils. CSIRO, Melbourne, pp 161–173
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273
Acknowledgments
The financial support of the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) is gratefully acknowledged. The authors are indebted to Mr. Gerhard Mayer, Mrs. Angelika Bölke, Mr. Jürgen Franz and Mr. Wolfgang Stein for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by L. Bavaresco.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussin, S., Geissler, N. & Koyro, HW. Effect of NaCl salinity on Atriplex nummularia (L.) with special emphasis on carbon and nitrogen metabolism. Acta Physiol Plant 35, 1025–1038 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1141-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1141-5