Abstract
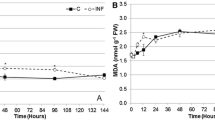
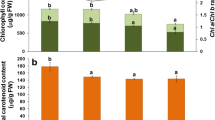
An experiment was designed to investigate the tolerance and response of the Kosteletzkya virginica (L.) Presl to one-instar bollworms of Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner). In this experiment, the insects obviously brought an enhancement in damaged rate of leaf area (DRLA), average diameter of bitten hole (ADBH) and average grade of leaf damage (AGLD) in K. virginica seedlings. When amount of insect increased to 4 per top leaf, the average DRLA, AABH, ADBH and AGLD were 8.6%, 9.2 mm, 2.7 mm and 2.0 mm, respectively, and the seedlings showed a potential insect-tolerance to this insect stress. Furthermore, with an increase of insect density, MDA, relative permeability of membrane (RPM), O −·2 production and soluble sugar concentration all enhanced, whereas activities of SOD and POD increased and subsequently declined. By statistical analysis, it was drawn that bio-toxicity of O −·2 was the first destroying factor, cell membrane decomposition ranked the second, and the destruction of membrane lipid peroxidation was the slightest to K. virginica seedlings. Moreover, under the insect stress, POD was the most significant factor in protecting the seedlings, soluble sugar acted as the subordinate one, and the protection of SOD was the slightest compared to two others. In addition, insect stress obviously affected chlorophyll-fluorescence characteristics, and resulted in a significant increase in Fo and qN, and a significant reduction in Fv/Fm, ETR and qP during experiment.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DRLA:
-
Damaged rate of leaf area
- ADBH:
-
Average diameter of bitten hole
- AABH:
-
Average amount of bitten hole
- RPM:
-
Relative permeability of membrane
- O −·2 :
-
Superoxide anion radical
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
References
Anjum MA (2008) Effect of NaCl concentrations in irrigation water on growth and polyamine metabolism in two citrus rootstocks with different levels of salinity tolerance. Acta Physiol Plant 30:43–52. doi:10.1007/s11738-007-0089-3
Blits KC, Gallagher JL (1990) Salinity tolerance of Kosteletzkya virginica. I. Shoot growth, lipid content, ion and water relations. Plant Cell Environ 13:409–418
Chen JM, Yu XP, Chen JW, Lu ZX, Cheng JA, Tao LY, Zhen XS, Xu HX (2003a) Relationship between photosynthesis changes in leaves of rice plants infested by whitebacked planthopper, Sogatella furciferia Horvath and its resistance. Acta Agric Nucleatae Sin 17:423–426 (in Chinese)
Chen JM, Yu XP, Cheng JA, Lu ZX, Xu HX (2003b) The changes of physiological indexes of different rice varieties after infestation by brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stal). Acta Phytophylacica Sin 30:225–231. doi:10.3321/j.issn:0577-7518.2003.03.001 (in Chinese)
Chen WH, Xu CM, Zhao B, Wang XD, Wang YC (2008) Improved Al tolerance of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) by exogenous polyamines. Acta Physiol Plant 30:121–127. doi:10.1007/s11738-007-0100-z
Christiane FS, Trevor G, Sergey S (2005) Nutritional and chlorophyll fluorescence responses of lucerne (Medicago sativa) to waterlogging and subsequent recovery. Plant Soil 270:31–45. doi:10.1007/s11104-004-1082-x
Davenport SB, Gallego SM, Benavides MP, Tomaro ML (2003) Behaviour of antioxidant defense system in the adaptive response to salt stress in Helianthus annuus L. cells. Plant Growth Regul 40:81–88
Edwards PJ, Wratten SD (1983) Wound induced defences in plants and their consequences for patterns of insect grazing. Oecologia (Berlin) 59:88–93
Epron D, Dreyer E, Breda N (1992) Photosynthesis of oak trees (Quercus petraea (Matt) Liebl.) during drought stress and under field conditions: diurnal course of net CO2 assimilation and photochemical efficiency of photosystem II. Plant Cell Environ 15:809–820. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.1992.tb02148.x
Feng YC, He GZ (1995) Compensation of cotton plants for fleahopper damage at the squares stage. Entomol Knowl 32:210–214 (in Chinese)
Foyer CH, Descourvieres P, Kunert KJ (1994) Protection against oxygen radicals: an important defense mechanism studied in transgenic plants. Plant Cell Environ 17:507–523
Gallagher JL (1985) Halophytic crops for cultivation at seawater salinity. Plant Soil 89:323–336
Gamon JA, Pearcy RW (1989) Leaf movement, stress avoidance and photosynthesis in Vitis californica. Oecologia 79:475–481
Gossett DR, Millhollon EP, Lucas MC (1994) Antioxidant response to NaCl stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive cultivars of cotton. Crop Sci 34:706–714
Groom QJ, Baker NR (1992) Analysis of light-induced depressions of photosynthesis in leaves of a white crop during the winter. Plant Physiol 100:1217–1223
Guo YQ, Tian ZY, Yan DL, Zhang J, Qin P (2009a) Effects of nitric oxide on salt stress tolerance in Kosteletzkya virginica. Life Sci J 6:67–75
Guo YQ, Tian ZY, Qin GY, Yan DL, Zhang J, Zhou WZ, Qin P (2009b) Gene expression of halophyte Kosteletzkya virginica seedlings under salt stress at early stage. Genetica 137:189–199. doi:10.1007/s10709-009-9384-9
Haldimann P, Strasser RJ (1999) Effects of anaerobiosis as probed by the polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence rise kinetic in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Photosynth Res 62:67–83
Hao YJ, Zhai H, Wang SH (1999) Changes of physiochemical substances in Malus baccata infected with Trichodorus nanjingensis. Acta Phytopathol Sin 29:82–85. doi:10.3321/j.issn:0412-0914.1999.01.016 (in Chinese)
Hori K, Atalay R (1980) Biochemical changes in the tissue of Chinese cabbage injured by the bug Lygus disponsi. Appl Entomol Zool 15:234–241
Inbar M, Doostar H, Leibee GL, Mayer RT (1999) The role of plant rapidly induced responses in asymmetric inter-specific interactions among insect herbivores. J Chem Ecol 25:1961–1979
Jebara S, Jebara M, Limam F, Aouani ME (2005) Changes in ascorbate peroxidase, catalase, guaiacol peroxidase and superoxide dismutase activities in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) nodules under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 162:929–936. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2004.10.005
Jiao DM, Li X, Ji BH (2005) Photoprotective effects of high level expression of C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in transgenic rice during photoinhibition. Photosynthetica 43:501–508
Khan MH, Panda SK (2008) Alterations in root lipid peroxidation and antioxidative responses in two rice cultivars under NaCl-salinity stress. Acta Physiol Plant 30:81–89. doi:10.1007/s11738-007-0093-7
Kirk JTO (1968) Studies on the dependence of chlorophyll synthesis on protein synthesis in Euglena gracilis, together with a nomogram for determination of chlorophyll concentration. Planta (Berl) 78:200–207
Kosola KR, Dickmann DI, Paul EA, Parry D (2001) Repeated insect defoliation effects on growth, nitrogen acquisition, carbohydrates, and root demography of poplars. Oecologia 129:65–74. doi:10.1007/s004420100694
Kudo G (2003) Variations in leaf traits and susceptibility to insect herbivory within a Salix miyabeana population under field conditions. Plant Ecol 169:61–69
Li K, Li ZY, Xu ZC (1997) A study on several factors of photosynthesis of Chinese pine damaged by Pine caterpillar. J Beijing For Univ 19:58–62 (in Chinese)
Li ZY, Wang Y, Chen HS, Fen Q, Li K (1999) Affection of contents of some substances in needle of Pinus tabulaeformis carr. induced by Dendrolimus spectabilis Butler. J Beijing For Univ 21:41–45. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-1522.1999.05.009 (in Chinese)
Li YQ, Xuan WJ, Wang HT, Sheng CF (2003) Physiological mechanism of over-compensation by cotton plants for simulated bollworm infestation on early squares. Acta Entomol Sin 46:267–271. doi:10.3321/j.issn:0454-6296.2003.03.002 (in Chinese)
Liu GJ, Huang HP, Xie XF, Gui LQ, Fang WR (1998) Study on the mechanisms of the resistance in early-season rice varieties to the striped stemborer (Chilo suppressalis) and its biochemical basis. J Southwest Agric Univ 20:512–515 (in Chinese)
Mabry CM, Wayne PW (1997) Defoliation of the annual herb Abutilon theophrasti: mechanisms underlying reproductive compensation. Oecologia 111:225–232
Masters GJ (1995) The effect of herbivore density on host plant mediated interactions between two insects. Ecol Res 10:125–133
Maxwell K, Johnson GN (2000) Chlorophyll fluorescence—a practical guide. J Exp Bot 51:659–668
Meng FX, Shen JL, Chu SP (2003) Temporal-spatial variation in efficacy of Bt cotton leaves against Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) and effect of weather conditions. Acta Entomol Sin 46:299–304 (in Chinese)
Polijakoff-Mayber A, Somers GF, Werker E, Gallagher JL (1994) Seeds of Kosteletzkya virginica (Malvaveae) their structure, germination and salt tolerance. II. Germination and salt tolerance. Am J Bot 81:54–59
Qiu J, Wang RM, Yan JZ, Hu J (2005) Seed film coating with uniconazole improves rape seedling growth in relation to physiological changes under waterlogging stress. Plant Growth Regul 47:75–81. doi:10.1007/s10725-005-2451-z
Ruan CJ, Qin P, Xi YG (2005) Floral traits and pollination modes in Kosteletzkya virginica (Malvaceae). Belg J Bot 137:49–55
Scandalias JG (1993) Oxygen stress and superoxide dismutase. Plant Physiol 101:7–12
Su JW, Gao F, Liu L, Ge F (2007) Components and emitting rate of volatiles released from the transgenic cotton damaged by cotton bollworm. Plant Prot 33:29–34 (in Chinese)
Uriarte M (2000) Interactions between goldenrod (Solidago altissima L.) and its insect herbivore (Trirhabda virgata) over the course of succession. Oecologia 122:521–528
Uritani I (1978) Biochemistry of host response to infection. Prog Phytochem 5:29–63
Xia NB, Tu QH, Song CY, Li ZY (1993) A study on the effects of compensation and super compensation of Chinese pine damaged by Chinese pine caterpillar. Acta Ecol Sin 13:121–129. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.1993.02.014 (in Chinese)
Xu WG, Qin P, Xie M, Lü WL, Zhong CX (1996) A study on trial planting ecology of Kostelezkya virginica in china. J Nanjing Univ (Nat Sci) 32:268–274 (in Chinese)
Yin JL, Zhou CL, Hong LZ, Wang K, Ding JH, Wang MW (2000) A study on introduction and cultivation of the salt-tolerant plant—Kostelezkya virginica. Jiangsu Agric Sci 22:29–31 (in Chinese)
Zehnder CB, Hunter MD (2007) Interspecific variation within the genus Asclepias in response to herbivory by a phloem-feeding insect herbivore. J Chem Ecol 33:2044–2053. doi:10.1007/s10886-007-9364-4
Zhang JX, Kirkham MB (1994) Drought-stress-induced changes in activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase in wheat species. Plant Cell Physiol 35:785–791
Zhang ZL, Qu WJ (2003) The measurement of MDA and soluble sugar. In: Zhang ZL, Qu WJ (eds) The experimental guide for plant physiology, 3rd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing, pp 274–277
Zhang GP, Tanakamaru Koji, Jun A, Shigenori M (2007) Influence of waterlogging on some anti-oxidative enzymatic activities of two barley genotypes differing in anoxia tolerance. Acta Physiol Plant 29:171–176. doi:10.1007/s11738-006-0022-1
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by 11.5 National Key Technology R & D Program of China (2006BAD09A04; 2006BAD09A08). And the kind assistance of Dr. Shuwen Wan in the revision of the manuscript is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by B. Barna.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Zhou, J., Wu, B. et al. Physiological factors for tolerance of Kosteletzkya virginica (L.) Presl to one-instar bollworms of Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner). Acta Physiol Plant 32, 519–529 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0429-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0429-6