Abstract
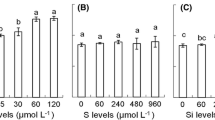
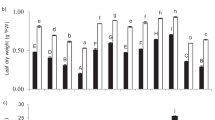
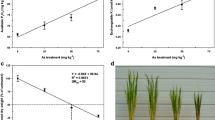
This paper reports on a hydroponics experiment that was conducted to investigate the effect of inorganic arsenics on the seedlings of the rice cultivar Shanyou63. The seedlings were subjected to two treatments, i.e., As(III) and As(V). The results showed that the morphological traits of the seedlings were significantly altered after the arsenic treatments. Analysis of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and arsenic contents of the roots and leaves of the seedlings indicated that the absorption of phosphorus and potassium was mainly affected by As(III), while that of nitrogen was mainly affected by As(V). The expression of 12 genes involved in the absorption and utilization of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium were all observed to be down-regulated after the arsenic treatments. As(V) significantly affected the absorption and utilization of nitrogen, while As(III) significantly affected those of phosphorus and potassium. The result obtained by real-time FQ-PCR regarding the difference in the gene expressions agreed with that of our hydroponics experiment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedin MJ, Meharg AA (2002) Relative toxicity of arsenite and arsenate on germination and early seedling growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 243:57–66
Abedin MJ, Feldman J, Meharg AA (2002) Uptake kinetics of arsenic species in rice plants. Plant Phys 128:1120–1128
Baker RS, Barrentine WL, Bowman DH et al (1976) Crop response and arsenic uptake following soil incorporation of MSMA. Weed Sci 24:322–326
Belay A, Claassens AS, Wehner FC (2002) Effect of direct nitrogen and potassium and residual phosphorus fertilizers on soil chemical properties, microbial components and maize yield under long-term crop rotation. Biol Fertil Soils 35:420–427
D’Ilio S, Alessandrelli M, Cresti R et al (2002) Arsenic content of various types of rice as determined by plasma-based techniques. Microchem J 73:195–201
Deuel LE, Swoboda AR (1972) Arsenic toxicity to cotton and soybeans. J Environ Qual 1:317–320
Frans R, Horton D, Burdette L (1988) Influence of MSMA on straighthead. Arsenic uptake and growth response in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Arkansas AES Rep Ser 32:1–12
Hu Y, Li JH, Zhu YG, Huang YZ et al (2005) Sequestration of As by iron plaque on the roots of three rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars in a low-P soil with or without P fertilizer. Environ Geochem Health 27:169–176
Kapustka LA, Lipton J, Galbraith H et al (1995) Metal and arsenic impacts to soils, vegetation communities and wildlife habitat in southwest Montana uplands contaminated by smelter emissions: II. Laboratory phytotoxicity studies. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1905–1912
Lamont WH (2003) Concentration of inorganic arsenic in samples of white rice from the United States. J Food Composit Anal 16:687–695
Liu WJ, Zhu YG, Smith FA et al (2004) Do phosphorus nutrition and iron plaque alter arsenate (As) uptake by rice seedlings in hydroponic culture? New Phytol 162:481–488
Liu WJ, Zhu YG, Smith FA (2005) Effect of iron and manganese plaques on arsenic uptake by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) grown in solution culture supplied with arsenate and arsenite. Plant Soil 277:127–138
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Marin AR, Masscheleyn PH, Patrick WH Jr (1992) The influence of chemical form and concentration of arsenic on rice growth and tissue arsenic concentration. Plant Soil 139:175–183
Marin AR, Masscheleyn PH, Patrick WH Jr (1993) Soil redox-pH stability of arsenic species and its influence on arsenic uptake by rice. Plant Soil 152:245–253
Onken BM, Hossner LR (1995) Plant uptake and determination of arsenic species in soil solution under flooded conditions. J Environ Qual 24:373–381
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Rahman MM et al (2007) Accumulation of arsenic in tissues of rice plant (Oryza sativa L.) and its distribution in fractions of rice grain. Chemo 69:942–948
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Rahman MM et al (2008) Straighthead disease of rice (Oryza sativa L.) induced by arsenic toxicity. Environ Exp Bot 62:54–59
Smith E, Naidu R, Alston AM (1998) Arsenic in the soil environment: a review. Adv Agron 64:149–195
Tang QY, Feng MG (2007) DPS Data processing system: experimental design, statistical analysis, and data mining. Science Press, Beijing
Tang T, Miller DM (1991) Growth and tissue composition of rice grown in soil treated with inorganic copper, nickel, and arsenic. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 26:561–569
Wang BL, Liu XN, Yu GR et al (1999) Nutritive equilibrium in rice plant populations for high yield. Pedo 9:77–82
Acknowledgments
This work was co-supported by the key program of ecology (0608537), the key program of science and technology (2003Y027), Fujian Province, and the program of education department of Fujian Province (JA08071, JA08055), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Aniol.
H. B. He contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H.B., He, H.B., Yang, G.D. et al. Effects of two species of inorganic arsenic on the nutrient physiology of rice seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 32, 245–251 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0399-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0399-8