Abstract
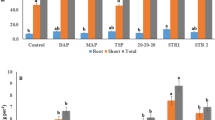
A pot experiment was carried out in a greenhouse to investigate the sequestration of As in iron plaques on root surface of three rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Phosphate (P) fertilization increased both plant biomass and tissue P concentrations significantly, indicating that the soils used in this study was highly P-deficient. Results from this study confirmed that low P supply improved the formation of iron plaque on rice roots. As a consequence, arsenic (As) concentrations in DCB-extracts with no P addition were significantly higher than those with P fertilization. Arsenic was highly sequestrated in iron plaque; arsenic concentration in iron was up to nearly 120 mg kg−1, while arsenic concentrations in roots were just several mg kg−1. Both arsenic and phosphate concentrations in iron plaque were highly positively correlated with the amounts of iron plaque (DCB-extractable Fe). Contrary to normal understanding that increasing P supply could reduced As accumulation in plants, results from the present study showed that P fertilization did not inhibit the As uptake by plants (As accumulation in aboveground), which was probably due to the fact that iron plaque formation was improved under low P conditions, thus leading to more As sequestration in the iron plaque. Thus results obtained in this study indicated that the iron plaque may inhibit the transfer of As from roots to shoots, and thus alter the P–As interaction in plant As uptake processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
MJ Abedin J Cotter-Howells AA. Meharg (2002) ArticleTitleArsenic uptake and accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa) irrigated with contaminated water Plant and Soil 240 311–319 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1015792723288
MJ Abedin J Feldmann AA. Meharg (2002) ArticleTitleUptake kinetics of arsenic species in rice plants. Plant Physiol 128 1120–1128 Occurrence Handle10.1104/pp.010733
RE Bacha LR. Hossner (1977) ArticleTitleCharacteristics formed on rice roots as affected by Fe and Mn additions Soil Sci Soc Am J 41 931–935 Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1977.03615995004100050025x
BK Biswas RK Dhar G Samanta et al. (1998) ArticleTitleDetailed study report of Samta, one of the arsenic affected village of Jessore District, Bangladesh Curr Sci 74 134–145
N Belzile A. Tessier (1990) ArticleTitleInteractions between arsenic and iron oxyhydroxides in laustrine sediments Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54 103–109 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-7037(90)90198-T
CC Chen JB Dixon FT. Turner (1980) ArticleTitleIron coatings on rice roots: morpology and models of development Soil Sci Soc Am J 44 1113–1119 Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050046x
SL Chen SJ Yeh MH Yang TH. Lin (1995) ArticleTitleTrace-element concentration and arsenic speciation in the well water of a Taiwan area with endemic blackfoot disease Biol Trace Element Res 48 263–274 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02789408
TR Chowdhury GK Basu BK. Mandal et al. (1999) ArticleTitleArsenic poisoning in the Ganges delta Nature 401 545–546
MM Dey MNI Miah BAA Mustafi M. Hossain (1996) Rice production constraints in Bangladesh: implications for further research priorities RE Evenson RW Herdt M Hossain (Eds) Rice Research in Asia: Progress and Priorities CAB International, International Rice Research Institute Manila, Philippines, Wallingford, UK 179–191
RK Dhar BK Biswas G. Samanta (1997) ArticleTitleGroundwater arsenic calamity in Bangladesh Curr Sci 73 48–59
H Galbraith K Lejeune J. Lipton (1995) ArticleTitleMetal and arsenic impacts to soils, vegetation communities, and wildlife habitat in southwest Montana uplands contaminated by smelter emissions: I Field evaluation. Environ Toxicol Chem 14 1895–1903
S Greipsson AA. Crowder (1992) ArticleTitleAmelioration of copper and nickel toxicity by iron plaque on roots of rice (Oryza sativ) Can J Bot 70 824–830
S. Greipsson (1994) ArticleTitleEffects of iron plaque on roots of rice on growth and metal concentration of seeds and plant tissues when cultivated in excess copper Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 25 2761–2769
S. Greipsson (1995) ArticleTitleEffect of iron plaque on roots of rice on growth of plants in excess zinc and accumulation of phosphorus in plants in excess copper or nickel J Plant Nutr 18 1659–1665
YZ Huang XC Qian GQ Wang (1992) ArticleTitleSyndrome of endemic arsenism and fluorosis: a clinical study. Chinese Med J 105 586–590
AL Juhsz R Naidu YG Zhu LS Wang JY Jiang ZH. Cao (2003) ArticleTitleToxicity issues associated with geogenic arsenic in the groundwater-soil-plant-human continuum. Bull Environ Contamin Toxicol 71 1100–1107
S. Kuo (1986) ArticleTitleConcurrent sorption of phosphate and zinc, cadmium, or calcium by a hydrous ferric oxide Soil Sci Soc Am J 50 1412–1419 Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1986.03615995005000060008x
W Liangfang H. Jinghong (1994) Chronic arsenism from drinking water in some areas of Xinjiang, China JO Nriagu (Eds) Arsenic in the Environment, Part II: Human Health and Ecosystem effects. John Wiley & Sons Inc. New York NY 159–172
KF Lin XQ Xu A Paul YL Xiang X. Jin (2001) ArticleTitleRelationship between As contents of farmers’ hair and of environment in As polluted area. Chinese Environ Sci 21 440–444
WJ Liu YG Zhu FA Smith SE. Smith (2004a) ArticleTitleDo phosphorus nutrition and iron plaque alter arsenate (As) uptake by rice seedlings in hydroponic culture? New Phytol 162 481–488 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01035.x
WJ Liu YG Zhu FA Smith SE. Smith (2004b) ArticleTitleDo iron plaque and genotypes affect arsenate uptake and translocation by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) grown in solution culture? J Exp Bot 55 1707–1703 Occurrence Handle10.1093/jxb/erh205
RK. Lu (1999) Analytical Methods for Soils and Agricultural Chemistry China Agricultural Science and Technology Press Beijing, China
KS Maclean WM Langille (1981) ArticleTitleArsenic in orchard and potato soils and plant tissue Plant Soil 61 413–418 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02182021
BK Mandal TR Chowdhury G Samanta et al. (1996) ArticleTitleArsenic in groundwater in seven districts of west Bengal, India: the biggest arsenic calamity in the world Curr Sci 70 976–986
BK Mandal TR Chowdhury G Samanta et al. (1997) ArticleTitleIn reply to “chronic arsenic toxicity in West Bengal.” Curr Sci 72 114–117
H. Marschner (1995) Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants Academic Press Ltd London, UK
Meharg AA. 2004 Arsenic in rice – understanding a new disaster for South-East Asia. Trends Plant Sci (in press).
AA Meharg MR. Macnair (1990) ArticleTitleAn altered phosphate uptake system in arsenate tolerant Holcus Lanatus New Phytol 116 29–35 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1469-8137.1990.tb00507.x
XG Meng GP Korfiatis S Bang KW Bang (2002) ArticleTitleCombined effects of anions on arsenic removal by iron hydroxides Toxicol Lett 133 103–111 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-4274(02)00080-2
R Nickson J McArthur W Burgess KM Ahmed P Ravenscroft M. Rahman (1998) ArticleTitleArsenic poisoning in Bangladesh groundwater Nature 395 338–338 Occurrence Handle10.1038/26387
AH Smith C Hopenhaynrich MN Bates et al. (1992) ArticleTitleCancer risks from arsenic in drinking water Environ Health Perspect 97 259–267
ML Otte MJ Dekkers J Rozema RA. Broekman (1991) ArticleTitleUptake of arsenic by Aster tripolium in relation to rhizosphere oxidation Can J Bot 69 2670–2677
ML Otte J Rozema L Koster MS Haarsma RA. Broekman (1989) ArticleTitleIron plaque on roots of Aster tripoliumL.: interaction with zinc uptake New Phytol 111 309–317 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1469-8137.1989.tb00694.x
Otte ML, Buijs EP, Riemer L, Rozema J, Broekman RA. 1987. The iron plaque on roots of salt marsh plants: a barrier to heavy metal uptake? Proceedings of the International Conference Heavy Metal in the Environment, New Orleans (USA) I, CEP Consultants, Edinburgh, pp. 407–409.
GJ Taylor AA. Crowder (1983a) ArticleTitleUptake and accumulation of heavy metals by Typha latifolia L. in wetlands of Sudbury, Ontario region Canad. J Bot 61 63–73
GJ Taylor AA. Crowder (1983) ArticleTitleUse of DCB technique for extraction of hydrous iron oxides from roots of wetland plants Am J Bot 70 1254–1257 Occurrence Handle10.2307/2443295
Ullah SM. 1998 Arsenic contamination of groundwater and irrigated soils of Bangladesh. Abstracts: International Conference on Arsenic Pollution of Groundwater in Bangladesh: Causes, Effects and Remedies, 8–12 February 1998. Dhaka Community Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh, pp. 133.
TG Wang JH. Peverly (1999) ArticleTitleIron oxidation states on root surfaces of a wetland plant (Phragmites australis) Soil Sci Soc Am J 63 247–252 Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1999.03615995006300010036x
ZM Xie CY. Huang (1998) ArticleTitleControl of arsenic toxicity in rice plants grown on an arsenic-polluted paddy soil Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 29 2471–2477 Occurrence Handle10.1080/00103629809370125
CH. Yan (1994) Arsenic distribution in soils JO Nriagu (Eds) Advances in Environmental Science and Technology, Arsenic in the environment. Part I: Cycling and characterization John Wiley & Sons Inc. New York, USA 17–49
ZH Ye AJM Baker MH Wong AJ. Willis (1998) ArticleTitleZinc, lead and cadmium accumulation and tolerance in Typha latifolia as affected by iron plaque on the root surface Aquat Bot 61 55–67 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3770(98)00057-6
XK Zhang FS Zhang DR. Mao (1998) ArticleTitleEffect of iron plaque outside roots on nutrient uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.): zinc uptake by Fe-deficient rice Plant and Soil 202 33–39 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004322130940
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Li, JH., Zhu, YG. et al. Sequestration of As by iron plaque on the roots of three rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars in a low-P soil with or without P fertilizer. Environ Geochem Health 27, 169–176 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-005-0132-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-005-0132-5