Abstract
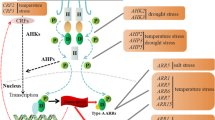
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases cascades mediate cellular responses to a great variety of different extracellular signals in plants. Activation of a MAP kinase occurs after phosphorylation by an upstream dual-specificity protein kinase, known as a MAP kinase kinase. However, only a few of the MAPK kinases in Arabidopsis have been investigated. An active AtMKK3, 35S:AtMPK1, 35S:AtMPK2, and 35S:AtMPK3 constructs were built and their transformed plants were generated. The kinase activity of AtMPK1 or AtMPK2 was stimulated by active AtMKK3 in transient analysis of tobacco leaves. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments indicated interaction between AtMKK3 and AtMPK1 or AtMPK2 in the coexpressed tissues of AtMKK3 and AtMPK1 or AtMKK3 and AtMPK2. RT-PCR analysis showed that AtMKK3 and AtMPK1, or AtMKK3 and AtMPK2 were co-expressed in diverse plant tissues. Plants overexpressing AtMKK3 exhibited an enhanced tolerance to salt and were more sensitive to ABA. Plants overexpressing AtMPK1 or AtMPK2 were also more sensitive to ABA. AtMPK1 or AtMPK2 can be activated by cold, salt, and ABA. AtMKK3, AtMPK1, and AtMPK2 genes were induced by ABA or stress treatments. All these data indicated that the ABA signal transmitted to a MAPK kinase signaling cascade and could be amplified through MAP kinase1 or MAP kinase2 for increasing salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu ML, Gomez-Gomez L (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415:977–983
Burnett EC, Desikan R, Moser RC, Neill SJ (2000) ABA activation of an MBP kinase in Pisum sativa epidermal peels correlates with stomatal responses to ABA. J Exp Bot 51:197–205
Calderini O, Glab N, Bergounioux C, Heberle-Bors E, Wilson CA (2001) Novel tobacco mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase, NtMEK1, activates the cell cycle-regulated p43Ntf6 MAP kinase. J Biol Chem 276:18139–18145
Cardinale F, Meskiene I, Ouaked F, Hirt H (2002) Convergence and divergence of stress-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways at the level of two distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases. Plant Cell 14:703–711
Chang C (2003) Ethylene signaling: the MAPK module has finally landed. Trends Plant Sci 8:365–368
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Droillard M, Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Lauriere C (2002) Different protein kinase families are activated by osmotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspensions, involvement of the MAP kinases AtMPK3 and AtMPK6. FEBS Lett 527:43–50
Ekengren SK, Liu Y, Schiff M, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Martin GB (2003) Two MAPK cascades, NPR1, and TGA transcription factors play a role in Pto-mediated disease resistance in tomato. Plant J 36:905–917
Guo H, Ecker JR (2004) The ethylene signaling pathway: new insights. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:40–49
Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Yoshida R, Yuasa T, Shinozaki K (2000) Various abiotic stresses rapidly activate Arabidopsis MAP kinases ATMPK4 and ATMPK6. Plant J 24:655–665
Jin H, Axtell MJ, Dahlbeck D, Ekwenna O, Zhang S, Staskawicz B, Baker B (2002) NPK1, an MEKK1-like mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase, regulates innate immunity and development in plants. Dev Cell 3:291–297
Jin H, Liu Y, Yang KY, Kim CY, Baker B, Zhang S (2003) Function of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in N gene-mediated resistance in tobacco. Plant J 33:719–731
Jonak C, Okresz L, Bogre L, Hirt H (2002) Complexity, cross talk and integration of plant MAP kinase signalling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:415–424
Knetsch MW, Wang M, Snaar-Jagalska E, Helmovaara-Dijkstra S (1996) Absicisic acid induces mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in barley aleurone protoplast. Plant Cell 8:1061–1067
Liu Y, Zhang S (2004) Phosphorylation of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase by MAPK6, a stress-responsive mitogen-activated protein kinase, induces ethylene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:3386–3399
Liu Y, Zhang S, Klessig DF (2000) Molecular cloning and characterization of a tobacco MAP kinase kinase that interacts with SIPK. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:118–124
Llave C, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC (2000) Virus-encoded suppressor of posttranscriptional gene silencing targets a maintenance step in the silencing pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13401–13406
Lu C, Han MH, Gevara-Garcia A, Fedoroff NV (2002) Mitogene-activated protein kinase signaling in postgermination arrest development by abscisic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:15812–15817
MAPK-Group (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci 7:301–308
Matsuoka D, Nanmori T, Sato K, Kikkawa U, Yasuda T (2002) Activation of AtMEK1, an Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, in vitro and in vivo: analysis of active mutants expressed in E. coli and generation of the active form in stress response in seedlings. Plant J 29:637–647
Melikant B, Giuliani C, Halbmayer-Watzina S, Limmongkon A, Heberle-Bors E, Wilson C (2004) The Arabidopsis thaliana MEK AtMKK6 activates the MAP kinase AtMPK13. FEBS Lett 576:5–8
Menke FLH, van Pelt JA, Pieterse CMJ, Klessig DF (2004) Silencing of the mitogen-activated protein kinase MPK6 compromises disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:897–907
Nakagami H, Pitzschke A, Hirt H (2005) Emerging MAP kinase pathways in plant stress signaling. Trends Plant Sci 10:339–345
Nishihama R, Soyano T, Ishikawa M, Araki S, Tanaka H, Asada T (2002) Expansion of the cell plate in plant cytokinesis requires a kinesin-like protein/MAPKKK complex. Cell 109:87–99
Petersen M, Naested H, Andreasson E, Lindhart U, Johansen B, Nielsen HB (2000) Arabidopsis MAP kinase 4 negatively regulates systemic acquired resistance. Cell 103:1111–1120
Quaked F, Rozhon W, Lecourieux D, Hirt H (2003) A MAPK pathway mediates ethylene signaling in plants. EMBO J 22:1282–1288
Ren D, Yang H, Zhang S (2002) Cell death mediated by MAPK is associated with hydrogen peroxide production in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277:559–565
Rental MG, Lecourieux D, Quaked F, Usher S, Petersen U, Okamoto N (2004) OX1 kinase is necessary for oxidative burst-mediated signaling in Arabidopsis. Nature 427:858–861
Rivas S, Romeis T, Jones JD (2002) The Cf-9 disease resistance protein is present in an approximately 420-kilodalton heteromultimeric membrane-associated complex at one molecule per complex. Plant Cell 14:689–702
Rohila JS, Chen M, Cerny R, Fromm ME (2004) Improved tandem affinity purification tag and methods for isolation of protein heterocomplexes from plants. Plant J 38:172–181
Soyano T, Nishihama R, Morikiyo K, Ishikawa M, Machida Y (2003) NQK1/-NtMEK1 is a MAPKK that acts in the NPK1 MAPKKK-mediated MAPK cascade and is required for plant cytokinesis. Genes Dev 17:1055–1067
Teige M, Scheikl E, Eulgem T, Dóczi R, Ichimura K, Shinozaki K (2004) The MKK2 pathway mediates cold and salt stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 15:141–152
Voronin V, Touraev A, Kieft H, van Lammeren AA, Heberle-Bors E, Wilson C (2001) Temporal and tissue-specific expression of the tobacco ntf4 MAP kinase. Plant Mol Biol 45:679–689
Voronin V, Aionesei T, Limmongkon A, Barinova I, Touraev A, Lauriere C (2004) The MAP kinase kinase NtMEK2 is involved in tobacco pollen germination. FEBS Lett 560:86–90
Xiong L, Yang Y (2003) Disease resistance and abiotic stress tolerance in rice are inversely modulated by an abscisic acid-inducible mitogen-activated protein kinase. Plant Cell 15:15745–15759
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2005). Organization of cis-acting regulatory elements in osmotic- and cold-stress responsive promoters. Trends Plant Sci 10:88–94
Yang KY, Liu Y, Zhang S (2001) Activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is involved in disease resistance in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:741–746
Zhang S, Liu Y (2001) Activation of salicylic acid-induced protein kinase, a mitogen activated protein kinase, induces multiple defense responses in tobacco. Plant Cell 13:1877–1889
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273
Zuo J, Niu QW, Chua NH (2000) Technical advance: an estrogen receptor-based transactivator XVE mediates highly inducible gene expression in transgenic plants. Plant J 24:265–273
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. John Alfano for the pPTN289 C-terminal HA vector and Dr. Nam-Hai Chua for providing the pER8 vector. We thank Dr. J. Chen and Ms. Mary Smith for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by funding from the Changjian University Research Initiative.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Janska.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwa, CM., Yang, XC. The AtMKK3 pathway mediates ABA and salt signaling in Arabidopsis . Acta Physiol Plant 30, 277–286 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-007-0117-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-007-0117-3