Abstract
Objective
To observe the therapeutic effect of mild moxibustion on irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) visceral hyperalgesia model rats and its regulatory effect on P2X3 receptors in the spinal cord, anterior cingutate cortex (ACC) and thalamic ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL).
Methods
Thirty 8-day-old newborn rats were randomly divided into a normal group (n=6) and a modeling group (n=24) according to the completely random number table method. Rats in the normal group were bred routinely, and those in the modeling group were subjected to preparing IBS chronic visceral hyperalgesia model using colorectal distention (CRD) in stimulation method. Rats successfully modelled were re-divided into a model group, a mild moxibustion group, a P2X3 receptor antagonist group, and a normal saline group according to the completely random number table method with 6 rats in each group. Rats in each group received corresponding interventions from the 37-day old, once a day for 7 consecutive days. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot assays were used to detect P2X3 protein expressions in the spinal cord, ACC and VPL of rats.
Results
Under different intensities of CRD stimulation, the abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) scores of the model group were significantly increased versus the normal group (all P<0.05); the AWR scores of the mild moxibustion group and the P2X3 receptor antagonist group were significantly reduced versus the model group (all P<0.01). The P2X3 protein expressions in rat spinal cord, ACC and VPL tissues of the model group were significantly increased versus the normal group (all P<0.01); the P2X3 protein expressions in rat spinal cord, ACC and VPL tissues of the mild moxibustion group and the P2X3 receptor antagonist group were significantly reduced versus the model group (all P<0.01).
Conclusion
Mild moxibustion can inhibit the P2X3 receptor expressions in the spinal cord, ACC, and VPL tissues of IBS visceral hyperalgesia model rats, which may be the mechanism of mild moxibustion in relieving the central sensitization of rats with IBS visceral hyperalgesia.
摘要
目的
观察温和灸对肠易激综合征(IBS)内脏痛敏模型大鼠的干预作用及其对脊髓、 前扣带回(ACC)和丘脑腹后外侧核(VPL)中P2X3受体的调节作用.
方法
按照完全随机数字表法将30只8日龄新生大鼠随机分为正常组(n=6)与造模组(n=24). 正常组常规饲养, 造模组采用直结肠球囊扩张(CRD)刺激法制备IBS慢性内脏痛敏大鼠模型. 将模型验证成功的造模大鼠按照完全随机数字表法重新分为模型组、 温和灸组、 P2X3受体拮抗剂组和生理盐水组, 每组6只. 各组大鼠从37日龄开始分别接受相应的干预, 每日1次, 连续7 d. 采用免疫组织化学法及免疫印迹法检测大鼠脊髓、 ACC和VPL内P2X3蛋白表达.
结果
在不同强度的CRD刺激下, 与正常组相比, 模型组AWR评分均明显升高(均P<0.05); 与模型组相比, 温和灸组及P2X3受体拮抗剂组AWR评分均显著降低(均P<0.01). 与正常组相比, 模型组大鼠脊髓、 ACC及VPL组织中P2X3蛋白的表达均显著升高(均P<0.01); 与模型组相比, 温和灸组及P2X3受体拮抗剂组大鼠脊髓、 ACC及VPL组织中P2X3蛋白的表达均显著降低(均P<0.01).
结论
温和灸能够抑制IBS内脏痛敏模型大鼠脊髓、 ACC及VPL组织内P2X3受体的表达, 这可能是温和灸缓解IBS内脏痛敏大鼠中枢敏化的效应机制.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ford AC, Lacy BE, Talley NJ. Irritable bowel syndrome. N Engl J Med, 2017, 376(26): 2566–2578.
Barshop K, Staller K. New pathways, new targets: visceral hypersensitivity pathogenesis in irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2016, 7(2): e146.
Farzaei MH, Bahramsoltani R, Abdollahi M, Rahimi R. The role of visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome: pharmacological targets and novel treatments. J Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2016, 22(4): 558–574.
Simren M, Tornblom H, Palsson OS, VAN-Tilburg MA, Oudenhove LV, Tack J, Whitehead WE. Visceral hypersensitivity is associated with GI symptom severity in functional GI disorders: consistent findings from five different patient cohorts. Gut, 2018, 67(2): 255–262.
Basso L, Benamar M, Mas-orea X, Deraison C, Blanpied C, Cenac N, Saoudi A, Gilles D. Endogenous control of inflammatory visceral pain by T cell-derived opioids in IL-10-deficient mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2020, 32(2): e13743.
Greenwood-VAN Meerveld B, Prusator DK, Johnson AC. Animal models of gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Animal models of visceral pain: pathophysiology, translational relevance, and challenges. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2015, 308(11): G885–G903.
Woolf CJ. Central sensitization: implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain, 2011, 152(3 Suppl): S2–S15.
Burnstock G. Release of vasoactive substances from endothelial cells by shear stress and purinergic mechanosensory transduction. J Anat, 1999, 194(Pt 3): 335–342.
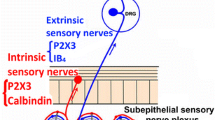
Burnstock G. Purinergic signalling in the gastrointestinal tract and related organs in health and disease. Purinergic Signal, 2014, 10(1): 3–50.
Burnstock G. Purinergic P2 receptors as targets for novel analgesics. Pharmacol Ther, 2006, 110(3): 433–454.
Burnstock G. Purine-mediated signalling in pain and visceral perception. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2001, 22(4): 182–188.
Burnstock G. Purinergic signalling in the urinary tract in health and disease. Purinergic Signal, 2014, 10(1): 103–155.
Burnstock G. The journey to establish purinergic signalling in the gut. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2008, 20(Suppl 1): 8–19.
Ruan HZ, Burnstock G. Localisation of P2Y1 and P2Y4 receptors in dorsal root, nodose and trigeminal ganglia of the rat. Histochem Cell Biol, 2003, 120(5): 415–426.
Lin SY, Corey DP. TRP channels in mechanosensation. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2005, 15(3): 350–357.
Zhang F, Wu L, Zhao J, Lü T, Hu Z, Weng Z, Wang S, Wu H, Liu H. Neurobiological mechanism of acupuncture for relieving visceral pain of gastrointestinal origin. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2017, 2017: 5687496.
Pei LX, Geng H, Guo J, Yang GH, Wang L, Shen RR, Xia SY, Ding M, Feng H, Lu J, Li J, Liu L, Shu YY, Fang XD, Wu XL, Wang XX, Weng SJ, Ju L, Chen X, Shen H, Sun JH. Effect of acupuncture in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Mayo Clin Proc, 2020, 95(8): 1671–1683.
Burnstock G. Acupuncture: a novel hypothesis for the involvement of purinergic signalling. Med Hypotheses, 2009, 73(4): 470–472.
Burnstock G. Purinergic mechanosensory transduction and visceral pain. Mol Pain, 2009, 5: 69.
Xu GY, Shenoy M, Winston JH, Mittal S, Pasricha PJ. P2X receptor-mediated visceral hyperalgesia in a rat model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity. Gut, 2008, 57(9): 1230–1237.
Weng ZJ, Wu LY, Zhou CL, Dou CZ, Shi Y, Liu HR, Wu HG. Effect of electroacupuncture on P2X3 receptor regulation in the peripheral and central nervous systems of rats with visceral pain caused by irritable bowel syndrome. Purinergic Signal, 2015, 11(3): 321–329.
Zhang F, Zhou Y, Wu HG, Weng ZJ, Zhang ZY, Zhao M, Xu Q, Liu HR, Zhou CL. Research of P2X3 receptor from DRG participating in moxibustion at Zusanli (ST 36) to relieve visceral pain in IBS rats. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2020, 39(6): 775–782.
Al-Chaer ED, Kawasaki M, Pasricha PJ. A new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development. Gastroenterology, 2000, 119(5): 1276–1285.
Li ZR. Experimental Acupuncture Science. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2004: 327–329.
Jarvis MF, Burgard EC, Mcgaraughty S, Honore P, Lynch K, Brennan TJ, Subieta A, Biesen TV, Cartmell J, Bianchi B, Niforatos W, Kage K, Yu H, Mikusa J, Wismer CT, Zhu CZ, Chu K, Lee CH, Stewart AO, Polakowski J, Cox BF, Kowaluk E, Williams M, Sullivan J, Faltynek C. A-317491, a novel potent and selective non-nucleotide antagonist of P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors, reduces chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99(26): 17179–17184.
Christianson JA, Traub RJ, Davis BM. Differences in spinal distribution and neurochemical phenotype of colonic afferents in mouse and rat. J Comp Neurol, 2006, 494(2): 246–259.
Sagami Y, Shimada Y, Tayama J, Nomura T, Satake M, Endo Y, Shoji T, Karahashi K, Hongo M, Fukudo S. Effect of a corticotropin releasing hormone receptor antagonist on colonic sensory and motor function in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut, 2004, 53(7): 958–964.
Rabitti S, Giovanardi CM, Colussi D. Acupuncture and related therapies for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2021, 55(3): 207–217.
Ma XP, Hong J, An CP, Zhang D, Huang Y, Wu HG, Zhang CH, Meeuwsen S. Acupuncture-moxibustion in treating irritable bowel syndrome: how does it work?. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(20): 6044–6054.
Huang Y, Zhang D, LI ZY, Yang YT, Wu LJ, Zhang J, Zhi FY, Li XY, Shi Z, Hong J, Ma XP. Moxibustion eases chronic inflammatory visceral pain in rats via MAPK signaling pathway in the spinal cord. J Pain Res, 2019, 12: 2999–3012.
Wang LD, Zhao JM, Huang RJ, Tan LY, Hu ZH, Weng ZJ, Wang K, Wu HG, Liu HR. Study on the mechanism underlying the regulation of the NMDA receptor pathway in spinal dorsal horns of visceral hypersensitivity rats by moxibustion. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2016, 2016: 3174608.
Krajewski JL. P2X3-containing receptors as targets for the treatment of chronic pain. Neurotherapeutics, 2020, 17(3): 826–838.
Al-Chaer ED, Feng Y, Willis WD. A role for the dorsal column in nociceptive visceral input into the thalamus of primates. J Neurophysiol, 1998, 79(6): 3143–3150.
Al-Chaer ED, Lawand NB, Westlund KN, Willis WD. Pelvic visceral input into the nucleus gracilis is largely mediated by the postsynaptic dorsal column pathway. J Neurophysiol, 1996, 76(4): 2675–2690.
Chen JH, Teng GX. The central sensory and transmission mechanism of visceral pain. Jiepouxue Jinzhan, 1998, (2): 24–31.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (上海市卫生 和计划生育委员会科研课题, No. 20174Y0015); National Natural Science Foundation of China (国家自然科学基金 项目, No. 81904301); National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 国家重点基础研究发展计划项目 No. 2015CB554501); Three-year Action Plan for the Development of Shanghai Traditional Chinese Medicine [上 海中医药事业发展三年行动计划项目, No. ZY(2018–2020)-CCCX-2004-01]; National Chinese Medicine Leading Talent Support Program-Qi Huang Scholar (国家 中医药领军人才支持计划-岐黄学者).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Author Wu Huan-gan is a member of the Editorial Board of Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science. The paper was handled by other editors and has undergone rigorous peer review process. Author Wu Huan-gan was not involved in the journal’s review or decisions related to this manuscript.
Additional information
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria in this experiment.
Co-first Authors: Zhang Zhi-ying, master degree candidate; Zhang Fang, M.M., research intern
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Zy., Zhang, F., Weng, Zj. et al. Regulatory effect of mild moxibustion on P2X3 receptors in spinal cord, anterior cingulate cortex and thalamic ventral posterolateral nucleus of rats with IBS visceral hyperalgesia. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 19, 239–248 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-021-1254-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-021-1254-8
Keywords
- Moxibustion Therapy
- Moxa Stick Moxibustion
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Visceral Pain
- Central Nervous System Sensitization
- Receptors, Purinergic P2X3
- Spinal Cord
- Brain