Abstract
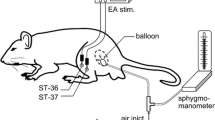
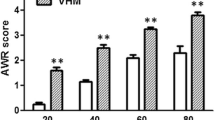
The aim of this study is to investigate the role of the purinergic receptor P2X3 in the peripheral and central nervous systems during acupuncture treatment for the visceral pain of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). A total of 24 8-day-old Sprague–Dawley (SD) neonatal male rats (SPF grade) were stimulated using colorectal distention (CRD) when the rats were awake. The modeling lasted for 2 weeks with one stimulation per day. After 6 weeks, the rats were randomly divided into three groups of eight each: (1) the normal group (NG, n = 8); (2) the model group (MG, n = 8); and (3) the model + electroacupuncture group (EA, n = 8) that received electroacupuncture at a needling depth of 5 mm at the Shangjuxu (ST37, bilateral) and Tianshu (ST25, bilateral) acupoints. The parameters of the Han’s acupoint nerve stimulator (HANS) were as follows: sparse-dense wave with a frequency of 2/100 Hz, current of 2 mA, 20 min/stimulation, and one stimulation per day; the treatment was provided for seven consecutive days. At the sixth week after the treatment, the abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) score was determined; immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry were used to measure the expression of the P2X3 receptor in myenteric plexus neurons, prefrontal cortex, and anterior cingulate cortex; and, a real-time PCR assay was performed to measure the expression of P2X3 messenger RNA (mRNA) in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and spinal cord. After stimulation with CRD, the expression levels of the P2X3 receptor in the inter-colonic myenteric plexus, DRG, spinal cord, prefrontal cortex, and anterior cingulate cortex were upregulated, and the sensitivity of the rats to IBS visceral pain was increased. Electroacupuncture (EA) could downregulate the expression of the P2X3 receptor and ease the sensitivity to visceral pain. The P2X3 receptor plays an important role in IBS visceral pain. The different levels of P2X3 in the peripheral enteric nervous system and central nervous system mediate the effects of the EA treatment of the visceral hyperalgesia of IBS.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Mahony L, McCarthy J, Kelly P et al (2005) Lactobacillus and bifidobacterium in irritable bowel syndrome: symptom responses and relationship to cytokine profiles. Gastroenterology 128(3):541–551
Kim DY, Camilleri M (2000) Serotonin: a mediator of the brain-gut connection. Am J Gastroenterol 95(10):2698–2709
Fukudo S, Nomura T, Muranaka M et al (1993) Brain-gut response to stress and cholinergic stimulation in irritable bowel syndrome. A preliminary study. J Clin Gastroenterol 17(2):133–141
Burnstock G, Kennedy C (2011) P2X receptors in health and disease. Adv Pharmacol 61:333–372
Burnstock G (2014) Purinergic signalling in the gastrointestinal tract and related organs in health and disease. Purinergic Signal 10(1):3–50
Burnstock G (2014) Purinergic signalling in the urinary tract in health and disease. Purinergic Signal 10(1):103–155. doi:10.1007/s11302-013-9395-y, Epub 2013 Nov 22
Burnstock G (2013) Purinergic signalling: pathophysiology and therapeutic potential. Keio J Med 62(3):63–73
Ochoa-Cortes F, Liñán-Rico A, Jacobson KA et al (2014) Potential for developing purinergic drugs for gastrointestinal diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 20(7):1259–1287. doi:10.1097/MIB.0000000000000047
Zhou EH, Ding GH, Wu HG, Qi L, Liu HR, Wang XM, Ma XP (2011) Immediate effect of acupuncture on colon motility in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan 29:293–296
Ma XP (2014) Acupuncture-moxibustion in treating irritable bowel syndrome: how does it work? World J Gastroenterol 20(20):6044–6054
Ji J, Lu Y, Liu H et al (2013) Acupuncture and moxibustion for inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:158352. doi:10.1155/2013/158352, Epub 2013 Sep 24
Wu HG, Jiang B, Zhou EH et al (2008) Regulatory mechanism of electroacupuncture in irritable bowel syndrome: preventing MC activation and decreasing SP VIP secretion. Dig Dis Sci 53(6):1644–1651
Liu HR, Wang XM, Zhou EH et al (2009) Acupuncture at both ST25 and ST37 improves the pain threshold of chronic visceral hypersensitivity rats. Neurochem Res 34(11):1914–1918
Huang RJ, Zhao JM, Wu LY et al (2014) Mechanisms underlying the analgesic effect of moxibustion on visceral pain in irritable bowel syndrome: a review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014:895914. doi:10.1155/2014/895914, Epub 2014 Jul 1
Burnstock G (2008) The journey to establish purinergic signalling in the gut. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20(Suppl 1):8–19
Giniatullin R, Nistri A (2013) Desensitization properties of P2X3 receptors shaping pain signaling. Front Cell Neurosci 7:245
Burnstock G (2013) Introduction and perspective, historical note. Front Cell Neurosci 7:227
Xu GY, Shenoy M, Winston JH et al (2008) P2X receptor-mediated visceral hyperalgesia in a rat model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity. Gut 57(9):1230–1237
Soares-Bezerra RJ, Calheiros AS, da Silva Ferreira NC et al (2013) Natural products as a source for new anti-inflammatory and analgesic compounds through the inhibition of purinergic P2X receptors. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 6(5):650–658
Burnstock G, Nistri A, Khakh BS et al (2014) ATP-gated P2X receptors in health and disease. Front Cell Neurosci 8:204
Scalera A, Loguercio C (2012) Focus on irritable bowel syndrome. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 16(9):1155–1171
Wang WS, Tu WZ, Cheng RD et al (2014) Electroacupuncture and A-317491 depress the transmission of pain on primary afferent mediated by the P2X3 receptor in rats with chronic neuropathic pain states. J Neurosci Res 92(12):1703–1713
Burnstock G (2011) Puncturing the myth-purinergic signaling, not mystical energy, may explain how acupuncture works. The Scientist
Al-Chaer ED, Kawasaki M, Pasricha PJ (2000) A new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development. Gastroenterology 119(5):1276–1285
Rong W, Spyer KM, Burnstock G (2002) Activation and sensitisation of low and high threshold afferent fibers mediated by P2X receptors in the mouse urinary bladder. J Physiol 541(Pt 2):591–600
Burnstock G (2001) Purine-mediated signalling in pain and visceral perception. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22(4):182–188
Shinoda M, Feng B, Gebhart GF (2009) Peripheral and central P2X receptor contributions to colon mechanosensitivity and hypersensitivity in the mouse. Gastroenterology 137(6):2096–2104
Tamir H, Gershon MD (1990) Serotonin-storing secretory vesicles. Ann N Y Acad Sci 600:53–66
Accarino AM, Azpiroz F, Malagelada JR (1997) Attention and distraction: effects on gut perception. Gastroenterology 113(2):415–422
Shinoda M, La JH, Bielefeldt K, Gebhart GF (2010) Altered purinergic signaling in colorectal dorsal root ganglion neurons contributes to colorectal hypersensitivity. J Neurophysiol 104(6):3113–3123
Weng ZJ, Wu LY, Lu Y et al (2013) Electroacupuncture diminishes P2X2 and P2X3 purinergic receptor expression in dorsal root ganglia of rats with visceral hypersensitivity. Neural Regen Res 8(9):802–808
North RA (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82(4):1013–1067
Xu KD, Liang T, Wang K et al (2010) Effect of pre-electroacupuncture on p38 and c-Fos expression in the spinal dorsal horn of rats suffering from visceral pain. Chin Med J (Engl) 123(9):1176–1181
Yu WC, Huang GY, Zhang MM et al (2008) Effect of connexin 43 knockout on acupuncture-induced down-regulation of c-fos expression in spinal dorsal horn in visceral pain mice. Acupunct Res 33(3):179–182
Dong M. (2011) Regulatory effects of electroacupuncture on P2X2,3 receptor and c-fos of rats with irritable bowel syndrome visceral sensitivity. Shang Hai University of T.C.M. Master thesis
Gibney SM, Gosselin RD, Dinan TG et al (2010) Colorectal distension-induced prefrontal cortex activation in the Wistar-Kyoto rat: implications for irritable bowel syndrome. Neuroscience 165(3):675–683
Elsenbruch S (2011) Abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome: a review of putative psychological, neural and neuro-immune mechanisms. Brain Behav Immun 25(3):386–394. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2010.11.010, Epub 2010 Nov 20
Shyu BC, Sikes RW, Vogt LJ, Vogt BA (2010) Nociceptive processing by anterior cingulate pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 103(6):3287–3301
Yan N, Cao B, Xu J et al (2012) Glutamatergic activation of anterior cingulate cortex mediates the affective component of visceral pain memory in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 97(1):156–164
Sikes RW, Vogt LJ, Vogt BA (2008) Distribution and properties of visceral nociceptive neurons in rabbit cingulate cortex. Pain 135(1–2):160–174
Naliboff BD, Berman S, Suyenobu B et al (2006) Longitudinal change in perceptual and brain activation response to visceral stimuli in irritable bowel syndrome patients. Gastroenterology 131(2):352–365
Burnstock G (2015) Physiopathological roles of P2X receptors in the central nervous system. Curr Med Chem 22(7):819–844
Wang J, Zhang X, Cao B, et al. (2013) Facilitation of synaptic transmission in the anterior cingulate cortex in viscerally hypersensitive rats. Cereb Cortex. [Epub ahead of print]
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, No. 20123107110008; the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 81403474); New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-13-0907); and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 program, No. 2009CB522900).
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Z. J. Weng, L. Y. Wu and C. L. Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, Z.J., Wu, L.Y., Zhou, C.L. et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on P2X3 receptor regulation in the peripheral and central nervous systems of rats with visceral pain caused by irritable bowel syndrome. Purinergic Signalling 11, 321–329 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-015-9447-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-015-9447-6