Abstract
Objective
To observe the effects of acupuncture plus spinal manipulations on the physical functioning and levels of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP) and osteoprotegerin (OPG) in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
Methods
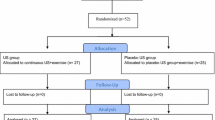
A total of 128 AS cases were allocated into a control group and an observation group using random number table method, with 64 cases in each group. Patients in both groups took sulfasalazine and meloxicam. Patients in the observation group received additional acupuncture plus spinal manipulations. The efficacy, Bath AS functional index (BASFI), Bath AS disease activity index (BASDAI), and the levels of ALP, ESR, CRP and OPG were compared between the two groups after eight weeks of treatment.
Results
After treatment, the symptom scores of traditional Chinese medicine in both groups were decreased (all P<0.05), and these scores in the observation group were significantly lower than in the control group (all P<0.05); the VAS, BASFI and BASDAI scores in both groups were decreased (all P<0.05), and these scores in the observation group were significantly lower than in the control group (all P<0.05); and the ALP, ESR, CRP and OPG levels in both groups were decreased (all P<0.05), and these levels in the observation group were significantly lower than in the control group (all P<0.05). The total efficacy rate was 92.2% in the observation group, versus 78.1% in the control group, presenting a statistical significance (P<0.05).
Conclusion
Conventional medication combined with acupuncture and spinal manipulations can improve clinical symptoms, accelerate the recovery of physical functioning, and reduce the ALP, ESR, CRP and OPG levels.
【摘要】
目的: 观察针刺加整脊手法对强直性脊柱炎(AS)患者躯体功能, 血清碱性磷酸酶(ALP), 血沉(ESR), C反应蛋 白(CRP)及骨保护素(OPG)的影响。方法: 将128例AS患者按随机数字表法分为对照组和观察组, 每组64例。两组均接 受口服柳氮磺胺吡啶及美洛昔康治疗, 观察组在此基础上加用针刺和整脊手法。治疗8周后比较两组疗效, Bath AS功 能指数评分(BASFI)以及Bath AS疾病活动指数(BASDAI)评分, 以及ALP, ESR, CRP和OPG水平。结果: 治疗后, 两组各项 中医症状评分均较治疗前下降(均P<0.05), 且观察组各项评分均低于对照组(均P<0.05); 两组VAS, BASFI及BASDAI评 分均较治疗前下降(均P<0.05), 且观察组三项评分均低于对照组(均P<0.05); 两组ALP, ESR, CRP及OPG水平均较治 疗前下降(均P<0.05), 且观察组各项水平均低于对照组(均P<0.05)。观察组总有效率92.2%, 对照组为78.1%, 两组差 异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论: 药物治疗基础上加用针刺和整脊手法治疗AS可有效改善临床症状, 促进患者躯体 功能恢复, 降低ALP, ESR, CRP和OPG水平。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang T, Li ZF, Li T, Yang XY, Zhang LP. Research survey on traditional Chinese medicine treatment for ankylosing spondylitis. Fengshibing Yu Guanjieyan, 2019, 8(7): 60–63.
Ruan XF, Lin H, Du P, Xiao JJ, He DC. Research advance in integrative Chinese and Western medicine for ankylosing spondylitis. Huanan Guofang Yixue Zazhi, 2019, 33(3): 221–223.
Han Q, Liang Q, Wu ZB, Leng N, Zhu P. Efficacy of biological agents combined with methotrexate and sulfasalazine for ankylosing spondylitis with hip joint involvement. Zhonghua Linchuang Mianyi He Biantai Fanying Zazhi, 2017, 11(4): 322–326.
Li YH, Xin XY, Qin HJ, Hailisi T. Clinical observations on warming-unblocking prescription Du moxibustion plus acupuncture for ankylosing spondylitis. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2019, 38(10): 1163–1167.
Yang XF. Yang-warming and Du-unblocking needling plus spinal manipulations for 41 cases with ankylosing spondylitis. Guangming Zhongyi, 2019, 34(18): 2858–2860.
Xu ST, Ge BF, Xu YK. Practical Orthopedics. 4th Edition. Beijing: People’s Military Medical Press, 2012: 1644–1651.
Zhang AL. Discussions on the integrative Chinese and Western medicine guideline for ankylosing spondylitis. Beijing: Paper Collections of the 7th National Integrative Chinese and Western Medicine Conference for Rheumatic Diseases, 2008: 6.
Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Guiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2002: 119–123.
Zhang LL, Nie H. Research advance in association between CD4+ T-cell subgroup disequilibrium and pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Xiandai Mianyixue, 2016, 36(4): 341–344.
Wang YX. Efficacy observation and nursing experience on moxibustion along the Governor Vessel for ankylosing spondylitis due to kidney deficiency. Zhongguo Nongcun Weisheng, 2019, 11(14): 58–59.
Zhao JL. Efficacy observation on the role of acupuncture in improving AS severity and patients’ physical functioning. Shaanxi Zhongyi, 2016, 37(7): 907–908.
Zhang L, Zhao XH, Chen GJ. Research advance on abnormal expressions of Tfh and B cells in pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Xiandai Mianyixue, 2016, 36(2): 146–149.
Ding FR, Jiang P, Liu W. Research advance on pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Shandong Yiyao, 2019, 59(17): 102–105.
Song JL. Clinical efficacy and safety observation on biological agent etanercept combined with functional exercise for ankylosing spondylitis. Zhongguo Yiyao Zhinan, 2019, 17(12): 106–107.
Ye XY, Ma CJ, Su SY, Peng JH, Dai YG, Zhang XF. Clinical effect of diuretic moxibustion therapy in treatment of kidney deficiency type ankylosing spondylitis. Linchuang He Shiyan Yixue Zazhi, 2019, 18(3): 270–274.
Huang ZY, Yang HY. Du-warming method for 27 cases of ankylosing spondylitis due to kidney deficiency. Huanqiu Zhongyiyao, 2018, 11(10): 1598–1601.
Li XL, Zhao HL, Song ZC, Wang HY, Qi WR, Yang F, Zhang YY, Qi LL, Lu Y. Clinical efficacy of comprehensive traditional Chinese medicine therapies for ankylosing spondylitis due to kidney deficiency. Da Yisheng, 2018, 3(9): 5–7, 62.
Zhang FH. Clinical Observation on Treating Ankylosing Spondylitis with Kidney Deficiency and Cold Syndrome by Warming Kidney and Unblocking Du Meridian. Harbin: Master Thesis of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, 2018.
Chen SS. Therapeutic observation on point-toward-point needling at points on the low back regions for residual back pain after percutaneous kyphoplasty. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2019, 17(2): 131–136.
Zhao D, Xu N, Yu TY, Zhao GR, Wang SL, Li YM, Sun YZ. Research advances in the mechanism of acupuncture treatment for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2019, 38(11): 1310–1314.
Zhang ZQ, Liu X, Zhong H, Deng DX, Li GM, Deng JQ, Liu ZP, Xie H, Chang XR. Therapeutic observation of tuina manipulation for lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2019, 17(2): 116–123.
Liu HB. Clinical study on warm-needling plus chiropractic for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2012, 31(1): 40–42.
Yao ML, Chen ZH, Zhang WD, Xu H, Wang TT, Hu RT. Clinical observation of sinew-regulating bone-setting manipulations plus exercise therapy for chronic non-specific low back pain. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2020, 18(1): 59–66.
Wu YZ, Zheng WN, Zhang FS. Clinical observation on acupuncture at Jiaji (EX-B 2) acupoints combined with Long’s manipulation in treatment of spine-related diseases. Linchuang Yixue, 2016, 36(12): 116–117.
Chen SY, Gao XF. Efficacy observation on needling Jiaji (EX-B 2) points combined with point application for ankylosing spondylitis. Sichuan Zhongyi, 2016, 34(10): 193–194
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Guangxi Scientific and Technology Key Research and Development Plan (广西科 学技术重点研发计划, No. ZXGC201701358).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author: Deng Gui-yi, bachelor, associate chief physician.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gui-yi, D., Jian-hui, H., Xing-mu, Z. et al. Effects of acupuncture plus spinal manipulations on physical functioning and biochemical indicators in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 19, 206–212 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-021-1241-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-021-1241-0
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Chiropractic
- Visual Analog Scale
- Pain Measurement
- Blood Sedimentation
- Spondylitis, Ankylosing