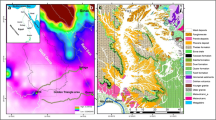
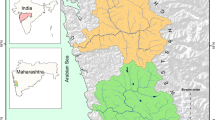
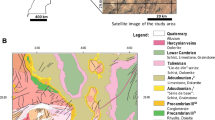
Abstract
A multidisciplinary approach using the integrated field of geosciences (e.g., geomorphology, geotectonics, geophysics, and hydrology) is established to conduct groundwater recharge potential mapping of the Kunur River Basin, India. The relative mean error (RME) calculation of the results of three applied techniques and water table data from twenty-four observation wells in the basin over the 2000–2010 period are presented. Nine subbasins were identified and ranked for the RME calculation, where the observation wells-based ranking was taken as standard order for comparison. A linear model has been developed using six factors (drainage density, surface slope, ruggedness index, lineament density, Bouguer gravity anomaly, and potential maximum water retention capacity) and a grid-wise weighted index. In a separate comparative approach, the sub-basin and grid-wise analyses have been conducted to identify the suitable spatial unit for watershed level hydrological modeling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad I, Verma V, Verma M K (2015). Application of Curve Number Method for Estimation of Runoff Potential in GIS Environment. 2nd International Conference on Geological and Civil Engineering, IPCBEE, 80, 16–20
Ajmal M, Moon G, Ahn J, Kim T (2015). Investigation of SCS-CN and its inspired modified models for runoff estimation in South Korean watersheds. J Hydro-environment Res, 9(4): 592–603
Anbazhagan S, Ramasamy S M, Das Gupta S (2005). Remote sensing and GIS for artificial recharge study, runoff estimation and planning in Ayyar basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Geol, 48(2): 158–170
Avinash K, Deepika B, Jayappa K S (2014). Basin geomorphology and drainage morphometry parameters used as indicators for groundwater prospect: insight from geographical information system (GIS) technique. Journal of Earth Science, 25(6): 1018–1032
Avinash K, Jayappa K S, Deepika B (2011). Prioritization of sub-basins based on geomorphology and morphometric analysis using remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS) techniques. Geocarto Int, 26(7): 569–592
Banerjee T, Das A L, Mukhopadhyay S C (2011). Prioritisation of Silai sub watersheds for erosion management using drainage morphometry and soil erosion rates. Geogr Rev India, 73(4): 323–338
Biswas S, Sudhakar S, Desai V R (1999). Prioritization of subwatersheds based on morphometric analysis of drainage basin: a remote sensing and GIS approach. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 27(3): 155–166
CGWB (Central GroundWater Board) (2010). Groundwater Scenario of India 2009–10. Ministry of Water Resources, Govt. of India
CGWB (Central Ground Water Board) (2014). Aquifer Systems of West Bengal. Ministry ofWater Resources, Govt. of India, Eastern Region, Kolkata
Chaudhary B S, Kumar M, Roy A K, Ruhal D S (1996). Application of Remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems in Groundwater investigations in Sohna block, Gurgaon District, Haryana (India). In: International Archives of Photogrametry and Remote sensing Vienna, vol. XXXI, Part B6, 18–23
Chow V T (1964). Handbook of Applied Hydrology. New York: McGraw-Hill
de Alwis D A, Easton Z M, Dahlke H E, Philpot W D, Steenhuis T S (2007). Unsupervised classification of saturated areas using a time series of remotely sensed images. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci, 11(5): 1609–1620
Dobrin M B (1976). Introduction to Geophysical Prospecting. New York: McGraw-Hill Bock Company
Drury S A (1993). Image Interpretation in Geology. UK: Chapman & Hall
Elbeih S F (2015). An overview of integrated remote sensing and GIS for groundwater mapping in Egypt. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 6 (1): 1–15
Elmahdy S I, Mohamed M M (2015). Automatic detection of near surface geological and hydrological features and investigating their influence on groundwater accumulation and salinity in southwest Egypt using remote sensing and GIS. Geocarto Int, 30(2): 132–144
Esper Angillieri M Y (2008). Morphometric analysis of Colanguil river basin and flash flood hazard, San Juan, Argentina. Environmental Geology, 55(1): 107–111
Falkenmark M (1994). Successfully coping with complex water scarcity: an issue of land/water integration. In: Gieske A, Gould J, eds. Proceedings of the Workshop on Integrated Water Resources Management, University of Botswana and Rural Industries Research Centre, Kanye-Gaborone, 11–26
Godebo T R (2005). Application of Remote Sensing and GIS for Geological Investigation and Groundwater Potential Zone Identification, Southeastern Ethiopian Plateau, Bale Mountains and the Surrounding Areas. Thesis of M. Sc. Dissertation, Department of Earth Sciences, Addis Ababa University, 43
Gopinath G, Seralathan P (2004). Identification of Groundwater Prospective Zones Using IRS-ID LISS III and Pump Test Methods. Journal of Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 32(4): 329–342
Gravelius H (1914). Grundrifi der gesamten Gewcisserkunde. Band I: Flufikunde (Compendium of Hydrology, vol. I. Rivers, in German). Germany: Goschen, Berlin
Gundalia M, Dholakia M (2014). Impact of Monthly Curve Number on Daily Runoff Estimation for Ozat Catchment in India. Open Journal of Modern Hydrology, 4(04): 144–155
Guo K, Wang J, Wang Y (2015). Application of ZY-3 remote sensing image in the research of Huashan experimental watershed. Proceedings of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences, 368: 51–56
Hadley R F, Schumm S A (1961). Sediment sources and drainage basin characteristics in upper Cheyenne River basin. Washington, DC: US Geological Survey, Water-Supply Paper. 1531–B, 198
Hajam R A, Hamid A, Bhat S (2013). Application of morphometric analysis for geo-hydrological studies using geo-spatial technology-A case study of Vishav Drainage Basin. Hydrol Current Res, 4: 157
Haridas V R, Aravmdan S, Gopinath G (1998). Remote sensing and its applications for groundwater favourable area identification. Qut J GARC, 6(1): 18–22
Haridas V R, Chandra Sekaran V A, Kumaraswamy K, Rajendran S, Unnikrishnan K (1994). Geomorphological and lineament studies of Kanjamalai using IRS-IA data with special reference to groundwater potentiality. Trans Inst Indian Geogr, 16(1): 35–41
Hidore J J (1964). Landform characteristics affecting watershed yields on the Mississippi–Missouri interfluve. In: Moore G A, ed. Proceedings of the Oklahoma Academy of Science. Edmond, Oklahoma: University of Central Oklahoma, 201–203
Horton R E (1932). Drainage basin characteristics. Trans Am Geophys Union, 13(1): 350–361
Horton R E (1945). Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins: hydro physical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol Soc Am Bull, 56(3): 275–370
Indian Meteorological Department (2014). IMD District wise normals, Barddhaman. Govt. of India
Javed A, Khanday Y M, Ahmed R (2009). Prioritization of subwatersheds based on morphometric and land use analysis using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 37(2): 261–274
Jiang D, Wang J, Huang Y, Zhou K, Ding X, Fu J (2014). The Review of GRACE Data Applications in Terrestrial Hydrology Monitoring. Advances in Meteorology, Volume 2014, Article ID 725131, 9 pages, http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/725131
Kale V S, Gupta A (2001). Introduction to geomorphology. Hyderabad, India: Orient Longman Ltd
Khan M A, Gupta V P, Moharana P C (2001). Watershed prioritization using remote sensing and geographical information system: a case study from Guhiya. India. J Arid Environ, 49(3): 465–475
Khan Z A, Tewari R C (2011). Palaeochannel and palaeohydrology of a Middle Siwalik (Pliocene) fluvial system, northern India. J Earth Syst Sci, 120(3): 531–543
Kirpich Z P (1940). Time of concentration of small agricultural watersheds. Civ Eng (NYNY), 6: 362
Kolker A S, Cable J E, Johannesson K H, Allison M A, Inniss L V (2013). Pathways and processes associated with the transport of groundwater in deltaic systems. J Hydrol (Amst), 498: 319–334
Koopmans B N (1983). Side looking Radar, a tool for geological surveys. Remote Sens Rev, 1(1): 19–69
Krishnamurthy J, Venkatesa Kumar N, Jayaraman V, Manivel M (1996). An approach to demarcate groundwater potential zones through remote sensing and a geographical information system. Int J Remote Sens, 17(10): 1867–1884
Kumar R, Raj H (2013). Mitigation of groundwater depletion hazards in India. Curr Sci, 104(10): 1271
Long D, Scanlon B R, Longuevergne L, Sun A Y, Fernando D N, Save H (2013). GRACE satellite monitoring of large depletion in water storage in response to the 2011 drought in Texas. Geophys Res Lett, 40(13): 3395–3401
Long D, Shen Y, Sun A, Hong Y, Longuevergne L, Yang Y, Li B, Chen L (2014). Drought and flood monitoring for a large karst plateau in Southwest China using extended GRACE data. Remote Sens Environ, 155: 145–160
Long L T, Kaufmann R D (2013). Acquisition and Analysis of Terrestrial Gravity Data. Delhi: Cambridge University Press
Longuevergne L, Scanlon B R, Wilson C R (2010). GRACE Hydrological estimates for small basins: evaluating processing approaches on the High Plains Aquifer, USA. Water Resour Res, 46(11): W11517
Magesh N S, Jitheshal K V, Chandrasekar N, Jini K V (2013). Geographical information system based morphometric analysis of Bharathapuzha River Basin, Kerla, India. Appl Water Sci, 3(2): 467–477
Mallinson D J, Smith C W, Culver S J, Riggs S R, Ames D (2010). Geological characteristics and spatial distribution of paleo-inlet channels beneath the outer banks barrier islands, North Carolina, USA. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci, 88(2): 175–189
Manu M S, Anirudhan S (2008). Drainage characteristics of Achankovil river basin, Kerala. J Geol Soc India, 71: 841–850
Martin A K, Gadiga B L (2015). Hydrological and Morphometric Analysis of Upper Yedzaram Catchmnet of Mubi in Adamawa State, Nigeria Using Geographical Information System (GIS). World Environment, 5(2): 63–69
McCauley J, Schaber F, Breed C S, Grolier M J, Haynes C V, Issawa B, Elachi C, Blom R (1982). Subsurface valleys and geo-archeology of the eastern Sahara revealed by Shuttle radar. Science, 218(4576): 1004–1020
Meijerink A M G (1996). Remote sensing applications to hydrology: groundwater. Hydrol Sci J, 41(4): 549–561
Menenti M, LI X, Wang J, Vereecken H, LI J, Mnacini M, Liu Q, Jia L, Kuenzer C, Huang S, Yesou H, Wen J, Ker Y, Cheng X, Gourmelen N, KE C, Ludwing R, LIN H, Eineder M, MA Y, Su ZB (2015). Hydrologic and Cryospheric Processes Observed From Space. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XL (7/W3): 1101–1110
Miller V C (1953). A quantitative geomorphic study of drainage basin characteristics in the Clinch mountain area. New York: Department of Geology, ONR, Columbia University, Virginia and Tennessee, Project NR389–402, Technical Report 3
Minor Irrigation Census (2001). Report on Census of Minor Irrigation Schemes (1993–94). Minor Irrigation Division, Ministry of Water Resources, Govt. of India, New Delhi
National Climate Centre (2006). Trends in the rainfall pattern over the India. India Meteorological Department, Pune, India
NGRI (1978). NGRI/GPH-1 to 5: Gravity Maps of India scale 1: 5,000,000. National Geophysical Research Institute, Hyderabad, India
NIH (National Institute of Hydrology) (1996–1997). Infiltration Studies in Sher-Umar River Doab in Narmada basin. Report No. CS (AR) 6/96-97, Jal Vighyan Bhawan, Roorkee, India
Niyogi M (1985). Groundwater resource of the Ajay Basin. In: Chatterjee S P, ed. Geographical Mosaic-Professor K.G. Bagechi Felicitation, Manasi Press, Calcutta, India, 165–182
Nooka Ratnam K, Srivastava Y K, Venkateswara Rao V, Amminedu E, Murthy K S R (2005). Check dam positioning by prioritization of micro watersheds using SYI model and morphometric analysis–remote sensing and GIS perspective. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 33(1): 25–38
NRSC (2014). National geomorphological and lineament mapping on 1:50,000 scale using Resourcesat-1 LISS-III data. Manual for Geomorphology and Lineament Mapping (Web Version), National Remote Sensing Centre, Hyderabad, India
Obi Reddy G P, Maji A K, Gajbhiye K S (2004). Drainage morphometry and its influence on landform characteristics in a basaltic terrain, central India: a remote sensing and GIS approach. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf, 6(1): 1–16
Pakhmode V, Kulkarni H, Deolankar S B (2003). Hydrological-drainage analysis in watershed-programme planning: a case from the Deccan basalt, India. Hydrogeol J, 11(5): 595–604
Philip G M, Watson D F (1982). A precise method for determining contoured surfaces. Aust Petrol Explor Assoc J, 22(1): 205–212
Prakash S R, Mishra D (1993). Identification of groundwater prospecting zones by using remote sensing and geoelectrical methods in and around Saidnager area, Dakar Block, Jalaun district, uttar pradesh. Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 21(4): 217–227
Prasad A S S S R S, Venkateswarlu N, Reddy P R (2005). Crustal density model along Gopali-Port Canning profile, West Bengal basin using seismic and gravity data. J Ind Geophys Union, 9(4): 235–239
Raghunath H M (2013). Hydrology: Principal, Analysis, Design (2nd Revised Ed.). New Delhi: New Age International Publishers
Rajwant U, Sharma U K (2015). Morphometric analysis of third order river basins to assess the vulnerability of Baner Khad Watershed towards erosional process, Himachal Pradesh, India. Himalayan Geology, 36 (1): 65–73
Ramalingam M, Santhakumar A R (2001). Case study on artificial recharge using remote sensing and GIS. www.GISdevelopment.net, accessed on January 2, 2014
Ramamoorthi A (1983). Snow-melt run-off studies using remote sensing data. Sadhana, 6: 279–286
Rango A, Ritchie J C (1996). Remote sensing application to hydrology. Hydrol Sci J, 41(4): 477–494
Ravindran K V, Jeyram A (1997). Groundwater prospects of Shahbad tehsil, Baran district and eastern Rajasthan: a remote sensing approach. Indian society of remote sensing, 25 (4): 239–246
Reddy J R (2005). A Textbook of Hydrology. New Delhi: University Science Press
Ringrose S, Vanderpost C, Matheson W (1998). Evaluation of vegetative criteria for near-surface groundwater detection using multispectral mapping and GIS techniques in semi-arid Botswana. Appl Geogr, 18 (4): 331–354
Roy A K, Ray P K C (1993). Groundwater investigation using remote sensing and geographic information techniques-A case study in Manabazar-II, Purulia (W.B.). Proceeding national symposium of north-eastern region, Guwahati, India, 180–184
Roy S, Mistri B (2013). Estimation of peak flood discharge for an ungauged river: a case study of the Kunur River, West Bengal. Geogr J, 2013(214140): 1–11
Roy S, Sahu A S (2015). Quaternary tectonic control on channel morphology over sedimentary low land: a case study in the Ajay-Damodar interfluve of Eastern India. Geoscience Frontiers, 6(6): 927–946
Sahu S, Saha D (2014). Geomorphologic, stratigraphic and sedimentologic evidences of tectonic activity in Sone–Ganga alluvial tract in Middle Ganga Plain, India. J Earth Syst Sci, 123:1335–1347
Samadder R K, Kumar S, Gupta R P (2011). Palaeochannels and their potential for artificial groundwater recharge in the western Ganga plains. J Hydrol (Amst), 400(1–2): 154–164
Sankar K (2002). Evaluation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing data in Upper Vaigai river basin, Tamil Nadu. India J Indian Soc Rem Sens, 30(3): 119–129
Saraf A K, Choudhury P R (1998). Integrated remote sensing and GIS for groundwater exploration and identification of artificial recharge sites. Int J Remote Sens, 19(10): 1825–1841
Saravanan S, Manjula R (2015). Geomorphology based semi-distributed approach for modeling rainfall-runoff modeling using GIS. Aquatic Procedia, 4: 908–916
Schultz G A (1997). Use of remote sensing data in a GIS environment for water resources management, Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems for Design and Operation of Water Resources Systems. In: Proceedings of Rabat Symposium S3, April 1997. IAHS Publ no. 242, 3–15
Schumm S A (1956). Evolution of drainage system and slope in badlands at Perth Amboy, New Jersey. Geol Soc Am Bull, 67(5): 597–646
Shah T (2009). Taming the Anarchy: Groundwater Governance in South Asia. Resources for the Future, Washington DC and International Water Management Institute, Colombo
Shah T (2011). Innovations in Groundwater Management: Examples from India. International Water Management Institute. http://rosenberg. ucanr.org/documents/argentina/Tushar ShahFinal.pdf
Shankar V P S, Kulkarni H, Krishnan S (2011). India’s groundwater challenge and the way forward. Econ Polit Wkly, XLVI(2): 37–45
Shi J, Wang J, Hsu A Y, O’Neill P E, Engman E T (1997). Estimation of bare surface soil moisture and surface roughness parameter using Lband SAR image data. IEEE Trans Geosci Rem Sens, 35(5): 1254–1266
Shi Z H, Chen L D, Fang N F, Qin D F, Cai C F (2009). Research on the SCS CN initial abstraction ratio using rainfall-runoff event analysis in the Three Gorges Area, China. Catena, 77(1): 1–7
Smith A B, Walker J P, Western A W (2004). Assimilation of gravity data into a soil moisture and groundwater column model. In: Teuling A J, Leijnse H, Troch P A, Sheffield J, Wood E F, eds. Proceedings of the 2nd international CAHMDA workshop on: The Terrestrial Water Cycle: Modelling and Data Assimilation Across Catchment Scales, Princeton, NJ, 135–137
Smith K G (1950). Standards for grading texture of erosional topography. American Journal of Science, 248: 655–668
Soil Conservation Service (1964). National engineering handbook. Section 4, Hydrology, Department of Agriculture, Washington, 450
Soil Conservation Service (1972). National engineering handbook. Section 4, Hydrology, Department of Agriculture, Washington, 762
Sreedevi P D, Subrahmanyam K, Ahmed S (2005). The significance of morphometric analysis for obtaining groundwater potential zones in a structurally controlled terrain. Environmental Geology, 47(3): 412–420
Sridhar A (2007). Discharge estimation from planform characters of the Shedhi River, Gujarat alluvial plain: present and past. J Earth Syst Sci, 116(4): 341–346
Sridhar A, Chamyal L S, Bhattacharjee F, Singhvi A K (2013). Early Holocene fluvial activity from the sedimentology and palaeohydrology of gravel terrace in the semi arid Mahi River Basin, India. J Asian Earth Sci, 66: 240–248
Srinivasa V S, Govindaiah S, Honne Gowda H (2008). Prioritization of sub-watersheds for sustainable development and management of natural resources: an integrated approach using remote sensing, GIS and socio-economic data. Curr Sci, 95: 345–354
Strahler A N (1957). Quantative Analysis of Watershed geomorphology. Transactions. American Geophysical Union, 38(6): 913–920
Strahler A N (1964). Quantitative geomorphology of drainage and channel networks. In: Chow V T, ed. Handbook of Applied Hydrology. New York: McGraw Hill Book Company, 439–476
Subba Rao N (2009). A numerical scheme for groundwater development in a watershed basin of basement terrain: a case study from India. Hydrogeol J, 17(2): 379–396
Subba Rao N, Chakradhar G K J, Srinivas V (2001). Identification of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing techniques in and around Guntur Town, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 29(1&2): 69–78
Suja Rose R S, Krishnan N (2009). Spatial analysis of groundwater potential using remote sensing and GIS in the Kanyakumari and Nambiyar Basins, India. J Indian Soc Remote Sens, 37(4): 681–692
Suresh M, Sudhakar S, Tiwari K N, Chowdary V M (2004). Prioritization of watersheds using morphometric parameters and assessment of surface water potential using remote sensing. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 32(3): 249–259
Thakkar A K, Dhiman S D (2007). Morphometric analysis and prioritization of miniwatersheds in Mohr watershed, Gujarat, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 35(4): 313–321
Todd D K, Mays L W (2005). Groundwater Hydrology (3rd edition). New York: John Wiley & Sons, 636
United State Geological Society (1997). Introduction to Potential Fields: Gravity. FS-239-95. Available onhttp://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/fs-0239-95/fs-0239-95.pdf, retrieved on 13th December, 2014
United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resource Conservation Service, and National Employee Development Centre (1999). SCS Runoff Equation: Module 205. Engineering and Hydrology Training Series, 1–27
van Dijk A I J M, Renzullo L J (2011). Water resource monitoring systems and the role of satellite observations. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci, 15(1): 39–55
Verma R K (1985). Gravity field, seismicity, and tectonics of the Indian peninsula and the Himalayas (Solid earth sciences library). Holland: D. Reidel Publishing Company
Wagener T, Wheater H S, Gupta H V (2004). Rainfall-Runoff Modelling In: Gauged and Ungauged Catchments. London: Imperial College Press
Wagner W, Naeimi V, Scipal K, de Jeu R, Martinez-Fernandez J (2007). Soil moisture from operational meteorological satellites. Journal of Hydrogeology, 15(1): 121–131
Wahr J, Swenson S, Zlotnicki V, Velicogna I (2004). Timevariable gravity from GRACE: fist results. Geophys Res Lett, 31(11): L11501
Yeh H F, Lin H I, Lee S T, Chang M H, Hsu K C, Lee C H (2014). GIS and SBF for estimating groundwater recharge of a mountainous basin in the Wu River watershed, Taiwan. J Earth Syst Sci, 123(3): 503–516
Zankhna S, Thakkar M G (2014). Palaeochannel investigations and geo hydrological significance of Saraswati River of Mainland Gujarat, India: using remote sensing and GIS techniques. J Environ Res Develop, 9(2): 472–479
Zhang H Y, Shi Z H, Fang N F, Guo M H (2015). Linking watershed geomorphic characteristics to sediment yield: evidence from the Loess Plateau of China. Geomorphology, 234: 19–27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, S., Sahu, A.S. Effectiveness of basin morphometry, remote sensing, and applied geosciences on groundwater recharge potential mapping: a comparative study within a small watershed. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 274–291 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-016-0558-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-016-0558-3