Abstract
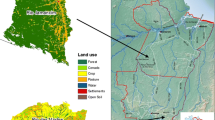
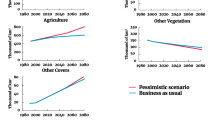
With rapid economic development and urbanization, land use in China has experienced huge changes in recent years; and this will probably continue in the future. Land use problems in China are urgent and need further study. Rapid land-use change and economic development make China an ideal region for integrated land use change studies, particularly the examination of multiple factors and global-regional interactions in the context of global economic integration. This paper presents an integrated modeling approach to examine the impact of global socio-economic processes on land use changes at a regional scale. We develop an integrated model system by coupling a simple global socio-economic model (GLOBFOOD) and regional spatial allocation model (CLUE). The model system is illustrated with an application to land use in China. For a given climate change, population growth, and various socio-economic situations, a global socio-economic model simulates the impact of global market and economy on land use, and quantifies changes of different land use types. The land use spatial distribution model decides the type of land use most appropriate in each spatial grid by employing a weighted suitability index, derived from expert knowledge about the ecosystem state and site conditions. A series of model simulations will be conducted and analyzed to demonstrate the ability of the integrated model to link global socioeconomic factors with regional land use changes in China. The results allow an exploration of the future dynamics of land use and landscapes in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolliger J, Lischke H, Green D G (2005). Simulating the spatial and temporal dynamics of landscapes using generic and complex models. Ecol Complex, 2(2): 107–116
Bousquet F, le Page C (2004). Multi-agent simulations and ecosystem management: a review. Ecol Modell, 176(3–4): 313–332
Brody S D (2003). Implementing the principles of ecosystem management through local land use planning. Popul Environ, 24(6): 511–540
Brown D G, Pijanowski B C, Duh J D (2000). Modeling the relationships between land use and land cover on private lands in the Upper Midwest, USA. Environ Manage, 59(4): 247–263
Brown M E, Funk C C (2008). Food security under climate change. Science, 319(5863): 580–581
Castella J C, Verburg P H (2007). Combination of process-oriented and pattern oriented models of land-use change in a mountain area of Vietnam. Ecol Modell, 202(3–4): 410–420
Crawford T W, Messina J P, Manson S, O’Sullivan D (2005). Complexity science, complex systems, and land use research: guest editorial. Environment plan B, 32: 792–798
deWit C T, van Keulen H, Seligman N G, Spharim I (1988). Application of interactive multiple goal programming techniques for analysis and planning of regional agricultural development. Agric Syst, 26(3): 211–230
Dietzel C, Clarke K C (2007). Toward optimal calibration of the SLEUTH land use change model. Transactions in GIS, 11(1): 29–45
Engelen G, White R, Uljee I, Drazan P (1995). Using cellular automata for integrated modeling of socio-environmental system. Environ Monit Assess, 34(2): 203–214
FAO (1995). Planning for sustainable use of land resource. Towards a new approach. Background paper to FAOs Task Managership for Chapter 10 of Agenda 21 of the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED). Prepared by Land and Water Development Division and approved by Interdepartmental Working Group on Land Use Planning, FAO
Foley J A, Defries R, Asner G P, Barford C, Bonan G, Carpenter S R, Chapin F S, Coe M T, Daily G C, Gibbs H K, Helkowski J H, Holloway T, Howard E A, Kucharik C J, Monfreda C, Patz J A, Prentice I C, Ramankutty N, Snyder P K (2005). Global consequences of land use. Science, 309(5734): 570–574
Gao Q, Yu M, Liu Y H, Xu H M, Xu X (2007). Modeling interplay between regional net ecosystem carbon balance and soil erosion for a crop-pasture region. J Geophys Res, 112(G4): G04005
Haberl H, Erb K H, Krausmann F, Loibl W, Schulz N, Weisz H (2001). Changes in ecosystem processes induced by land use: human appropriation of aboveground NPP and its influence on standing crop in Austria. Global Biogeochem Cycles, 15(4): 929–942
He C, Okada N, Zhang Q, Shi P, Li J (2008). Modelling dynamic urban expansion processes incorporating a potential model with cellular automata. Landsc Urban Plan, 86(1): 79–91
Hilferink K, Rietveld P (1999). Land use scanner: an integrated GIS based model for long term projections of land use in urban and rural areas. J Geogr Syst, 1(2): 155–177
Jiang L, Cui X, Xu X, Jiang Y, Rounsevell M, Murray-Rust D, Liu YH (2013) A simple global food system model. Agricultural Economics, (in press)
Kline J D, Moses A, Lettman G J, Azuma D L (2007). Modeling forest and range land development in rural locations, with examples from eastern Oregon. Landsc Urban Plan, 80(3): 320–332
Krausmann F (2001). Land use and industrial modernization: an empirical analysis of human influence on the functioning of ecosystems in Austria 1830–1995. Land Use Policy, 18(1): 17–26
Krausmann F, Haberl H, Schulz N B, Erb K H, Darge E, Gaube V (2003). Land use change and socio-economic metabolism in Austria-part I: driving forces of land-use change: 1950–1995. Land Use Policy, 20(1): 1–20
Kruseman G, Ruben R, Hengsdijk H, van Ittersum M (1995). Farm household modeling for estimating the effectiveness of price instruments in land use policy. Neth J Agric Sci, 43: 111–123
Kuyvenhoven A, Ruben R, Kruseman G (1995). Options for sustainable agricultural systems and policy instruments to reach them. In: Ecoregional Approaches for Sustainable Land Use and Food Production, 12–16 December 1994, ISNAR. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 187–212
Lambin E F, Rounsevell M D A, Geist H J (2000). Are agricultural landuse models able to predict changes in land-use intensity? Agric Ecosyst Environ, 82(1–3): 321–331
Lee X, Goulden M, Hollinger D, Barr A, Black TA, Bohrer G, Bracho R, Drake B, Goldstein A, Gu L, Katul G, Kolb T, Law BE, Margolis H, Meyers T, Monson R, Munger W, Oren R, Tha Paw UK, Richardson AD, Schmid HP, Staebler R, Wofsy S, Zhao L (2011). Observed increase in local cooling effect of deforestation at higher latitudes. Nature, 4790: 384–387 doi:10.1038/nature10588
Lin G, Ho S (2003). China’s land resources and land-use change: insights from the 1996 land survey. Land Use Policy, 20(2): 87–107
Liu J, Diamond J (2005). China’s environment in a globalizing world. Nature, 435(7046): 1179–1186
Liu J, Zhang Z, Xu X (2009). Spatial patterns and driving forces of land use change in China in the early 21st century. Acta Geogr Sin, 64(12): 1411–1420
Mas J F, Puig H, Palacio J L, Sosa-Lo’pez A (2004). Modelling deforestation using GIS and artificial neural networks. Environ Model Softw, 19(5): 461–471
Moss R, Edmonds J, Hibbard K, Manning MR, Rose S K, van Vuuren D P, Carter T R, Emori S, Kainuma M, Kram T, Meehl G A, Mitchell J F B, Nakicenovic N, Riahi K, Smith S J, Stouffer R J, Thomson AM, Weyant J P, Wilbanks T J (2010). The nest generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment. Nature, 463(7282): 747–756
Muetzelfeldt R, Massheder J (2003). The Simile visual modeling environment. Eur J Agron, 18(3–4): 345–358
Overmars K P, Verburg P H, Veldkamp T (2007). Comparison of a deductive and an inductive approach to specify land suitability in a spatially explicit land use model. Land Use Policy, 24(3): 584–599
Penning de Vries F W T, van Keulen H, Rabbinge R (1995). Natural resources and limits to food production in 2040. In: Eco-regional Approaches for Sustainable Land Use and Food Production, 12–16 December 1994. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 65–87
Pijanowski B C, Alexandridis K T, Müller D (2006). Modelling urbanization patterns in two diverse regions of the world. J Land Use Sci, 1(2–4): 83–108
Pijanowski B C, Gage S H, Long D T, Cooper W E (2000). A land transformation model for the Saginaw Baywatershed. In: Sanderson J, Harris L D, eds. Landscape Ecology: A Top Down Approach. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishing, 708pp
Pontius R G Jr, Cornell J D, Hall C A S (2001). Modeling the spatial pattern of land-use change with GEOMOD2: application and validation. Agric Ecosyst Environ, 85(1–3): 191–203
Pourebrahim S, Hadipour M, Bin Mokhtar M (2011). Integration of spatial suitability analysis for land use planning in coastal areas; case of Kuala Langat District, Selangor, Malaysia. Landsc Urban Plan, 101(1): 84–97
Rabbinge R, van Latesteijn H C (1992). Long-term options for land use in the European Community. Agric Syst, 40(1–3): 195–210
Rindfuss R R, Entwisle B, Walsh S J, An L, Badenoch N, Brown D G, Deadman P, Evans T P, Fox J, Geoghegan J, Gutmann M, Kelly M, Linderman M, Liu J, Malanson G P, Mena C F, Messina J P, Moran E F, Parker D C, Parton W, Prasartkul P, Robinson D T, Sawangdee Y, Vanwey L K, Verburg P H (2008). Land use change: complexity and comparisons. J Land Use Sci, 3(1): 1–10
Schulp C J E, Nabuurs G J, Verburg P H (2008). Future carbon sequestration in Europe-effects of land use change. Agric Ecosyst Environ, 127(3–4): 251–264
Soares-Filho B S, Nepstad D C, Curran LM, Cerqueira G C, Garcia R A, Ramos C A, Voll E, McDonald A, Lefebvre P, Schlesinger P (2006). Modelling conservation in the Amazon basin. Nature, 440(7083): 520–523
Sohl T L, Sayler K L, Drummond M A, Loveland T R (2007). The FORE-SCE model: a practical approach for projecting land cover change using scenario-based modeling. J Land Use Sci, 2(2): 103–126
Tao F, Yokozawa M, Zhang Z (2009). Modelling the impacts of weather and climate variability on crop productivity over a large area: a new process-based model development, optimization, and uncertainties analysis. Agric Meteorol, 149(5): 831–850
Tebaldi C, Lobell D B (2008). Towards probabilistic projections of climate change impacts on global crop yields. Geophys Res Lett, 35(8): L08705
Tongeren F V (2008). Agricultural Policy Design and Implementation: A Synthesis. OECD Food, Agriculture and Fisheries Working Papers, 7: doi:10.1787/243786286663
Tongeren F V, Meijl H V, Surry Y (2001). Global models applied to agricultural and trade policies: a review and assessment. Agric Econ, 26(2): 149–172
Turner B L 2nd, Lambin E F, Reenberg A (2007). The emergence of land change science for global environmental change and sustainability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104(52): 20666–20671
Veldkamp A, Fresco L O (1996). CLUE-CR: an integrated multi-scale model to simulate land use change scenarios in Costa Rica. Ecol Modell, 91(1–3): 231–248
Verburg P H, Eickhout B, Meijl H V (2008). A multi-scale, multi-model approach for analyzing the future dynamics of European land use. Ann Reg Sci, 42(1): 57–77
Verburg P H, Overmars K P (2009). Combining top-down and bottomup dynamics in land use modeling: exploring the future of abandoned farmlands in Europe with the Dyna-CLUE model. Landscape Ecol, 24(9): 1167–1181
Verburg P H, Schot P P, Dijst MJ, Veldkamp A (2004). Land use change modelling: current practice and research priorities. Geol J, 61: 309–324
Verburg P H, Schulp C J E, Witte N, Veldkamp A (2006). Downscaling of land use change scenarios to assess the dynamics of European landscapes. Agric Ecosyst Environ, 114(1): 39–56
Verburg P H, Soepboer W, Veldkamp A, Limpiada R, Espaldon V, Mastura S S (2002). Modeling the spatial dynamics of regional land use: the CLUE-S model. Environ Manage, 30(3): 391–405
Verburg P H, van de Steeg J, Veldkamp A, Willemen L (2009). From land cover change to land function dynamics: a major challenge to improve land characterization. J Environ Manage, 90(3): 1327–1335
Verburg P H, de Koning G H J, Kok K, Veldkamp A, Bouma J (1999). A spatial explicit allocation procedure for modeling the pattern of land use change based upon actual land use. Ecol Modell, 116(1): 45–61
Verburg P H, Erb K H, Mertz O, Espindola G (2013) Land System Science: between global challenges and local realities. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 5(5): 433–437 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2013.08.001
Wu WB, Yang P, Tang H J (2007). Regional variability of efects of land use system on soil properties. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2007, 40(8): 1697–1702
Xu X, Gao Q, Liu Y H, Wang J A, Zhang Y (2009). Coupling a land use model and an ecosystem model for a crop-pasture zone. Ecol Modell, 220(19): 2503–2511
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xia Xu is currently associate professor of the State key laboratory of Earth Surface Processes and Resource Ecology of Beijing Normal University. She earned her Master’s degree in natural resources management, and Ph. D degree in ecological modeling, from Beijing Normal University, China in 2001 and 2006, respectively. She has been engaged in the application of geographic information systems, remote sensing, and spatial analysis of resources in the field of ecological environment. Her research program is focused on the sustainability of land resource base. She is concerned about issues such as global climate change, land use change, ecosystem model simulation, and the mutual coupling between land use and ecological environment models. She has published more than 20 papers. Currently, Xia Xu presides over the National Natural Science Foundation of China and a special topic of 973 projects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Gao, Q., Peng, C. et al. Integrating global socio-economic influences into a regional land use change model for China. Front. Earth Sci. 8, 81–92 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-013-0421-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-013-0421-8