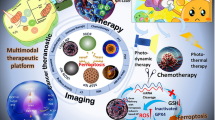
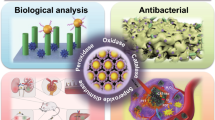
Abstract
The anticancer and antibacterial potential of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles have been investigated using different biological assays. Also, an induction heating study was performed to check the magnetic hyperthermia application of synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles. An antimicrobial study was performed against gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial strains. Among them, the Staphylococcus aureus bacterial strain showed maximum antimicrobial activity with a 15 mm zone of inhibition for 500 µg/mL of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The antioxidant activity was ascertained through a DPPH (1, 1-diphenyl-2, picryl-hydrazyl) assay. Fe3O4 nanoparticles showed 30.57% free radical scavenging activity due to its antioxidative nature. The anticancer potential of Fe3O4 nanoparticles was evaluated against the breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) cell lines and fibroblast (L929) cell line using 3-(4, 5-dimethythiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) cytotoxicity assay. Fe3O4 nanoparticles proved to be toxic to the MDA-MB-231 cell line even at a concentration of 3.125 µg mL−1, and an increase in cytotoxicity to 89% from 20% was observed with the rise in Fe3O4 nanoparticles concentration to 100 µg mL−1. The observed cytotoxicity for the L929 cell line is low revealing the biocompatible nature of synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Also, the biocompatibility for invitro application was examined using angiogenesis activity which does not show any antiangiogenics activity of synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Additionally, the inductive heating characteristic of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in an alternating current (AC) magnetic field was examined at a frequency of 278 kHz, and for the different magnetic fields of 13.3, 20.0, and 26.7 kA m−1 for 600 s with different suspension concentrations of Fe3O4 nanoparticles as 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and 5.0 mg mL−1. The highest rise in temperature of 60.63 °C was observed for 5 mg mL−1 at a magnetic field of 26.7 kA m−1 with a specific absorption rate (SAR) value of 85 Wg−1 which makes them suitable for hyperthermia application. The study shows promising antimicrobial, antioxidative, anticancer, and induction heating properties. Herein, the present study reveals the potential of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for improved therapeutic applications and effective bactericidal propensity.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
On request to the corresponding author, data on work will be available.
References
Arsalani S, Hadadian Y, Mazon E, Guidelli E, Kava E, Ramos A, Gualdi A, Pavan T, Baffa O, Carneiro A (2022) Uniform size PEGylated iron oxide nanoparticles as a potential theranostic agent synthesized by a simple optimized coprecipitation route. J Magn Magn 564:170091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.170091
Chaudhary R, Nawaz K, Khan A, Hano C, Abbasi B, Anjum S (2020) An overview of the algae-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biomolecules 10(11):1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111498
Cho S, Jarrett B, Louie A, Kauzlarich S (2006) Gold-coated iron nanoparticles: a novel magnetic resonance agent for T1 and T2 weighted imaging. Nanotechnology 17(3):640. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/3/004
Cross S, Fataftah M, Jonderian A, McCalla E, Blum A (2023) Preparation and characterization of ultra-small, monodisperse CoxFe3-xO4 nanoparticles. J Magn Magn 567:170345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.170345
Darwish M, Kim H, Lee H, Ryu C, Lee J, Yoon J (2019) Synthesis of magnetic ferrite nanoparticles with high hyperthermia performance via a controlled co-precipitation method. Nanomaterials 9(8):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081176
Das S, Diyali S, Vinothini G, Perumalsamy B, Balakrishnan G, Ramasamy T, Dharumadurai D, Biswas B (2020) Synthesis, morphological analysis, antibacterial activity of iron oxide nanoparticles and the cytotoxic effect on lung cancer cell line. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04953
Gatoo M, Naseem S, Arfat M, Mahmood Dar A, Qasim K, Zubair S (2014) Physicochemical properties of nanomaterials: implication in associated toxic manifestations. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/498420
Ghutepatil P, Salunkhe A, Khot V, Pawar S (2019) APTES (3-aminopropyltriethoxy silane) functionalized MnFe2O4 nanoparticles: a potential material for magnetic fluid hyperthermia. Chem Pap 73:2189–2197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-00768-z
Gudkov S, Burmistrov D, Serov D, Rebezov M, Semenova A, Lisitsyn A (2021) Do iron oxide nanoparticles have significant antibacterial properties? Antibiotics 10(7):884. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070884
Gupta A, Gupta M (2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26(18):3995–4021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.10.012
Hajalilou A, Ferreira L, Jorge M, Reis C, Cruz M (2021) Superparamagnetic Ag-Fe3O4 composites nanoparticles for magnetic fluid hyperthermia. J Magn Magn 537:168242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.168242
Huang Z, Tang F (2005) Preparation, structure, and magnetic properties of mesoporous magnetite hollow spheres. J Colloid Interface Sci 281(2):432–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.121
Jabir M, Rashid T, Nayef U, Albukhaty S, AlMalki F, Albaqami J, AlYamani A, Taqi Z, Sulaiman G (2022) Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus α-hemolysin production using nanocurcumin capped Au@ZnO nanocomposite. Bioinorg Chem Appl. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2663812
Jeun M, Lee S, Kyeong Kang J, Tomitaka A, Wook Kang K, Il Kim Y, Takemura Y, Chung K, Kwak J, Bae S (2012) Physical limits of pure superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for a local hyperthermia agent in nanomedicine. Appl Phys Lett 100(9):092406. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3689751
Kalaiselvan C, Thorat N, Sahu N (2021) Carboxylated PEG-functionalized MnFe2O4 nanocubes synthesized in a mixed solvent: morphology, magnetic properties, and biomedical applications. ACS Omega 6(8):5266–5275. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05382
Khashan S, Dagher S, Tit N, Alazzam A, Obaidat I (2017) Novel method for synthesis of Fe3O4@TiO2 core/shell nanoparticles. Surf Coat Technol 322:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.05.045
Kumar A, Leeds N, Fuller G, Van Tassel P, Maor M, Sawaya R, Levin V (2000) Malignant gliomas: MR imaging spectrum of radiation therapy-and chemotherapy-induced necrosis of the brain after treatment. Radiology 217(2):377–384. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.217.2.r00nv36377
Kumar R, Inbaraj B, Chen B (2010) Surface modification of superparamagnetic iron nanoparticles with calcium salt of poly (γ-glutamic acid) as coating material Mater. Res Bull 45(11):1603–1607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2010.07.017
Kumar H, Bhardwaj K, Nepovimova E, Kuča K, Singh Dhanjal D, Bhardwaj S, Bhatia S, Verma R, Kumar D (2020) Antioxidant functionalized nanoparticles: a combat against oxidative stress. Nanomaterials 10(7):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071334
Lemine O, Algessair S, Madkhali N, Al-Najar B, El-Boubbou K (2023) Assessing the heat generation and self-heating mechanism of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia application: the effects of concentration, frequency, and magnetic field. Nanomaterials 13(3):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030453
Lu A, Salabas E, Schüth F (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(8):1222–1244. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200602866
Mornet S, Vasseur S, Grasset F, Duguet E (2004) Magnetic nanoparticle design for medical diagnosis and therapy. J Mater Chem 14(14):2161–2175. https://doi.org/10.1039/B402025A
Müller R, Dutz S, Neeb A, Cato A, Zeisberger M (2013) Magnetic heating effect of nanoparticles with different sizes and size distributions. J Magn Magn 328:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.09.064
Munir T, Mahmood A, Rasul A, Imran M, Fakhar-e-Alam M (2023) Biocompatible polymer functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Mater Chem Phys 301:127677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.127677
Narayanaswamy V, Sambasivam S, Saj A, Alaabed S, Issa B, Al-Omari I, Obaidat I (2021) Role of magnetite nanoparticles size and concentration on hyperthermia under various field frequencies and strengths. Molecules 26(4):796. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040796
Patel N, Mulla N, Khot V, Patil R (2023) Anticancer activity of surface functionalized magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles—effect of polymer coating. Emergent Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-023-00611-y
Patil P, Bansode P, Gajare S, Deshmukh A, Tiwari A, Khot V, Patil S, Pore D, Rashinkar G (2023) Nano-magnetite supported N-heterocyclic carbene-gold complex with pendant ferrocenyl group as a multi-modal anti-breast cancer agent. Res Chem Intermed 49(11):5141–5161. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2024573/v1
Perveen S, Nadeem R, Rehman S, Afzal N, Anjum S, Noreen S, Saeed R, Amami M, Al-Mijalli S, Iqbal M (2022) Green synthesis of iron (Fe) nanoparticles using Plumeria obtusa extract as a reducing and stabilizing agent: antimicrobial, antioxidant and biocompatibility studies. Arab J Chem 15(5):103764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.103764
Shah M, Fawcett D, Sharma S, Tripathy S, Poinern G (2015) Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles via biological entities. Mater 8(11):7278–7308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8115377
Suba S, Vijayakumar S, Vidhya E, Punitha V, Nilavukkarasi M (2021) Microbial mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles derived from Lactobacillus spp.: characterizations, antimicrobial and biocompatibility efficiencies. Sens Int 2:100104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sintl.2021.100104
Sun J, Zhou S, Hou P, Yang Y, Weng J, Li X, Li M (2007) Synthesis and characterization of biocompatible Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A 80(2):333–341. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.30909
Vassallo M, Martella D, Barrera G, Celegato F, Coïsson M, Ferrero R, Olivetti ES, Troia A, Sozeri H, Parmeggiani C, Wiersma DS (2023) Improvement of hyperthermia properties of iron oxide nanoparticles by surface coating. ACS Omega 8(2):2143–2154. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c06244
Vibhute A, Nille O, Kolekar G, Rohiwal S, Patil S, Lee S, Tiwari A (2022) Fluorescent carbon quantum dots functionalized by poly l-lysine: efficient material for antibacterial, bioimaging and antiangiogenesis applications. J Fluoresc 32(5):1789–1800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-022-02977-4
Wilczewska A, Niemirowicz K, Markiewicz K, Car H (2012) Nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Pharmacol Rep 64(5):1020–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1734-1140(12)70901-5
Wildeboer R, Southern P, Pankhurst Q (2014) On the reliable measurement of specific absorption rates and intrinsic loss parameters in magnetic hyperthermia materials. J Phys D Appl Phys 47(49):495003. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/47/49/495003
Yasemian A, Kashi M, Ramazani A (2019) Surfactant-free synthesis and magnetic hyperthermia investigation of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles at different reaction temperatures. Mater Chem Phys 230:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.03.032
Yuan Y, Tasciuc D (2011) Comparison between experimental and predicted specific absorption rate of functionalized iron oxide nanoparticle suspensions. J Magn Magn 323(20):2463–2469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.05.018
Zakariya N, Majeed S, Jusof W (2022) Investigation of antioxidant and antibacterial activity of iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPS) synthesized from the aqueous extract of Penicillium spp. Sens Int 3:100164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sintl.2022.100164
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge D. Y. Patil Education Society (Deemed to be University), Kolhapur, India, for financial support through the intramural project (DYPES/DU/2022/2855).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NNP carried out an investigation and formal analysis, data curation, and original—draft writing; VMK provided resources and formal analysis, carried out modification, creation, and presentation, and visualization of the manuscript. RSP carried out funding acquisition, administration, supervision, and manuscript editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest, declared by the authors.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, N.N., Khot, V.M. & Patil, R.S. Biological activities of iron oxide-based magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Pap. 78, 3857–3869 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-024-03358-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-024-03358-w