Abstract
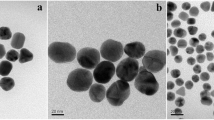
There has been a rush into the green synthesis of nanoparticles in recent years. However, the direct comparison of the toxicity of biosynthesized nanoparticles and chemically synthesized nanoparticles was seldom reported. Herein, a green route for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles (Bio-AuNPs) was developed by incubation of gold precursors with Oocystis sp. algal extract. The toxicity of Bio-AuNPs and citrate-stabilized AuNPs (Chem-AuNPs) was further compared by using another microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and its higher trophic level Daphnia magna as the model organisms. The exposure of Chem-AuNPs induced the aggregation of algal cells and dramatically inhibited the growth of C. vulgaris at 5 mg/L, while no significant inhibitory effect was observed for Bio-AuNPs at 20 mg/L. Additionally, the 24 and 48 h LC50 of Bio-AuNPs to D. magna were much higher than those of Chem-AuNPs. The data directly demonstrated that Bio-AuNPs have better biosafety than Chem-AuNPs, making them potentially useful in biomedical fields and cancer therapy and diagnosis.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastus NG, Comenge J, Puntes V (2011) Kinetically controlled seeded growth synthesis of citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: size focusing versus ostwald ripening. Langmuir 27:11098–11105
Bhatnagar A, Vilar VJP, Ferreira C, Botelho CMS, Boaventura RAR (2012) Optimization of nickel biosorption by chemically modified brown macroalgae (Pelvetia canaliculata). Chem Eng J 193:256–266
Botha TL, Boodhia K, Wepener V (2016) Adsorption, uptake and distribution of gold nanoparticles in daphnia magna following long term exposure. Aquat Toxicol 170:104–111
Bozich JS, Lohse SE, Torelli MD, Murphy CJ, Hamers RJ, Klaper RD (2014) Surface chemistry, charge and ligand type impact the toxicity of gold nanoparticles to daphnia magna. Environ Sci: Nano 1:260–270
Camas M, Celik F, Camas AS, Ozalp HB (2019) Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using marine bacteria and box-behnken design optimization. Part Sci Technol 37:31–38
Dykman L, Khlebtsov N (2012) Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: recent advances and perspectives. Chem Soc Rev 41:2256–2282
Fan Y, He C, Li YL (2022) Iron oxide clusters on g-C3N4 promote the electron-hole separation in photo-Fenton reaction for efficient degradation of wastewater. Chem Pap. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02419-2
Faried M, Shameli K, Miyake M, Hajalilou A, Zamanian A, Zakaria Z, Abouzari-lotf E, Hara H, Khairudin NBBA, Nordin MFBM (2016) A green approach for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles using ultrasonic radiation’s times in sodium alginate media: characterization and antibacterial evaluation. J Nanomater 2016:4941231
Feurtet-Mazel A, Mornet S, Charron L, Mesmer-Dudons N, Maury-Brachet R, Baudrimont M (2016) Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by the living freshwater diatom Eolimna minima, a species developed in river biofilms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:4334–4339
Hackbarth FV, Girardi F, de Souza S, de Souza AAU, Boaventura RAR, Vilar VJP (2014) Marine macroalgae Pelvetia canaliculata (Phaeophyceae) as a natural cation exchanger for cadmium and lead ions separation in aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 242:294–305
Her S, Jaffray DA, Allen C (2017) Gold nanoparticles for applications in cancer radiotherapy: mechanisms and recent advancements. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 109:84–101
Huo C, Yuan CG, Li YK, Liu PL, Liu JF (2017) Characterization and quantification of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles using Chenopodium aristatum L. stem extract. J Clust Sci 28:2953–2967
Huo C, Khoshnamvand M, Liu P, Liu C, Yuan CG (2019) Rapid mediated biosynthesis and quantification of AuNPs using persimmon (Diospyros Kaki L.f) fruit extract. J Mol Struct 1178:366–374
Huo C, Hao Z, Yuan C, Chen Y, Liu J (2022) Probing the phytosynthesis mechanism of gold and silver nanoparticles by sequential separation of plant extract and molecular characterization with ultra-high-resolution mass spectrometry. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 10:3829–3838
Khoshnamvand M, Ashtiani S, Chen Y, Liu J (2020a) Impacts of organic matter on the toxicity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles to green microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Environ Res 185:109433
Khoshnamvand M, Ashtiani S, Liu J (2020b) Acute toxicity of gold nanoparticles synthesized from macroalga saccharina japonica towards daphnia magna. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:22120–22126
Khoshnamvand M, Hao Z, Fadare OO, Hanachi P, Chen Y, Liu J (2020c) Toxicity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles to aquatic organisms of different trophic levels. Chemosphere 258:127346–127346
Kim DY, Saratale RG, Shinde S, Syed A, Ameen F, Ghodake G (2018) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Laminaria japonica extract: Characterization and seedling growth assessment. J Clean Prod 172:2910–2918
Kitching M, Ramani M, Marsili E (2015) Fungal biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles: mechanism and scale up. Microb Biotechnol 8:904–917
Li L, Zhang Z (2016) Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using green alga Pithophora oedogonia with their electrochemical performance for determining carbendazim in soil. Int J Electrochem Sci 11:4550–4559
Lomeli-Rosales DA, Zamudio-Ojeda A, Reyes-Maldonado OK, Lopez-Reyes ME, Basulto-Padilla GC, Lopez-Naranjo EJ, Zuniga-Mayo VM, Velazquez-Juarez G (2022) Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of capsicum Chinense plant. Molecules 27:1692
OECD (2012) Test No 211: Daphnia magna Reproduction Test. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. OECD Publishing, Paris
Oukarroum A, Bras S, Perreault F, Popovic R (2012) Inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles in two green algae, Chlorella vulgaris and Dunaliella tertiolecta. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:80–85
Pancha I, Chokshi K, Maurya R, Trivedi K, Patidar SK, Ghosh A, Mishra S (2015) Salinity induced oxidative stress enhanced biofuel production potential of microalgae Scenedesmus sp CCNM 1077. Bioresour Technol 189:341–348
Perreault F, Bogdan N, Morin M, Claverie J, Popovic R (2012) Interaction of gold nanoglycodendrimers with algal cells (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii) and their effect on physiological processes. Nanotoxicology 6:109–120
Qu Y, Shen W, Pei X, Ma F, You S, Li S, Wang J, Zhou J (2017) Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by Trichoderma SP WL-Go for azo dyes decolorization. J Environ Sci 56:79–86
Rajkumar R, Ezhumalai G, Gnanadesigan M (2021) A green approach for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles by chlorella vulgaris and its application in photocatalytic dye degradation activity. Environ Technol Innov 21:101282
Romero N, Visentini FF, Marquez VE, Santiago LG, Castro GR, Gagneten AM (2020) Physiological and morphological responses of green microalgae chlorella vulgaris to silver nanoparticles. Environ Res 189:109857
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C, Li XN, Rotello VM (2012) Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem Rev 112:2739–2779
Sharma VK, Yngard RA, Lin Y (2009) Silver nanoparticles: green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 145:83–96
Shunmugam R, Balusamy R, Kumar V, Menon S, Lakshmi T, Perumalsamy H (2021) Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using marine microbe (Vibrio alginolyticus) and its anticancer and antioxidant analysis. J King Saud Univ Sci 33:101260
Sridharan R, Monisha B, Kumar PS, Gayathri KV (2022) Carbon nanomaterials and its applications in pharmaceuticals: a brief review. Chemosphere 294:133731
Tayemeh MB, Esmailbeigi M, Shirdel I, Joo HS, Johari SA, Banan A, Nourani H, Mashhadi H, Jami MJ, Tabarrok M (2020) Perturbation of fatty acid composition, pigments, and growth indices of Chlorella vulgaris in response to silver ions and nanoparticles: a new holistic understanding of hidden ecotoxicological aspect of pollutants. Chemosphere 238:124576
Thanh-Luu P (2019) Effect of silver nanoparticles on tropical freshwater and marine microalgae. J Chem 2019:1–7
Torabfam M, Yuce M (2020) Microwave-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using dried extracts of chlorella vulgaris and antibacterial activity studies. Green Process Synth 9:283–293
Turner A, Brice D, Brown MT (2012) Interactions of silver nanoparticles with the marine macroalga, Ulva lactuca. Ecotoxicology 21:148–154
Wei C, Zhang Y, Guo J, Han B, Yang X, Yuan J (2010) Effects of silica nanoparticles on growth and photosynthetic pigment contents of scenedesmus obliquus. J Environ Sci 22:155–160
Xu S, Zhu Q, Xu S, Yuan M, Lin X, Lin W, Qin Y, Li Y (2021) The phase behavior of n-ethylpyridinium tetrafluoroborate and sodium-based salts ATPS and its application in 2-chlorophenol extraction. Chin J Chem Eng 33:76–82
Yin Y, Yang X, Hu L, Tan Z, Zhao L, Zhang Z, Liu J, Jiang G (2016) Superoxide-mediated extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Environ Sci Technol Lett 3:160–165
Yu S, Yin Y, Liu J (2013) Silver nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Sci: Process Impacts 15:78–92
Yugay YA, Usoltseva RV, Silant’ev VE, Egorova AE, Karabtsov AA, Kumeiko VV, Ermakova SP, Bulgakov VP, Shkryl YN (2020) Synthesis of bioactive silver nanoparticles using alginate, fucoidan and laminaran from brown algae as a reducing and stabilizing agent. Carbohydr Polym 245:116547
Zhu Q, Xu S, Wu W, Qi Y, Lin Z, Li Y, Qin Y (2022) Hierarchical hollow zinc oxide nanocomposites derived from morphology-tunable coordination polymers for enhanced solar hydrogen production. Angew Chem Int Ed 61:e202205312
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21620102008, 22076198).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, W., Yang, R., Yu, S. et al. Comparative study on the toxicity of biosynthesized and chemically synthesized gold nanoparticles. Chem. Pap. 77, 1999–2007 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02602-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02602-5