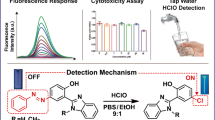
Abstract
A new pyrene-based fluorescent probe (PM) for detection of hypochlorite was synthesized through the reaction of aldehyde with methylene and well characterized. PM presents highly selective fluorescence enhancement response toward OCl− over a variety of different analytes, including metal ions, anions and some compounds with redox properties via the unique reaction of Meldrum’s acid with OCl−. The results of mass spectra, FTIR spectra and density functional theory calculation demonstrated that the fluorescence enhancement of PM is attributed to the inhibition of intramolecular charge transfer due to the protonation of O atoms on Meldrum’s acid molecule after the oxidation reaction of OCl− on PM. The fluorescence intensity of PM at 517 nm in aqueous solution displayed a good linear relationship with the concentration of OCl− in a wide range with a low detection limit of 4.24 μM. Additionally, the viability of HepG-2 cell after being incubated in 15 μM PM solution for 24 h can reach 90%, indicating that PM has very low cytotoxicity. PM can recognize OCl− in living cells by the fluorescent confocal imaging. PM has the potential application in detection and recognition of OCl− in environmental systems and living organisms.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andzelm J, Huzinaga S (1984) Gaussian basis sets for molecular calculations. Elsevier Science, New York
Becke AD (1993) Density-functional thermochemistry III. The role of exact exchange. J Chem Phys 98(7):5648–5652. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.464913
Behrend L, Henderson G, Zwacka RM (2003) Reactive oxygen species in oncogenic transformation. Biochem Soc Trans 31(6):1441–1444. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0311441
Cao L, Zhang R, Zhang W, Du Z, Liu C, Ye Z, Yuan J (2015) A ruthenium (II) complex-based lysosome-targetable multisignal chemosensor for in vivo detection of hypochlorous acid. Biomaterials 68:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.07.052
Chen SM, Lu JX, Sun CD, Ma HM (2010) A highly specific ferrocene-based fluorescent probe for hypochlorous acid and its application to cell imaging. Analyst 135(3):577–582. https://doi.org/10.1039/b921187j
Cheng GH, Fan JL, Sun W, Cao JF, Hu C, Peng XJ (2014) A near-infrared fluorescent probe for selective detection of hclo based on se-sensitized aggregation of heptamethine cyanine dye. Chem Commun 50(8):1018–1020. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc47864e
Cheng S, Li A, Pan X, Wang H, Zhang C, Li J, Qi X (2021) A near-infrared fluorescent probe for highly specific and ultrasensitive detection of hypochlorite ions in living cells. Anal Bioanal Chem 413(17):4441–4450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03398-1
Fang FC (2004) Antimicrobial reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: concepts and controversies. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(10):820–832. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1004
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA, (2010) Gaussian 09, revision b.01
Gebicka L, Banasiak E (2012) Hypochlorous acid-induced heme damage of hemoglobin and its inhibition by flavonoids. Toxicol Vitr 26(6):924–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2012.04.010
Hu JJ, Ye S, Yang D (2017) Fluorescent probes for HOCl imaging. Isr J Chem 57(3–4):251–258. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201600113
Kenmoku S, Urano Y, Kojima H, Nagano T (2007) Development of a highly specific rhodamine-based fluorescence probe for hypochlorous acid and its application to real-time imaging of phagocytosis. J Am Chem Soc 129(23):7313–7318. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja068740g
Klebanoff SJ, Kettle AJ, Rosen H, Winterbourn CC, Nauseef WM (2013) Myeloperoxidase: a front-line defender against phagocytosed microorganisms. J Leukoc Biol 93(2):185–198. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0712349
Legault CY (2009) CYL view, 1.0b; Université de Sherbrooke: Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada
Li L, Wang X, Sun C, Xu T, Yang Z, Zhang Z, Meng X (2020) Design of a two-photon fluorescent probe for ratiometric imaging of endogenous hypochlorite in mitochondria. Dyes Pigments 181:108548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.108548
Lin WY, Long LL, Chen BB, Tan W (2009) A ratiometric fluorescent probe for hypochlorite based on a deoximation reaction. Chem Eur J 15(10):2305–2309. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200802054
Lou XD, Zhang Y, Li QQ, Qin JG, Li Z (2011) A highly specific rhodamine-based colorimetric probe for hypochlorites: a new sensing strategy and real application in tap water. Chem Commun 47(11):3189–3191. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cc04911e
Malle E, Buch T, Grone HJ (2003) Myeloperoxidase in kidney disease. Kidney Int 64(6):1956–1967. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00336.x
Nicholls SJ, Hazen SL (2005) Myeloperoxidase and cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(6):1102–1111. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000163262.83456.6d
Pattison DI, Davies MJ (2006) Reactions of myeloperoxidase-derived oxidants with biological substrates: gaining chemical insight into human inflammatory diseases. Curr Med Chem 13(27):3271–3290. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986706778773095
Prokopowicz ZM, Arce F, Biedron R, ChiangC LL, Ciszek M, Katz DR, Nowakowska M, Ztoczny S, Marcinkiewicz J, Chain BM (2010) Hypochlorous acid: anatural adjuvant that facilitates antigen processing, cross-priming, and the induction of adaptive immunity. J Immunol 184:824–835. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0902606
Setsukinai K, Urano Y, Kakinuma K, Majima HJ, Nagano T (2003) Development of novel fluorescence probes that can reliably detect reactive oxygen species and distinguish specific species. J Biol Chem 278(5):3170–3175. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M209264200
Sun ZN, Liu FQ, Chen Y, Tam PKH, Yang D (2008) A highly specific bodipy-based fluorescent probe for the detection of hypochlorous acid. Org Lett 10(11):2171–2174. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol800507m
Venkatesan P, Wu SP (2015) A turn-on fluorescent probe for hypochlorous acid based on the oxidation of diphenyl telluride. Analyst 140(4):1349–1355. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4an02116a
Wang TR, Zhang XF, Huang XQ, Cao XQ, Shen SL (2021) Rapid and selective visualization of mitochondrial hypochlorite by a red region water-soluble fluorescence probe. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 247(15):119115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.119115
Whiteman M, Rose P, Siau JL, Cheung NS, San Tan G, Halliwell B, Armstrong JS (2005) Hypochlorous acid-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 and human fetal liver cells: role of mitochondrial permeability transition. Free Radic Biol Med 38(12):1571–1584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.02.030
Winterbourn CC (2002) Biological reactivity and biomarkers of the neutrophil oxidant, hypochlorous acid. Toxicology 181:223–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00286-X
Xi LL, Guo XF, Wang CL, Wu WL, Huang MF, Miao JY, Zhao BX (2018) A near-infrared ratiometric fluorescent probe for rapid and selective detection of hypochlorous acid in aqueous solution and living cells. Sens Actuators B 255:666–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.073
Xu M, Kelley SP, Glass TE (2018) A multi-component sensor system for detection of amphiphilic compounds. Angew Chem Int Ed 57(39):12741–12744. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201807221
Yang YT, Whiteman M, Gieseg SP (2012) HOCl causes necrotic cell death in human monocyte derived macrophages through calcium dependent calpain activation. Biochim Et Biophys Acta BBA-Mol Cell Res 1823:420–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.09.019
Yang Y, Zhou T, Jin M, Zhou K, Liu D, Li X, Yin C (2019) Thiol-Chromene “Click” reaction triggered self-immolative for NIR visualization of thiol flux in physiology and pathology of living cells and mice. J Am Chem Soc 142(3):1614–1620. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b12629
Yue Y, Huo F, Yin C, Escobedo JO, Strongin RM (2016) Recent progress in chromogenic and fluorogenic chemosensors for hypochlorous acid. Analyst 141(6):1859–1873. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AN00158K
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Wang G, He Y (2014) Study on fluorescent switching of naphthopyran and pyrene-containing dyad and copolymer in solutions and films. Dyes Pigment 102:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2013.10.043
Zhang YR, Liu Y, Feng X, Zhao BX (2017) Recent progress in the development of fluorescent probes for the detection of hypochlorous acid. Sens Actuators b: Chem 240:18–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.066
Zhang L, Liu XA, Gillis KD, Glass TE (2019) A high-affinity fluorescent sensor for catecholamine: application to monitoring norepinephrine exocytosis. Angew Chem Int Ed 58(23):7611–7614. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201810919
Zhang W, Huo F, Yue Y, Zhang Y, Chao J, Cheng F, Yin C (2020) Heat stroke in cell tissues related to sulfur dioxide level is precisely monitored by light-controlled fluorescent probes. J Am Chem Soc 142(6):3262–3268. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13936
Zhong X, Yang Q, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Dai Z (2020) Aggregation-induced fluorescence probe for hypochlorite imaging in mitochondria of living cells and zebrafish. J Mater Chem B 8(33):7375–7381. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TB01496F
Zhu N, Guo X, Pang S, Chang Y, Liu X, Shi Z, Feng S (2020) Mitochondria-immobilized unimolecular fluorescent probe for multiplexing imaging of living cancer cells. Anal Chem 93(15):11103–11110. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c01213
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 22075040). The authors also acknowledge the supports from Jilin Provincial Department of Education.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, 22075040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, N., Zhou, X., Zhong, T. et al. A new pyrene-based “turn-on” fluorescent probe for highly selective detection of hypochlorite in aqueous solution and in living cells. Chem. Pap. 77, 197–205 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02475-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02475-8