Abstract
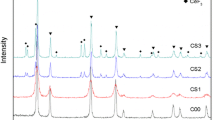
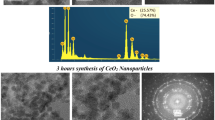
Cerium dioxide (CeO2) nanoparticles were synthesized by sol–gel-based hydrothermal method. During synthesis, cerium(III) chloride heptahydrate (CeCl3⋅7H2O) was used as cerium source; ammonia (NH3), tetraethylammonium hydroxide (C8H21NO), tetra-n-butyl ammonium hydroxide (C16H37NO), benzyl trimethyl ammonium hydroxide (C10H17NO) and benzyl triethyl ammonium hydroxide (C13H23NO) ionic liquids were used as catalyst, deionized water (H2O) was used as hydrolysis agent and solvent, and 2-aminopropanoic acid (C3H6NO2) was used as stabilizing agent. The nano-CeO2 particles were characterized by several techniques X-ray diffractometer (XRD), particle size analyzer, Branauer–Emmett–Teller analyzer (BET), ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometer (UV–Vis), transmission electron microscope (TEM). XRD characterization confirms that CeO2 crystals were analyzed as cubic fluorite structure. The full width at half maximum (FWHM) values referring to [111] lattice planes of CeO2 indicate a decrease in crystallinity associated with different bases used during synthesis of particles. Small sized crystals were formed in weak ionization degree and branched structures. As the crystallite size decreases, both agglomeration and the hydrodynamic diameter increases as expected. The size distribution of nano-CeO2 particles obtained by precipitation using different bases with a pH of 10 decreases from 25.92 to 20.57 nm. The size of nanoparticles prepared using ammonia at pH 9 and 8 are 15.60 and 9.50 nm, respectively. The most significant surface area change occurred in particles obtained using benzyl trimethyl ammonium hydroxide (BTMAH) and benzyl triethyl ammonium hydroxide (BTEAH). Such a significant reduction in surface area is believed to be due to the agglomeration or aggregation of particles with small crystallite size, resulting in smaller sized crystals as the alkyl group chain length and branching increase. These irregularities may result from the agglomeration and formation of large clusters observed by the TEM. The obtained CeO2 nanoparticles are crystalline and can readily be dispersed in water without any additional processing or surfactant agent. Well-defined strong absorbance peak located at 200–800 nm was observed for all samples. The bandgap increases with the decrease in particle size, meaning that smaller particles exhibit better UV absorption. The fact that the particles obtained in the presence of BTMAH and BTEAH cut off longer wavelength proved that it is due to lower bandgap energies.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhumaimess M, Aldosari O, Alshammari H, Kamel MM, Betiha MA, Hassan HMA (2019) Ionic liquid green synthesis of CeO2 nanorods and nano-cubes: investigation of the shape dependent on catalytic performance. J Mol Liq 279:649–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2019.02.014
Artiglia L, Van Bokhoven JA, Ghosalya MK, Li X, Beck A (2021) Size of ceria particles influences surface hydroxylation and hydroxyl stability. J Phys Chem C 125(17):9303–9309. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.JPCC.1C01718
Athawale AA, Bapat MS, Desai PA (2009) Hydroxide directed routes to synthesize nanosized cubic ceria (CeO2). J Alloy Compd 1–2(484):211–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2009.03.125
Bokare AD, Choi W (2014) Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes. J Hazard Mater 275:121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2014.04.054
Bumajdad A, Eastoe J, Mathew A (2009) Cerium oxide nanoparticles prepared in self-assembled systems. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 147–148(C):56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CIS.2008.10.004
Calvache-Muñoz J, Prado FA, Rodríguez-Páez JE (2017) Cerium oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and tentative mechanism of particle formation. Colloids Surf A 529:146–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2017.05.059
Chen HI, Chang HY (2005) Synthesis of nanocrystalline cerium oxide particles by the precipitation method. Ceram Int 31(6):795–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2004.09.006
Chowdhury S, Lin K-S (2011) Synthesis and characterization of 1D ceria nanomaterials for CO oxidation and steam reforming of methanol. J Nanomater 2011:16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/157690
Deshmukh R, Mehra A, Thaokar R (2017) Formation and shape-control of hierarchical cobalt nanostructures using quaternary ammonium salts in aqueous media. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 8(1):494–505. https://doi.org/10.3762/BJNANO.8.53
Duan X, Ma J, Lian J, Zheng W (2014) The art of using ionic liquids in the synthesis of inorganic nanomaterials. CrystEngComm 16(13):2550–2559. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE41203B
Fathi MH, Hanifi A (2013) Sol–gel derived nanostructure hydroxyapatite powder and coating: aging time optimisation. Adv Appl Ceram 108(6):363–368. https://doi.org/10.1179/174367609X414080
Gao X, Guo Q, Tang G, Zhu W, Yang X, Luo Y (2020) TBAOH assisted synthesis of ultrathin BiOCl nanosheets with enhanced charge separation efficiency for superior photocatalytic activity in carbamazepine degradation. J Colloid Interface Sci 570:242–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2020.02.065
Gao X, Gong C, Wang X, Zhu W, Luo Y (2021) Facile synthesis of cobalt doped BiOCl ultrathin nanosheets as superior photocatalyst for degradation of carbamazepine under visible light. J Solid State Chem 298:122131. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSSC.2021.122131
Gnanam S, Gajendiran J, Ramana Ramya J, Ramachandran K, Gokul Raj S (2021) Glycine-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of pure and europium doped CeO2 nanoparticles and their structural, optical, photoluminescence, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties. Chem Phys Lett 763:138217. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CPLETT.2020.138217
Greasley SL, Page SJ, Sirovica S, Chen S, Martin RA, Riveiro A, Hanna JV, Porter AE, Jones JR (2016) Controlling particle size in the Stöber process and incorporation of calcium. J Colloid Interface Sci 469:213–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2016.01.065
Gulicovski JJ, Braćko I, Milonjić SK (2014) Morphology and the isoelectric point of nanosized aqueous ceria sols. Mater Chem Phys 148(3):868–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2014.08.063
Gupta SK, Mao Y (2021) A review on molten salt synthesis of metal oxide nanomaterials: status, opportunity, and challenge. Prog Mater Sci 117:100734. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PMATSCI.2020.100734
Habib IY, Kumara NTRN, Lim CM, Mahadi AH (2018) Dynamic light scattering and zeta potential studies of ceria nanoparticles. Solid State Phenom 278:112–120. https://doi.org/10.4028/WWW.SCIENTIFIC.NET/SSP.278.112
Hu Z-X (2002) Sol–gel processing with inorganic metal salt precursors—Google Patents. https://patents.google.com/patent/US20020120016. Accessed 14 Mar 2022
Jyothi PSP, Anitha B, Smitha S, Vibitha BV, Krishna PGA, Tharayil NJ (2020) DNA-assisted synthesis of nanoceria, its size dependent structural and optical properties for optoelectronic applications. Bull Mater Sci 43(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12034-020-02102-W/FIGURES/7
Kalidindi S (2020) Effect of aging time on stiffness in acid catalyzed silica sol–gels. All theses. https://tigerprints.clemson.edu/all_theses/3470
Kanie K, Sasaki T, Nakaya M, Muramatsu A (2013) Quaternary ammonium hydroxide-assisted solvothermal synthesis of monodispersed ITO nanoparticles with a cubic shape. Chem Lett 42(7):738–740. https://doi.org/10.1246/CL.130263
Lee JS, Choi SC (2004) Crystallization behavior of nano-ceria powders by hydrothermal synthesis using a mixture of H2O2 and NH4OH. Mater Lett 58(3–4):390–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(03)00508-1
Liu IT, Hon MH, Teoh LG (2017) The synthesis, characterization and optical properties of nanocrystallined cerium dioxide by the hydrothermal method. Mater Trans 58(3):505–508. https://doi.org/10.2320/MATERTRANS.M2016285
Mohammadi MR, Fray DJ (2010) Nanostructured TiO2–CeO2 mixed oxides by an aqueous sol–gel process: effect of Ce:Ti molar ratio on physical and sensing properties. Sens Actuators, B Chem 150(2):631–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2010.08.029
Murata Y, Adachi M (2004) Formation of highly dispersed cerium oxide with cubic structure prepared by alkoxide-surfactant system. J Mater Sci 39(24):7397–7399. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000048760.33910.BD
Nadeem M, Khan R, Afridi K, Nadhman A, Ullah S, Faisal S, Mabood ZU, Hano C, Abbasi BH (2020) Green synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2 NPs) and their antimicrobial applications: a review. Int J Nanomed 15:5951. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S255784
Nadjia L, Abdelkader E, Naceur B, Ahmed B (2018) CeO2 nanoscale particles: synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity under UVA light irradiation. J Rare Earths 36(6):575–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JRE.2018.01.004
Novel method to control the size of well-crystalline ceria particles by hydrothermal method (2021) https://pdfslide.net/documents/novel-method-to-control-the-size-of-well-crystalline-ceria-particles-by-hydrothermal.html. 13 Sept 2021
Palard M, Balencie J, Maguer A, Hochepied JF (2010) Effect of hydrothermal ripening on the photoluminescence properties of pure and doped cerium oxide nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys 120(1):79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2009.10.025
Pandiyan N, Murugesan B, Sonamuthu J, Samayanan S, Mahalingam S (2019) [BMIM] PF6 ionic liquid mediated green synthesis of ceramic SrO/CeO2 nanostructure using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Ceram Int 45(9):12138–12148. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2019.03.116
Patuwan SZ, Arshad SE (2021) Important synthesis parameters affecting crystallization of zeolite T: a review. Materials (basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/MA14112890
Rezaei M, Mirkazemi SM, Alamolhoda S (2021) The role of PVA surfactant on magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel hydrothermal method. J Supercond Novel Magn 34(5):1397–1408. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10948-021-05830-0
Sahoo SK, Mohapatra M, Singh AK, Anand S (2010) Hydrothermal synthesis of single crystalline nano CeO2 and its structural, optical, and electronic characterization. Mater Manuf Process 25(9):982–989. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2010.480995
Saravanakumar K, Sathiyaseelan A, Mariadoss AVA, Wang MH (2021) Antioxidant and antidiabetic properties of biocompatible ceria oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles in mouse fibroblast NIH3T3 and insulin resistant HepG2 cells. Ceram Int 47(6):8618–8626. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2020.11.230
Tok AIY, Boey FYC, Dong Z, Sun XL (2007) Hydrothermal synthesis of CeO2 nano-particles. J Mater Process Technol 190(1–3):217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMATPROTEC.2007.02.042
Uekawa N (2020) Synthesis of defect and valence state tuned metal oxide nanoparticles with colloid chemical solution process: control of optical and electrical characteristics. Chem Lett 50(1):87–95. https://doi.org/10.1246/CL.200638
Wang C, Chen F, Tang Y, Chen X, Qian J, Chen Z (2018) Advanced visible-light photocatalytic property of biologically structured carbon/ceria hybrid multilayer membranes prepared by bamboo leaves. Ceram Int 44(6):5834–5841. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2017.11.027
Wu N-C, Shi E-W, Zheng Y-Q, Li W-J (2002) Effect of pH of medium on hydrothermal synthesis of nanocrystalline cerium(IV) oxide powders. J Am Ceram Soc 85(10):2462–2468. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1151-2916.2002.TB00481.X
Xu C, Qu X (2014) Cerium oxide nanoparticle: a remarkably versatile rare earth nanomaterial for biological applications. NPG Asia Mater 6(3):e90–e90. https://doi.org/10.1038/am.2013.88
Xu Y, Mofarah SS, Mehmood R, Cazorla C, Koshy P, Sorrell CC (2021) Design strategies for ceria nanomaterials: untangling key mechanistic concepts. Mater Horiz 8(1):102–123. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH00654H
Yu S-H, Cölfen H, Fischer A (2004) High quality CeO2 nanocrystals stabilized by a double hydrophilic block copolymer. Colloids Surf A 1–3(243):49–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2004.05.006
Yulizar Y, Kusrini E, Apriandanu DOB, Nurdini N (2020) Datura metel L. leaves extract mediated CeO2 nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterizations, and degradation activity of DPPH radical. Surf Interfaces 19:100437. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SURFIN.2020.100437
Zhang H, Dong Q, Shan P, Pan D, Fan B, Li R (2021) Manuscript for publication in Microporous and Mesoporous Materials synthesis of highly crystallized SSZ-13 with a small amount of organic structure-directing agent in the presence of seeds. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 324:1. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2021.111287
Zou H, Luan Y, Ge J, Wang Y, Zhuang G, Li R, Li Z (2011) Synthesis of ZnO particles on zinc foil in ionic-liquid precursors. CrystEngComm 13(7):2656–2660. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CE00788A
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Akdeniz University’s Scientific Research Project Coordination Unit for supporting this work with project number 2011.02.0121.030.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZYA contributed to investigation, methodology and writing—review editing. MA contributed to investigation and methodology. EA contributed to supervision and project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeşil Acar, Z., Asiltürk, M. & Arpaç, E. Preparation of ceria by combined sol–gel and hydrothermal method: insights from the effects of different bases on the particle size distribution. Chem. Pap. 76, 4927–4939 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02217-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02217-w