Abstract
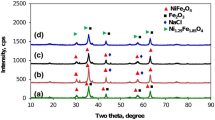
In this research, manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized using the sol-gel hydrothermal process through different hydrothermal durations and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) contents. The synthesized NPs were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) techniques. The effect of adding PVA as a surfactant and hydrothermal treatment duration on phase formation, microstructure, and magnetic properties of NPs have been discussed in this article. Rietveld-refined XRD patterns proved formation of magnetite and nonstoichiometric manganese ferrite phases along with MnFe2O4 in samples. The existence of a hematite phase was observed in samples prepared without PVA at the hydrothermal durations of 15 and 20 h, while adding PVA caused the hematite phase to disappear. FESEM images showed that adding PVA caused angular and coarser particles to form. The hysteresis loops of the samples confirmed the ferrimagnetic behavior of some samples while others presented superparamagnetic characteristics depending on their processing conditions. The saturation magnetization (Ms) and magnetic coercivity (Hc) values of NPs varied between 38 and 64 emu/g and 15–85 Oe, respectively. Addition of PVA with the average hydrothermal duration of 7.5 h provides the sample with the highest Ms (equal to 64 emu/g), which is mainly composed of MnFe2O4, Mn1.03Fe1.97O4, and Fe3O4. On the other hand, the sample P10 prepared with PVA addition at the hydrothermal treatment duration of 10 h presented the highest value of MnFe2O4 according to the Rietveld refinement results of XRD patterns performed by Maud program.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaudon, M., Pailhé, N., Wattiaux, A., Demourgues, A.: Structural defects in AFe2O4 (A= Zn, Mg) spinels. Mater. Res. Bull. 44(3), 479–484 (2009)
Kadam, R., Biradar, A., Mane, M., Shirsath, S.E.: Sol-gel auto-combustion synthesis of Li3xMnFe2− xO4 and their characterizations. J. Appl. Phys. 112(4), 043902 (2012)
Gorter, E.W.: Saturation magnetization and crystal chemistry of ferrimagnetic oxides. I. II. Theory of ferrimagnetism. Philips Res. Rep. 9(295-320), 321–365 (1954)
Lu, J., Ma, S., Sun, J., Xia, C., Liu, C., Wang, Z., Zhao, X., Gao, F., Gong, Q., Song, B.: Manganese ferrite nanoparticle micellar nanocomposites as MRI contrast agent for liver imaging. Biomaterials. 30(15), 2919–2928 (2009)
Arulmurugan, R., Jeyadevan, B., Vaidyanathan, G., Sendhilnathan, S.: Effect of zinc substitution on Co–Zn and Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 288, 470–477 (2005)
Hamdeh, H.H., Ho, J., Oliver, S., Willey, R., Oliveri, G., Busca, G.: Magnetic properties of partially-inverted zinc ferrite aerogel powders. J. Appl. Phys. 81(4), 1851–1857 (1997)
Musat, V., Potecasu, O., Belea, R., Alexandru, P.: Magnetic materials from co-precipitated ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 167(2), 85–90 (2010)
Haun, J.B., Yoon, T.J., Lee, H., Weissleder, R.: Magnetic nanoparticle biosensors. Wiley interdisciplinary reviews. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2(3), 291–304 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.84
Kumar, C.S., Mohammad, F.: Magnetic nanomaterials for hyperthermia-based therapy and controlled drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63(9), 789–808 (2011)
Sahoo, B., Devi, K.S.P., Dutta, S., Maiti, T.K., Pramanik, P., Dhara, D.: Biocompatible mesoporous silica-coated superparamagnetic manganese ferrite nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and MR imaging applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 431, 31–41 (2014)
Zipare, K., Dhumal, J., Bandgar, S., Mathe, V., Shahane, G.: Superparamagnetic manganese ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis and magnetic properties. J. Nanosci. Nanoeng. 1(3), 178–182 (2015)
Vignesh, R.H., Sankar, K.V., Amaresh, S., Lee, Y.S., Selvan, R.K.: Synthesis and characterization of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for impedometric ammonia gas sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 220, 50–58 (2015)
Rahmayeni, R., Oktavia, Y., Stiadi, Y., Arief, S., Zulhadjri, Z.: Spinel ferrite of MnFe2O4 synthesized in Piper betle Linn extract media and its application as photocatalysts and antibacterial. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 42, 1–10 (2020)
Makridis, A., Topouridou, K., Tziomaki, M., Sakellari, D., Simeonidis, K., Angelakeris, M., Yavropoulou, M.P., Yovos, J.G., Kalogirou, O.: In vitro application of Mn-ferrite nanoparticles as novel magnetic hyperthermia agents. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2(47), 8390–8398 (2014)
Patade, S.R., Andhare, D.D., Somvanshi, S.B., Jadhav, S.A., Khedkar, M.V., Jadhav, K.: Self-heating evaluation of superparamagnetic MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for magnetic fluid hyperthermia application towards cancer treatment. Ceram. Int. 46(16), 25576–25583 (2020)
Chandunika, R., Vijayaraghavan, R., Sahu, N.K.: Magnetic hyperthermia application of MnFe2O4 nanostructures processed through solvents with the varying boiling point. Mater. Res. Express. 7(6), 064002 (2020)
Majidi, S., Zeinali Sehrig, F., Farkhani, S.M., Soleymani Goloujeh, M., Akbarzadeh, A.: Current methods for synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Artif. Cells, Nanomed. Biotechnol. 44(2), 722–734 (2016)
Aghajanzadeh, M., Naderi, E., Zamani, M., Sharafi, A., Naseri, M., Danafar, H.: In vivo and in vitro biocompatibility study of MnFe2O4 and Cr2Fe6O12 as photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy and drug delivery of anti-cancer drugs. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 46(5), 846–851 (2020)
Wang, Z., Liu, J., Li, T., Liu, J., Wang, B.: Controlled synthesis of MnFe 2 O 4 nanoparticles and Gd complex-based nanocomposites as tunable and enhanced T 1/T 2-weighted MRI contrast agents. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2(29), 4748–4753 (2014)
Sharma, U.S., Sharma, R.N., Shah, R.: Physical and magnetic properties of manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 4(8), 14–17 (2014)
Augustin, M., Balu, T.: Synthesis and characterization of metal (Mn, Zn) ferrite magnetic nanoparticles. Mater. Today: Proc. 2(3), 923–927 (2015)
Deraz, N., Alarifi, A.: Controlled synthesis, physicochemical and magnetic properties of nano-crystalline Mn ferrite system. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7, 5534–5543 (2012)
Phumying, S., Labuayai, S., Swatsitang, E., Amornkitbamrung, V., Maensiri, S.: Nanocrystalline spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M= Ni, Co, Mn, Mg, Zn) powders prepared by a simple aloe vera plant-extracted solution hydrothermal route. Mater. Res. Bull. 48(6), 2060–2065 (2013)
Hashim, M., Shirsath, S.E., Meena, S., Mane, M., Kumar, S., Bhatt, P., Kumar, R., Prasad, N., Alla, S., Shah, J.: Manganese ferrite prepared using reverse micelle process: structural and magnetic properties characterization. J. Alloys Compd. 642, 70–77 (2015)
Gao, R.-R., Zhang, Y., Yu, W., Xiong, R., Shi, J.: Superparamagnetism and spin-glass like state for the MnFe2O4 nano-particles synthesized by the thermal decomposition method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(16), 2534–2538 (2012)
Bellusci, M., Aliotta, C., Fiorani, D., La Barbera, A., Padella, F., Peddis, D., Pilloni, M., Secci, D.: Manganese iron oxide superparamagnetic powder by mechanochemical processing. Nanoparticles functionalization and dispersion in a nanofluid. J. Nanopart. Res. 14(6), 1–11 (2012)
Aslibeiki, B., Kameli, P., Ehsani, M., Salamati, H., Muscas, G., Agostinelli, E., Foglietti, V., Casciardi, S., Peddis, D.: Solvothermal synthesis of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles: the role of polymer coating on morphology and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 399, 236–244 (2016)
Şimşek, T., Akansel, S., Özcan, Ş., Ceylan, A.: Synthesis of MnFe2O4 nanocrystals by wet-milling under atmospheric conditions. Ceram. Int. 40(6), 7953–7956 (2014)
Hou, X., Feng, J., Ren, Y., Fan, Z., Zhang, M.: Synthesis and adsorption properties of spongelike porous MnFe2O4. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 363(1-3), 1–7 (2010)
Goswami, P.P., Choudhury, H.A., Chakma, S., Moholkar, V.S.: Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52(50), 17848–17855 (2013)
Ibrahim, I., Ali, I.O., Salama, T.M., Bahgat, A., Mohamed, M.M.: Synthesis of magnetically recyclable spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M= Zn, Co, Mn) nanocrystals engineered by sol gel-hydrothermal technology: high catalytic performances for nitroarenes reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 181, 389–402 (2016)
Rajput, N.: Methods of preparation of nanoparticles-a review. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 7(6), 1806 (2015)
Scano, A., Ennas, G., Frongia, F., La Barbera, A., López-Quintela, M.A., Marongiu, G., Paschina, G., Peddis, D., Pilloni, M., Vázquez-Vázquez, C.: Mn–ferrite nanoparticles via reverse microemulsions: synthesis and characterization. J. Nanopart. Res. 13(7), 3063–3073 (2011)
Suryanarayana, C., Prabhu, B.: Synthesis of nanostructured materials by inert-gas condensation methods. In: Nanostructured Materials, pp. 47–90. Elsevier (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-081551534-0.50004-X
Grammatikopoulos, P., Steinhauer, S., Vernieres, J., Singh, V., Sowwan, M.: Nanoparticle design by gas-phase synthesis. Adv. Phys.: X. 1(1), 81–100 (2016)
Iles, G.N., Baker, S., Thornton, S., Binns, C.: Enhanced capability in a gas aggregation source for magnetic nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 105(2), 024306 (2009)
Oprea, B., Martínez, L., Román, E., Vanea, E., Simon, S., Huttel, Y.: Dispersion and functionalization of nanoparticles synthesized by gas aggregation source: opening new routes toward the fabrication of nanoparticles for biomedicine. Langmuir. 31(51), 13813–13820 (2015)
Moras, K., Schaarschuch, R., Riehemann, W., Zinoveva, S., Modrow, H., Eberbeck, D.: Production and characterisation of magnetic nanoparticles produced by laser evaporation for ferrofluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 293(1), 119–126 (2005)
Indira, T., Lakshmi, P.: Magnetic nanoparticles–a review. Int. J. Pharmaceut. Sci. Nanotechnol. 3(3), 1035–1042 (2010)
Islam, K., Haque, M., Kumar, A., Hoq, A., Hyder, F., Hoque, S.M.: Manganese ferrite nanoparticles (MnFe2O4): size dependence for hyperthermia and negative/positive contrast enhancement in MRI. Nanomaterials. 10(11), 2297 (2020)
Wu, W., He, Q., Jiang, C.: Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 3(11), 397–415 (2008)
Biehl, P., Von der Lühe, M., Dutz, S., Schacher, F.H.: Synthesis, characterization, and applications of magnetic nanoparticles featuring polyzwitterionic coatings. Polymers. 10(1), 91 (2018)
Rane, A.V., Kanny, K., Abitha, V., Thomas, S.: Methods for synthesis of nanoparticles and fabrication of nanocomposites. In: Synthesis of inorganic nanomaterials, pp. 121–139. Woodhead Publishing (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-101975-7.00005-1
Zhu, Y.-F., Du, R.-G., Chen, W., Qi, H.-Q., Lin, C.-J.: Photocathodic protection properties of three-dimensional titanate nanowire network films prepared by a combined sol–gel and hydrothermal method. Electrochem. Commun. 12(11), 1626–1629 (2010)
Suchanek, W.L., Riman, R.E.: Hydrothermal synthesis of advanced 668 ceramic powders. In: Advances in Science and Technology, vol. 45, pp. 184–193. Trans Tech Publications Ltd (2006). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AST.45.184
Boulos, M., Guillemet-Fritsch, S., Mathieu, F., Durand, B., Lebey, T., Bley, V.: Hydrothermal synthesis of nanosized BaTiO3 powders and dielectric properties of corresponding ceramics. Solid State Ionics. 176(13-14), 1301–1309 (2005)
Chen, Z., Zhan, G., Wu, Y., He, X., Lu, Z.: Sol–gel-hydrothermal synthesis and conductive properties of Al-doped ZnO nanopowders with controllable morphology. J. Alloys Compd. 587, 692–697 (2014)
Yu, H., Ouyang, S., Yan, S., Li, Z., Yu, T., Zou, Z.: Sol–gel hydrothermal synthesis of visible-light-driven Cr-doped SrTiO 3 for efficient hydrogen production. J. Mater. Chem. 21(30), 11347–11351 (2011)
Singhal, S., Namgyal, T., Singh, J., Chandra, K., Bansal, S.: A comparative study on the magnetic properties of MFe12O19 and MAlFe11O19 (M= Sr, Ba and Pb) hexaferrites with different morphologies. Ceram. Int. 37(6), 1833–1837 (2011)
Brunacci, N., Wischke, C., Naolou, T., Neffe, A.T., Lendlein, A.: Influence of surfactants on depsipeptide submicron particle formation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 116, 61–65 (2017)
Rao, J.P., Geckeler, K.E.: Polymer nanoparticles: preparation techniques and size-control parameters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 36(7), 887–913 (2011)
Cullity, B.D., John, W.: Weymouth: elements of X-ray diffraction. Am J Phys. 25(6), 394–395 (1957)
Jalalian, M., Mirkazemi, S., Alamolhoda, S.: The effect of poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) surfactant on phase formation and magnetic properties of hydrothermally synthesized CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 363–367 (2016)
Yao, L., Xi, Y., Xi, G., Feng, Y.: Synthesis of cobalt ferrite with enhanced magnetostriction properties by the sol− gel− hydrothermal route using spent Li-ion battery. J. Alloys Compd. 680, 73–79 (2016)
Yalçın, O., Bayrakdar, H., Özüm, S.: Spin-flop transition, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of α-Fe2O4 spinel type ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 343, 157–162 (2013)
Barakat, N.A., Park, S.J., Khil, M.S., Kim, H.Y.: Preparation of MnO nanofibers by novel hydrothermal treatment of manganese acetate/PVA electrospun nanofiber mats. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 162(3), 205–208 (2009)
Angermann, A., Töpfer, J., Da Silva, K., Becker, K.: Nanocrystalline Mn–Zn ferrites from mixed oxalates: synthesis, stability and magnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 508(2), 433–439 (2010)
Hsiang, H.-I., Tsai, J.-Y.: Titanate coupling agent effects on nonaqueous Co 2 Z ferrite suspensions dispersion. J. Mater. Sci. 41(19), 6339–6346 (2006)
Rak Z.S.: From nanosize powders to a diesel soot converter. In: Baraton M.I., Uvarova I. (eds) Functional gradient materials and surface layers prepared by fine particles technology. NATO Science Series (Series II: Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry), vol 16. Springer, Dordrecht (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0702-3_9
Jun, Y.W., Choi, J.S., Cheon, J.: Shape control of semiconductor and metal oxide nanocrystals through nonhydrolytic colloidal routes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45(21), 3414–3439 (2006)
Shi, R., Gao, G., Yi, R., Zhou, K., Qiu, G., Liu, X.: Controlled synthesis and characterization of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Chin. J. Chem. 27(4), 739–744 (2009)
Dixit, S.G., Mahadeshwar, A.R., Haram, S.K.: Some aspects of the role of surfactants in the formation of nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 133(1-2), 69–75 (1998)
Özgür, Ü., Alivov, Y., Morkoç, H.: Microwave ferrites, part 1: fundamental properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 20(9), 789–834 (2009)
Li, J., Yuan, H., Li, G., Liu, Y., Leng, J.: Cation distribution dependence of magnetic properties of sol–gel prepared MnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322(21), 3396–3400 (2010)
Mosivand, S., Monzon, L., Kazeminezhad, I., Coey, J.M.D.: Influence of growth conditions on magnetite nanoparticles electro-crystallized in the presence of organic molecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14(5), 10383–10396 (2013)
Mohammed, E., Malini, K., Kurian, P., Anantharaman, M.: Modification of dielectric and mechanical properties of rubber ferrite composites containing manganese zinc ferrite. Mater. Res. Bull. 37(4), 753–768 (2002)
Mostafa, N.Y., Zaki, Z., Heiba, Z.: Structural and magnetic properties of cadmium substituted manganese ferrites prepared by hydrothermal route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 329, 71–76 (2013)
Hochepied, J., Pileni, M.: Magnetic properties of mixed cobalt–zinc ferrite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 87(5), 2472–2478 (2000)
Kumar, L., Kumar, P., Kar, M.: Cation distribution by Rietveld technique and magnetocrystalline anisotropy of Zn substituted nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 551, 72–81 (2013)
Mostafa, N.Y., Hessien, M., Shaltout, A.A.: Hydrothermal synthesis and characterizations of Ti substituted Mn-ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 529, 29–33 (2012)
Bolarín-Miró, A.M., Vera-Serna, P., Sánchez-De Jesús, F., Cortés-Escobedo, C.A., Martínez-Luevanos, A.: Mechanosynthesis and magnetic characterization of nanocrystalline manganese ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 22(8), 1046–1052 (2011)
Pourbafarani, S., Mozaffari, M., Amighian, J.: Investigation of phase formation and magnetic properties of Mn ferrite nanoparticles prepared via low-power ultrasonic assisted co-precipitation method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 26(3), 675–678 (2013)
Zhang, Y., Nan, Z.: Modified magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 by CTAB with coprecipitation method. Mater. Lett. 149, 22–24 (2015)
Šepelák, V., Bergmann, I., Menzel, D., Feldhoff, A., Heitjans, P., Litterst, F., Becker, K.: Magnetization enhancement in nanosized MgFe2O4 prepared by mechanosynthesis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316(2), e764–e767 (2007)
Chlan, Vaojtěch.: Hyperfine Interactions in Ferrites with spinel structure. Praha, 2013. Rigorózní práce. Univerzita Karlova, Matematicko-fyzikální fakulta, Katedra fyziky kondenzovaných látek. http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11956/60890. Accessed October 11 2020
Lin, C.-S., Hwang, C.-C., Huang, T.-H., Wang, G.-P., Peng, C.-H.: Fine powders of SrFe12O19 with SrTiO3 additive prepared via a quasi-dry combustion synthesis route. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 139(1), 24–36 (2007)
Gubbala, S., Nathani, H., Koizol, K., Misra, R.: Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn, Zn–Mn, and Ni–Mn ferrites synthesized by reverse micelle technique. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 348(1-4), 317–328 (2004)
Victory, M., Pant, R., Phanjoubam, S.: Synthesis and characterization of oleic acid coated Fe–Mn ferrite based ferrofluid. Mater. Chem. Phys. 240, 122210 (2020)
Son, S., Swaminathan, R., McHenry, M.: Structure and magnetic properties of rf thermally plasma synthesized Mn and Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 93(10), 7495–7497 (2003)
Kanitz, A., Hoppius, J.S., del Mar Sanz, M., Maicas, M., Ostendorf, A., Gurevich, E.L.: Synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles by ultrashort pulsed laser ablation of iron in different liquids. ChemPhysChem. 18(9), 1155–1164 (2017)
Vijayakumar, R., Koltypin, Y., Felner, I., Gedanken, A.: Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of pure nanometer-sized Fe3O4 particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 286(1), 101–105 (2000)
Yetim, N.K., Baysak, F.K.U., Koç, M.M., Nartop, D.: Characterization of magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles with fluorescent properties for potential multipurpose imaging and theranostic applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 18278–18288 (2020)
Yetim, N.K., Aslan, N., Koç, M.M.: Structural and catalytic properties of Fe3O4 doped Bi2S3 novel magnetic nanocomposites: p-nitrophenol case. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8(5), 104258 (2020)
Kavousi, F., Goodarzi, M., Ghanbari, D., Hedayati, K.: Synthesis and characterization of a magnetic polymer nanocomposite for the release of metoprolol and aspirin. J. Mol. Struct. 1183, 324–330 (2019)
Tumturk, H., Sahin, F., Turan, E.: Magnetic nanoparticles coated with different shells for biorecognition: high specific binding capacity. Analyst. 139(5), 1093–1100 (2014)
Hedayati, K., Goodarzi, M., Kord, M.: Green and facile synthesis of Fe3O4-PbS magnetic nanocomposites applicable for the degradation of toxic organic dyes. Main Group Metal Chem. 39(5-6), 183–194 (2016)
Lwin, N., Fauzi, M.A., Sreekantan, S., Othman, R.: Physical and electromagnetic properties of nanosized Gd substituted Mg–Mn ferrites by solution combustion method. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 461, 134–139 (2015)
Ceylan, A., Ozcan, S., Ni, C., Shah, S.I.: Solid state reaction synthesis of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320(6), 857–863 (2008)
Nawale, A.B., Kanhe, N.S., Patil, K., Bhoraskar, S., Mathe, V., Das, A.: Magnetic properties of thermal plasma synthesized nanocrystalline nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4). J. Alloys Compd. 509(12), 4404–4413 (2011)
Jacintha, A.M., Umapathy, V., Neeraja, P., Rajkumar, S.R.J.: Synthesis and comparative studies of MnFe 2 O 4 nanoparticles with different natural polymers by sol–gel method: structural, morphological, optical, magnetic, catalytic and biological activities. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 7(4), 375–387 (2017)
Amighian, J., Mozaffari, M., Nasr, B.: Preparation of nano-sized manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) via coprecipitation method. Phys. Status Solidi C. 3(9), 3188–3192 (2006)
Aslibeiki, B., Kameli, P., Ehsani, M.: MnFe2O4 bulk, nanoparticles and film: a comparative study of structural and magnetic properties. Ceram. Int. 42(11), 12789–12795 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaei, M., Mirkazemi, S.M. & Alamolhoda, S. The Role of PVA Surfactant on Magnetic Properties of MnFe2O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Sol-Gel Hydrothermal Method. J Supercond Nov Magn 34, 1397–1408 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05830-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05830-0