Abstract
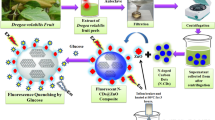
Green-fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots (g-CQDs) were synthesized via a simple and convenient one-step hydrothermal method using Passiflora edulis sims shell as a carbon source and m-phenylenediamine as a nitrogen source and applied to the detection of uric acid. Unlike most reported blue fluorescent probes, the obtained g-CQDs showed bright-green fluorescence under ultraviolet light with a high quantum yield of 37.6%. Moreover, the g-CQDs exhibit outstanding photostability and high sensitivity, an excellent linearity ranging from 1 to 17 µM, and a great limit of detection of 0.94 µM, which renders them suitable for the determination of uric acid in human urine with remarkable selectivity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeosun WA, Asiri AM, Marwani HM, Rahman MM (2020) Enzymeless electrocatalytic detection of uric acid using polydopamine/polypyrrole copolymeric film. ChemistrySelect 5:156–164. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201903628
Amjadi M, Hallaj T, Kouhi Z (2018) An enzyme-free fluorescent probe based on carbon dots—MnO2 nanosheets for determination of uric acid. J Photochem Photobiol A-Chem 356:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.02.002
Azmi NE, Ramli NI, Abdullah J, Hamid MAA, Sidek H, Abd Rahman S, Ariffin N, Yusof NA (2015) A simple and sensitive fluorescence based biosensor for the determination of uric acid using H2O2-sensitive quantum dots/dual enzymes. Biosens Bioelectron 67:129–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.07.056
Basu A, Suryawanshi A, Kumawat B, Dandia A, Guin D, Ogale SB (2015) Starch (Tapioca) to carbon dots: an efficient green approach to an on-off-on photoluminescence probe for fluoride ion sensing. Analyst 140:1837–1841. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4an02340d
Bortolotti M, Polito L, Battelli MG, Bolognesi A (2021) Xanthine oxidoreductase: one enzyme for multiple physiological tasks. Redox Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.101882
Brouwer AM (2011) Standards for photoluminescence quantum yield measurements in solution (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl Chem 83:2213–2228. https://doi.org/10.1351/PAC-REP-10-09-31
Dineshkumar R, Devikala S (2021) Facile synthesis of fluorescent carbon quantum dots from Betel leafs (Piper betle) for Fe3+ sensing. Mater Today-Proc 34:488–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.096
Durai L, Kong CY, Badhulika S (2020) One-step solvothermal synthesis of nanoflake-nanorod WS2 hybrid for non-enzymatic detection of uric acid and quercetin in blood serum. Mater Sci Eng C 107:110217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110217
Hagiwara K, Horikoshi S, Serpone N (2021) Luminescent monodispersed carbon quantum dots by a microwave solvothermal method toward bioimaging applications. J Photochem Photobiol A 415:113310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2021.113310
Hoan BT, Huan PV, Van HN, Nguyen DH, Tam PD, Nguyen KT, Pham VH (2018) Luminescence of lemon-derived carbon quantum dot and its potential application in luminescent probe for detection of Mo6+ ions. Luminescence 33:545–551. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3444
Jiang K, Sun S, Zhang L, Wang Y, Cai C, Lin H (2015) Bright-yellow-emissive N-doped carbon dots: preparation, cellular imaging, and bifunctional sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:23231–23238. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b07255
Jiang L, Wang L, Zhan D-S, Jiang W-R, Fodjo EK, Hafez ME, Zhang Y-M, Zhao H, Qian R-C, Li D-W (2021) Electrochemically renewable SERS sensor: a new platform for the detection of metabolites involved in peroxide production. Biosens Bioelectron. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112918
Jiao Y, Xing Y, Li K, Li Z, Zhao G (2021) Enzyme-coupled fluorescence sensor for sensitive determination of uric acid and uricase inhibitor. Luminescence. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3919Ahead
Jin D, Seo M-H, Bui The H, Quoc-Thai P, Conte ML, Thangadurai D, Lee Y-I (2016) Quantitative determination of uric acid using CdTe nanoparticles as fluorescence probes. Biosens Bioelectron 77:359–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.09.057
Kalaiyarasan G, Hemlata C, Joseph J (2019) Fluorescence turn-on, specific detection of cystine in human blood plasma and urine samples by nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots. ACS Omega 4:1007–1014. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b03187
Li DY, Wang SP, Azad F, Su SC (2020a) Single-step synthesis of polychromatic carbon quantum dots for macroscopic detection of Hg2+. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110141
Li W, Huang S, Wen H, Luo Y, Cheng J, Jia Z, Han P, Xue W (2020b) Fluorescent recognition and selective detection of nitrite ions with carbon quantum dots. Anal Bioanal Chem 412:993–1002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02325-9
Li F, He TS, Wu SH, Peng ZJ, Qiu P, Tang XM (2021) Visual and colorimetric detection of uric acid in human serum and urine using chitosan stabilized gold nanoparticles. Microchem J 164:7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.105987
Liang C, Lan Y, Sun Z, Zhou L, Li Y, Liang X, Qin X (2020) Synthesis of carbon quantum dots with iron and nitrogen fromPassiflora edulisand their peroxidase-mimicking activity for colorimetric determination of uric acid. Microchim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04391-8
Lu Q, Deng J, Hou Y, Wang H, Li H, Zhang Y (2015) One-step electrochemical synthesis of ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets and their application to the detection of uric acid. Chem Commun 51:12251–12253. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc04231c
Lu H-F, Li J-Y, Zhang M-M, Wu D, Zhang Q-L (2017) A highly selective and sensitive colorimetric uric acid biosensor based on Cu(II)-catalyzed oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine. Sens Actuators B Chem 244:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.12.127
Luo PJG, Sahu S, Yang ST, Sonkar SK, Wang JP, Wang HF, LeCroy GE, Cao L, Sun YP (2013) Carbon “quantum” dots for optical bioimaging. J Mater Chem B 1:2116–2127. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb00018d
Matai I, Sachdev A, Gopinath P (2015) Self-assembled hybrids of fluorescent carbon dots and PAMAM dendrimers for epirubicin delivery and intracellular imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:11423–11435. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b02095
Papavasileiou MV, Karamanou AG, Kalogeropoulos P, Moustakas G, Patsianis S, Pittaras A (2016) Uric acid blood levels and relationship with the components of metabolic syndrome in hypertensive patients. J Hum Hypertens 30:414–417. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2015.53
Perez-Ruiz F, Calabozo M, Erauskin GG, Ruibal A, Herrero-Beites AM (2002) Renal underexcretion of uric acid is present in patients with apparent high urinary uric acid output. Arthritis Rheum-Arthritis Care Res 47:610–613. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.10792
Prathumsuwan T, Jaiyong P, In I, Paoprasert P (2019) Label-free carbon dots from water hyacinth leaves as a highly fluorescent probe for selective and sensitive detection of borax. Sensors Actuators B-Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126936
Rao LS, Tang Y, Li ZT, Ding XR, Liang GW, Lu HG, Yan CM, Tang KR, Yu BH (2017) Efficient synthesis of highly fluorescent carbon dots by microreactor method and their application in Fe3+ ion detection. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biolog Appl 81:213–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.07.046
Sahatiya P, Jones SS, Badhulika S (2018) 2D MoS2-carbon quantum dot hybrid based large area, flexible UV-vis-NIR photodetector on paper substrate. Appl Mater Today 10:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2017.12.013
Shen T-Y, Jia P-Y, Chen D-S, Wang L-N (2021) Hydrothermal synthesis of N-doped carbon quantum dots and their application in ion-detection and cell-imaging. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 248:119282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.119282
Tafreshi FA, Fatahi Z, Ghasemi SF, Taherian A, Esfandiari N (2020) Ultrasensitive fluorescent detection of pesticides in real sample by using green carbon dots. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230646
Vandarkuzhali SAA, Jeyalakshmi V, Sivaraman G, Singaravadivel S, Krishnamurthy KR, Viswanathan B (2017) Highly fluorescent carbon dots from Pseudo-stem of banana plant: applications as nanosensor and bio-imaging agents. Sensors Actuators B-Chem 252:894–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.06.088
Vlassa M, Filip M, Dragomir C (2021) Simultaneous quantifications of four purine derivatives biomarkers in cow milk by SPE HPLC-DAD. Czech J Food Sci 39:122–130. https://doi.org/10.17221/297/2020-cjfs
Wan Y, Wang M, Zhang K, Fu Q, Gao M, Wang L, Xia Z, Gao D (2019) Facile and green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from the flowers of Abelmoschus manihot (Linn.) Medicus for sensitive detection of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol and cellular imaging. Microchem J 148:385–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.05.026
Wang H, Lu Q, Hou Y, Liu Y, Zhang Y (2016) High fluorescence S, N co-doped carbon dots as an ultra-sensitive fluorescent probe for the determination of uric acid. Talanta 155:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.04.020
Wang M, Liu Y, Ren G, Wang W, Wu S, Shen J (2018) Bioinspired carbon quantum dots for sensitive fluorescent detection of vitamin B12 in cell system. Anal Chim Acta 1032:154–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.05.057
Wang X, Yao Q, Tang X, Zhong H, Qiu P, Wang X (2019) A highly selective and sensitive colorimetric detection of uric acid in human serum based on MoS2-catalyzed oxidation TMB. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:943–952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1524-6
Wang C, Xu J, Li H, Zhao W (2020) Tunable multicolour S/N co-doped carbon quantum dots synthesized from waste foam and application to detection of Cr3+ ions. Luminescence 35:1373–1383. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3901
Wang X, Duan Q, Zhang B, Cheng X, Wang S, Sang S (2021) Ratiometric fluorescence detection of Cd2+based on N, S co-doped carbon quantum dots/Au nanoclusters. Microchem J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106269
Xin XL, Zhang MH, Zhao JW, Han CY, Liu XP, Xiao ZY, Zhang LL, Xu B, Guo WY, Wang RM, Sun DF (2017) Fluorescence turn-on detection of uric acid by a water-stable metal-organic nanotube with high selectivity and sensitivity. J Mater Chem C 5:601–606. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tc05034d
Xu XY, Ray R, Gu YL, Ploehn HJ, Gearheart L, Raker K, Scrivens WA (2004) Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J Am Chem Soc 126:12736–12737. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja040082h
Xu H, Yang X, Li G, Zhao C, Liao X (2015) Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots for selective detection of tartrazine in food samples. J Agric Food Chem 63:6707–6714. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02319
Xue ZP, Gao H, Li XL (2018) A Green and lower-temperature synthesis of two-color fluorescent nitrogen dopedgraphene quantum dots. Dyes Pigm 156:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2018.04.032
Yang YX, Huo DQ, Wu HX, Wang XF, Yang JS, Bian MH, Ma Y, Hou CJ (2018a) N, P-doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for carbendazim detection based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Sensors Actuators B-Chem 274:296–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.07.130
Yang WN, Zhang H, Lai JX, Peng XY, Hu YP, Gu W, Ye L (2018b) Carbon dots with red-shifted photoluminescence by fluorine doping for optical bio-imaging. Carbon 128:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.11.069
Yu C, Qin D, Jiang X, Zheng X, Deng B (2021) Facile synthesis of bright yellow fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots and their applications to an off-on probe for highly sensitive detection of methimazole. Microchem J 168:106480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106480
Yuan C, Qin X, Xu Y, Shi R, Cheng S, Wang Y (2021) Dual-signal uric acid sensing based on carbon quantum dots and o-phenylenediamine. Spectrochim Acta Part A-Mol Biomol Spectrosc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.119678
Zhang S-R, Cai S-K, Wang G-Q, Cui J-Z, Gao C-Z (2021) One-step synthesis of N, P-doped carbon quantum dots for selective and sensitive detection of Fe2+ and Fe3+ and scale inhibition. J Mol Struct 1246:131173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.131173
Zhao J (2013) A simple, rapid and reliable high performance liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous determination of creatinine and uric acid in plasma and urine. Anal Methods 5:6781–6787. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ay41061g
Zhao M, Zhou MF, Feng H, Cong XX, Wang XL (2016) Determination of tryptophan, glutathione, and uric acid in human whole blood extract by capillary electrophoresis with a one-step electrochemically reduced graphene oxide modified microelectrode. Chromatographia 79:911–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-016-3115-z
Zhao C, Jiao Y, Hu F, Yang Y (2018) Green synthesis of carbon dots from pork and application as nanosensors for uric acid detection. Spectrochim Acta Part A-Mol Biomol Spectrosc 190:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.09.037
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Opening project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Calcium Carbonate Resources Comprehensive Utilization No. HZXYKFKT201907.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, GW., Lan, Yw., Peng, Yq. et al. Carbon quantum dots with green fluorescence as a probe for detecting uric acid. Chem. Pap. 76, 3627–3638 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02071-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02071-w