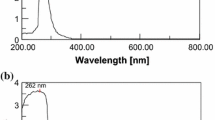
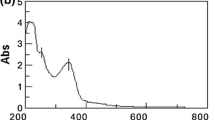
Abstract
The use of surfactants to enhance the efficacy of most conventional drugs is the recent progress of pharmacology. The rationale of this research is to design and develop surfactant incorporated drugs to overcome the challenges of antibiotic resistance. Herein, we report the synthesis of a novel surfactant-based Schiff base ligand (DDAP2C) from dodecylamine (DDA) and pyrrole-2-carboxaldehyde (P2C) and its two metal complexes, Ni-DDAP2C and Zn-DDAP2C. Characterization was performed by spectroscopic techniques such as 1H and 13CNMR, electronic absorption spectral study, FT-IR, and ESI-mass spectrometry. They were further characterized by elemental microanalysis, powder X-ray diffraction, SEM-EDAX, and TGA/DTA analyses to obtain significant structural information. The conductance study revealed non-electrolytic nature. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) of the synthesized compounds was calculated using conductivity data. We extended our study to derive various surface properties and thermodynamic parameters from the CMC calculations. The popular Coats–Redfern equation was used to compute the kinetic and thermodynamic properties. Powder X-ray diffraction was performed to determine the crystallinity, crystallite size, microstrain, and dislocation density of the crystals. Geometry optimization was performed by running the MM2 job in CsChemOffice Ultra 16 programs and ArgusLab 4.0.1 version software. The antibacterial potency of the ligand and metal complexes was demonstrated by the standard Kirby–Bauer paper disk diffusion technique for E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, Enterococci, and S. aureus bacteria. Their actual potency against all pathogens was further assessed quantitatively by evaluating the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) tests and revealed a significant bacterial growth inhibition.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data are included in the manuscript and are available for the readers.
References
Abdou SN, Faheim AA, Alaghaz MA, A-N, (2013) Synthesis, spectral characterization, cyclic voltammetry, molecular modeling and catalytic activity of Sulfa-drug divalent metal complexes. Curr Synth Syst Biol 02:112. https://doi.org/10.4172/2332-0737.1000112
Abdul Rub M (2019) Aggregation and interfacial phenomenon of amphiphilic drug under the influence of pharmaceutical excipients (green/biocompatible gemini surfactant). PLoS ONE 14:1. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211077
Ahmad N, Anouar EH, Tajuddin AM et al (2020) Synthesis, characterization, quantum chemical calculations and anticancer activity of a Schiff base NNOO chelate ligand and Pd(II) complex. PLoS ONE 1:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231147
Al-Radadi NS, Zayed EM, Mohamed GG, Abd El Salam HA (2020) Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, molecular docking, and evaluation of antibacterial potential of transition metal complexes obtained using triazole chelating ligand. J Chem 2020:1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1548641
Al Zoubi W, Al-Hamdani AAS, Ahmed SD, Ko YG (2017) A new azo-Schiff base: Synthesis, characterization, biological activity and theoretical studies of its complexes. Appl Organomet Chem 1:3895. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.3895
Almarhoon ZM, Al-Onazi WA, Alothman AA et al (2019) Synthesis, DNA binding, and molecular docking studies of dimethylaminobenzaldehyde-based bioactive Schiff bases. J Chem 2019:1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8152721
Alturiqi AS, Alaghaz ANMA, Ammar RA, Zayed ME (2018) Synthesis, spectral characterization, and thermal and cytotoxicity studies of Cr(III), Ru(III), Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) complexes of Schiff base derived from 5-hydroxymethylfuran-2-carbaldehyde. J Chem 2018:1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5816906
Alwadani N, Fatehi P (2018) Synthetic and lignin-based surfactants: challenges and opportunities. Carbon Resour Convers 1:126–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crcon.2018.07.006
Aly SA, Fathalla SK (2020) Preparation, characterization of some transition metal complexes of hydrazone derivatives and their antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Arab J Chem 13:3735–3750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2019.12.003
Ambika S, Manojkumar Y, Arunachalam S et al (2019) Biomolecular Interaction, anti-cancer and anti-angiogenic properties of cobalt(III) Schiff base complexes. Sci Rep 9:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39179-1
Anestopoulos I, Kiousi DE, Klavaris A et al (2020) Surface active agents and their health-promoting properties: molecules of multifunctional significance. Pharmaceutics 12:1–35. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070688
Anila BN, Nair MKM, Sreedharan J, Sylas VP (2017) Synthesis, characterization, molecular modeling, antimicrobial and DNA binding studies of cobalt(II) complexes of 2, 3-(Diimino-4’-antipyrinyl)butane with varying counter ions. Asian J Chem 29:1757–1760. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2017.20344
Attwood D (1983) Biological implications of surfactant presence in formulations 7.1
Badawi EA, Abdel-Rahman MA, Mostafa A, Abdel-Rahman M (2019) Determination of the crystallite size & micro-strain by novel method from XRD profile. Appl Phys 2:1–15. https://doi.org/10.31058/j.ap.2019.21001
Baecker D, Sesli Ö, Knabl L et al (2021) Investigating the antibacterial activity of salen/salophene metal complexes: Induction of ferroptosis as part of the mode of action. Eur J Med Chem 209:112907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112907
Barbosa HFG, Attjioui M, Paula A, et al (2017) Synthesis, characterization and biological activities of biopolymeric Schiff bases prepared with chitosan and salicylaldehydes and their Pd(II) and Pt(II) complexes. molecules 22:1. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111987
Bhattarai A, Pathak K, Dev B (2017) Cationic and anionic surfactants interaction in water and methanol-water mixed solvent media. J Mol Liq 229:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.12.021
Bhowon MG, Li Kam Wah H, Dosieah A et al (2004) Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic activity of metal Schiff base complexes derived from pyrrole-2-carboxaldehyde. Synth React Inorg Met Chem 34:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1081/SIM-120027314
Bouzerafa B, Aggoun D, Ouennoughi Y et al (2017) Synthesis, spectral characterization and study of thermal behavior kinetics by thermogravimetric analysis of metal complexes derived from salicylaldehyde and alkylamine. J Mol Struct 1142:48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.04.029
Brown P, Bushmelev A, Butts CP et al (2013) Properties of new magnetic surfactants. Langmuir 29:3246–3251. https://doi.org/10.1021/la400113r|
Buldurun K, Turan N, Savcı A, Çolak N (2019) Synthesis, structural characterization and biological activities of metal(II) complexes with Schiff bases derived from 5-bromosalicylaldehyde: Ru(II) complexes transfer hydrogenation. J Saudi Chem Soc 23:205–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2018.06.002
Canpolat E, Kaya M (2005) Studies on mononuclear chelates derived from substituted Schiff-base ligands: Synthesis and characterization of a new 5-bromosalicyliden-p- aminoacetophenoneoxime and its complexes with Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II). Russ J Coord Chem 31:790–794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11173-005-0170-7
Chandar SCN, Santhakumar K, Arumugham MN (2009) Metallosurfactant Schiff base cobalt(III) coordination complexes. Synthesis, characterization, determination of CMC values and biological activities. Transit Met Chem 34:841–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-009-9272-2
Chaudhary NK, Mishra P (2018) Bioactivity of some divalent M(II) complexes of penicillin-based Schiff base ligand: synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, and thermal study. J Saudi Chem Soc 22:601–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2017.10.003
Chaudhary NK, Guragain B (2019) Synthesis, thermal characterization and in vitro antibacterial assessment of Co(II) and Cd(II) Complexes of Schiff base derived from amoxicillin and thiophene-2-carbaldehyde. Asian J Chem 31:1. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2019.21882
Chaudhary NK, Guragain B, Chaudhary A, Chaudhary SK (2021) Heteroleptic cadmium complex of glimepiride–metformin mixed ligand: synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial study. Chem Pap 75:3215–3226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01535-9
Coats A, Redfern JP (1963) Thermogravimetric analysis. Analyst 88:1
Danish M, Raza MA, Khalid H et al (2020) New metal complexes of sulfonamide: synthesis, characterization, in-vitro anticancer, anticholinesterase, antioxidant, and antibacterial studies. Appl Organomet Chem 35:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.6033
de Araújo EL, Barbosa HFG, Dockal ER, Cavalheiro ÉTG (2017) Synthesis, characterization, and biological activity of Cu(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II) complexes of biopolymeric Schiff bases of salicylaldehydes and chitosan. Int J Biol Macromol 95:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.109
Donner A, Trepka B, Theiss S et al (2019) NHC-Metallosurfactants as active polymerization catalysts. Langmuir 35:16514–16520. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b02152
El-Samanody ESA, AbouEl-Enein SA, Emara EM (2018) Molecular modeling, spectral investigation and thermal studies of the new asymmetric Schiff base ligand; (E)-N’-(1-(4-((E)-2-hydroxybenzylideneamino)phenyl)ethylidene)morpholine-4-carbothiohydrazide and its metal complexes: Evaluation of their antibacterial. Appl Organomet Chem 32:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4262
Fekri R, Salehi M, Asadi A, Kubicki M (2019) Synthesis, characterization, anticancer and antibacterial evaluation of Schiff base ligands derived from hydrazone and their transition metal complexes. Inorganica Chim Acta 484:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2018.09.022
Gaber M, Khedr AM, Elsharkawy M (2017) Characterization and thermal studies of nano-synthesized Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) complexes with adipohydrazone ligand as new promising antimicrobial and antitumor agents. Appl Organomet Chem e3885. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.3885
Gaber M, El-Wakiel N, El-Baradie K, Hafez S (2019) Chromone Schiff base complexes: synthesis, structural elucidation, molecular modeling, antitumor, antimicrobial, and DNA studies of Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) complexes. J Iran Chem Soc 16:169–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-018-1494-9
Garg P, Kaur G, Chaudhary GR (2016) Transition metal based single chained surfactants: Synthesis, aggregation behavior and enhanced photoluminescence properties of fluorescein. RSC Adv 6:108573–108582. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra21811c
Gherras H, Yahiaoui A, Hachemaoui A et al (2018) Synthesis and characterization of poly (2,5-diyl pyrrole-2-pyrrolyl methine) semiconductor copolymer. J Semicond 39:1. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-4926/39/10/102001
Gupta B, Kumari A, Belwal S et al (2020) Synthesis, characterization of platinum(II) complexes of Schiff base ligands and evaluation of cytotoxic activity of platinum nanoparticles. Inorg Nano-Metal Chem 1:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2020.1728552
Halawa AH, El-Gilil SMA, Bedair AH et al (2017) Synthesis, biological activity and molecular modeling study of new Schiff bases incorporated with indole moiety. Zeitschrift Fur Naturforsch - Sect C J Biosci 72:467–475. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2017-0025
Han H, Ruan WJ, Zhao XJ et al (2003) Binuclear transition metal complexes of unsymmetrical tetradentate Schiff base ligands. Synth React Inorg Met Chem 33:1011–1023. https://doi.org/10.1081/SIM-120021934
Hankare PP, Chavan SS (2003) Studies on some binuclear metal complexes with tetradentate ligand derived from 5-(2′-thiazolylazo)salicylaldehyde and 2-aminophenol. Synth React Inorg Met Chem 33:423–434. https://doi.org/10.1081/SIM-120019996
Ilker MF, Nüsslein K, Tew GN, Coughlin EB (2004) Tuning the hemolytic and antibacterial activities of amphiphilic polynorbornene derivatives. J Am Chem Soc 126:15870–15875. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja045664d
Jain RK, Mishra AP (2016) Microwave synthesis, spectral, thermal, 3D molecular modeling analysis and antimicrobial activities of some transition metal complexes of Schiff bases derived from 5-bromosalicylaldehyde. J Saudi Chem Soc 20:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2012.06.002
Justin Dhanaraj C, Salin Raj SS (2020) Synthesis, characterization and biological studies of Schiff base metal complexes derived from 4-aminoantipyrine, acetamide, and p-phenylenediamine. Inorg Chem Commun 108087:1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2020.108087
Kabeer H, Hanif S, Arsalan A et al (2019) Structural-dependent N, O-donor imine-appended Cu(II)/Zn(II) complexes : synthesis, spectral, and in vitro pharmacological assessment. ACS Omega. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03762
Kajal A, Bala S, Kamboj S et al (2013) Schiff Bases : A Versatile Pharmacophore. J Catal 2013:1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/893512
Kaur G, Garg P, Kaur B et al (2018) Cationic double chained metallosurfactants: Synthesis, aggregation, cytotoxicity, antimicrobial activity and their impact on structure of Bovine serum albumin. Soft Matter. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00535D
Khashi M, Davoodnia A, Prasada Rao Lingam VS (2015) DMAP catalyzed synthesis of some new pyrrolo[3,2-e][1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidines. Res Chem Intermed 41:5731–5742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-014-1697-3
Kumar N, Tyagi R (2014) Dimeric surfactants: Promising ingredients of cosmetics and toiletries. Cosmetics 1:3–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics1010003
Kumar R, Paul T, Jana O, Mani G (2016) Regioselective Mannich bases of pyrrole-2-carbaldehyde and binuclear copper(II) complexes of bis(iminopyrrolyl) ligand containing the piperazine ring. Inorganica Chim Acta 445:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2016.02.023
Lakshmipraba J, Arunachalam S, Solomon RV et al (2015) Surfactant-copper(II) Schiff base complexes: Synthesis, structural investigation, DNA interaction, docking studies, and cytotoxic activity. J Biomol Struct Dyn 33:877–891. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2014.918523
Lobana TS, Kumari P, Bawa G et al (2012) Pyrrole-2-carbaldehyde thiosemicarbazonates of Nickel(II) and palladium(II): Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopy. Zeitschrift Fur Anorg Und Allg Chemie 638:804–810. https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.201200012
Lutfullina GG, Abdullin IS, Bujanova AG (2013) Study of surface active characteristics of developed detergent for fur treatment. Tenside, Surfactants, Deterg 50:90–92. https://doi.org/10.3139/113.110236
Mahmoud WH, Fatma MMO, Gehad NS (2018) Synthesis, characterization, spectroscopic and theoretical studies of transition metal complexes of new nano Schiff base derived from L - histidine and 2 - acetylferrocene and evaluation of biological and anticancer activities. Appl Organomet Chem 1:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4386
Maneedaeng A, Phoemboon S, Chanthasena P, Chudapongse N (2018) Synthesis, interfacial properties, and antimicrobial activity of a new cationic gemini surfactant. Korean J Chem Eng 35:2313–2320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-018-0133-6
Mangamamba T, Ganorkar MC, Swarnabala G (2014) Characterization of complexes synthesized using Schiff base ligands and their screening for toxicity two fungal and one bacterial species on rice pathogens. Int J Inorg Chem 2014:22. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/736538
Manjuraj T, Yuvaraj T, Jayanna N, et al (2020) Spectral, DFT studies, molecular docking and antibacterial activity of Schiff base derived from furan-2-carbaldehyde and their metal (II) complexes. J Turkish Chem Soc Sect A Chem 7:447–460. https://doi.org/10.18596/jotcsa.467859
Maurya RC, Patel P, Rajput S (2003) Synthesis and characterization of mixed ligand complexes of Cu(II), Ni(II), Co(II), Zn(II), Sm(III), and U(VI)O2, with a Schiff base derived from the sulfa drug sulfamerazine and 2,2′-bipyridine. Synth React Inorg Met Chem 33:801–816. https://doi.org/10.1081/SIM-120021647
Mbugua SN, Sibuyi NRS, Njenga LW et al (2020) New Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) Complexes Based on Pyrrole Schiff Bases: Synthesis, Characterization, X-ray Structure, and Anticancer Activity. ACS Omega 5:14942–14954. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00360
Mehta SK, Kaur R (2013) Self-aggregation and solution behavior of synthesized organo transition metal (Co, Fe, Zn) amphiphilic complexes. J Colloid Interface Sci 393:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.11.001
Mehta SK, Kaur R, Chaudhary GR (2012) Self-aggregation and solution behavior of copper and nickel-based surfactants. Colloids Surface A Physicochem Eng Asp 403:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2012.03.062
Mohamed GG, Omar MM, El-Ela MSA, Hindy AMM (2011) Preparation of macrocyclic Schiff-base ligand and antibacterial activities of transition metal complexes thereof. Toxicol Environ Chem 93:57–72. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2010.501033
Nami SAA, Ullah I, Alam M et al (2016) Synthesis, characterization, molecular docking, and biological studies of self-assembled transition metal dithiocarbamates of substituted pyrrole-2-carboxaldehyde. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 160:392–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.05.010
Naureen B, Miana GA, Shahid K et al (2021) Iron (III) and zinc (II) monodentate Schiff base metal complexes: Synthesis, characterisation and biological activities. J Mol Struct 1231:129946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.129946
Negm NA, Zaki MF (2008) Structural and biological behaviors of some nonionic Schiff-base amphiphiles and their Cu(II) and Fe(III) metal complexes. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 64:179–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2008.01.018
Negm NA, Zaki MF, Salem MAI (2010) Cationic Schiff base amphiphiles and their metal complexes: Surface and biocidal activities against bacteria and fungi. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 77:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.01.012
Orojloo M, Nourian F, Arabahmadi R, Amani S (2015) Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) complexes derived from a new Schiff base-2-((Z)-(3-methylpyridine-2- yleimino)methyl)phenol and synthesis of nano sized metal oxide particles from these compounds. Quim Nov 38:1187–1191. https://doi.org/10.5935/0100-4042.20150128
Patel DD, Patel KR (2020) Ni(II) and Zn(II) Schiff base complexes: Synthesis, characterization, and study of thermodynamic parameters and activation energy. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.079
Patel NB, Khan IH (2011) Synthesis of 1,2,4-triazole derivatives containing benzothiazoles as pharmacologically active molecule. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 26:527–534. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2010.535794
Paul P, Bhattacharya S (2014) Palladium complexes of pyrrole-2-aldehyde thiosemicarbazone: Synthesis, structure and spectral properties. J Chem Sci 126:1547–1555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-014-0699-4
Prasad HSN, Ananda AP, Najundaswamy S et al (2021) Design, synthesis and molecular docking studies of novel piperazine metal complexes as potential antibacterial candidate against MRSA. J Mol Struct 1232:130047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130047
Priya Dharsini GR, Thanaraj C, Velladurai R (2020) Metal chelates of tridentate (NNO) 1,2,4-triazine Schiff base: Synthesis, physico-chemical investigation, and pharmacological screening. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 30:2315–2322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01413-8
Rajiv K, Rajni J (2011) Computational approach on architecture and tailoring of organic metal complexes derived from streptomycin and Zn, Cd and Pb: antimicrobial effectiveness. Appl Organomet Chem 25:791–798. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.1838
Reiss A, Cioater N, Dobritescu A et al (2021) Bioactive Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) complexes containing a tridentate sulfathiazole-based (ONN) Schiff base. Molecules 26:1. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26103062
Reshma R, Joseyphus RS, Dasan A, John L (2019) Synthesis and spectral characterization of metal complexes of Schiff base derived from indole-3-carboxaldehyde and L-histidine as potent biocides. J Coord Chem 72:3326–3337. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2019.1695126
Rojas S, Devic T, Horcajada P (2017) Metal organic frameworks based on bioactive components. J Mater Chem B 5:2560–2573. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB03217F
Sharaby CM (2005) Studies of some new cyclodiphosphazane complexes of Fe(III), Fe(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), and Cd(II). Synth React Inorganic, Met Nano-Metal Chem 35:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1081/SIM-200035687
Sheng T, Fu Z, Wang X et al (2012) Solvothermal synthesis and luminescence properties of BaCeF 5, and BaCeF 5: Tb 3+, Sm 3+ nanocrystals: An approach for white light emission. J Phys Chem C 116:19597–19603. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp306935k
Siddappa K, Mane SB, Manikprabhu D (2014) Spectral characterization and 3D molecular modeling studies of metal complexes involving the O, N-donor environment of quinazoline-4(3H)-one Schiff base and their biological studies. Sci World J 2014:1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/817365
Singh BK, Mishra P, Prakash A, Bhojak N (2017) Spectroscopic, electrochemical and biological studies of the metal complexes of the Schiff base derived from pyrrole-2-carbaldehyde and ethylenediamine. Arab J Chem 10:S472–S483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.10.007
Singh BK, Prakash A, Rajour HK et al (2010) Spectroscopic characterization and biological activity of Zn(II), Cd(II), Sn(II), and Pb(II) complexes with Schiff base derived from pyrrole-2-carboxaldehyde and 2-amino phenol. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 76:376–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2010.03.031
Srivastava VK (2021) Synthesis, characterization, and biological studies of some biometal complexes. Futur J Pharm Sci 7:455–460. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-021-00191-w
Stephansen KB, García-díaz M, Jessen F et al (2015) Interactions between surfactants in solution and electrospun protein fibers-effects on release behavior and fiber properties. Mol Biol Int. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00614
Tatsumi T, Imai Y, Kawaguchi K et al (2014) Antimicrobial activity of cationic Gemini surfactant containing an oxycarbonyl group in the lipophilic portion against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. J Oleo Sci 63:137–140. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess13089
Teran R, Guevara R, Mora J et al (2019) Characterization of antimicrobial, antioxidant, and leishmanicidal activities of Schiff base derivatives of 4-aminoantipyrine. Molecules 24:1. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152696
Tsantis ST, Tzimopoulos DI, Holynska M (2020) Oligonuclear actinoid complexes with Schiff bases as ligands — Older Achievements and Recent Progress
Turan N, Buldurun K, Çolak N, Özdemir Ä (2019) Preparation and spectroscopic studies of Fe(II), Ru(II), Pd(II), and Zn(II) complexes of Schiff base containing terephthalaldehyde and their transfer hydrogenation and Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. Open Chem 17:571–580. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2019-0074
Tyagi P, Chandra S, Saraswat BS, Sharma D (2015) Design, spectral characterization, DFT and biological studies of transition metal complexes of Schiff base derived from 2-aminobenzamide, pyrrole and furan aldehyde. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 143:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.02.027
Tyagi P, Tyagi M, Agrawal S et al (2017) Synthesis, characterization of 1,2,4-triazole Schiff base derived 3d-metal complexes: Induces cytotoxicity in HepG2, MCF-7 cell line, BSA binding fluorescence, and DFT study. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 171:246–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.08.008
Uçar I, Bulut I, Bulut A, Büyükgüngör O (2008) Synthesis, crystal structure, spectroscopic and electrochemical properties of nickel(II) dipicolinate complex with ethylisonicotinate. J Coord Chem 61:2449–2456. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958970801927076
Upadhyay A, Vaidya S, Venkatasai VS et al (2013) Synthesis and characterization of 3d and 4f metal complexes of Schiff base ligands. Polyhedron 66:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2013.02.039
Vinusha HM, Kollur SP, Revanasiddappa HD et al (2019) Preparation, spectral characterization and biological applications of Schiff base ligand and its transition metal complexes. Results Chem 1:100012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2019.100012
Wagay TA, Ismail K (2017) Thermal, aggregation, counterion binding, light scattering, and adsorption behavior of cis-chlorobis (ethylenediamine) dodecylaminecobalt(III) perchlorate metallosurfactant in aqueous sodium perchlorate medium. Colloid Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-017-4145-2
Zaky R, Fekri A (2017) Solvent-free mechanochemical synthesis of Zn(II), Cd(II), and Cu(II) complexes with 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(2-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)-ethylidene)hydrazinyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile. Green Process Synth 7:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2017-0057
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Department of Chemistry, Mahendra Morang Adarsh Multiple Campus, Biratnagar (Tribhuvan University) for providing research facilities in pursuing this work. We also acknowledge SAIF-STIC Cochin, SAIF-IIT Bombay, and SAIF-CDRI Lucknow, India, for spectral analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.K.C. designed the study. J.A. experimented and performed analysis. J.A. and N.K.C. prepared the manuscript. A.B. and N.K.C. critically revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adhikari, J., Bhattarai, A. & Chaudhary, N.K. Synthesis, characterization, physicochemical studies, and antibacterial evaluation of surfactant-based Schiff base transition metal complexes. Chem. Pap. 76, 2549–2566 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02062-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02062-x