Abstract
Background and Objectives
Obesity and its related comorbidities are associated with serious health risks. This trial evaluated the safety and effectiveness of the ORBERA® Intragastric Balloon System (IGB) as an adjunct to lifestyle intervention in a post-marketing clinical setting.
Methods and Materials
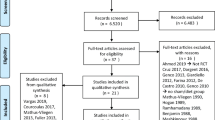
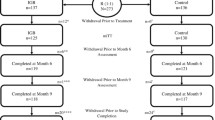
In this multicenter study, 258 adults with a body mass index of 30–40 kg/m2 were treated with the IGB as an adjunct to weight reduction and followed for up to 12 months. The primary objective was to demonstrate in a post-marketing clinical setting that the incidence of device and procedure-related serious adverse events (SAEs) after 26 weeks of IGB treatment is no greater than 15%.
Results
The incidence of device and procedure-related SAEs was 8.9% with a 1-sided upper limit confidence interval of 12.4%, compared with the 9.6% overall SAE rate seen in the US pivotal study; therefore, the primary safety endpoint was met. The key secondary effectiveness endpoint was also met with a mean maximum %TBWL of 12.5 being achieved at the time of IGB removal (26 weeks).
Conclusions
The post-marketing safety and effectiveness profile of the IGB are consistent with what was observed in the US pivotal study. No new risks were identified.
Clinical trial registration: Clinical Trials.gov NCT02828657

Similar content being viewed by others
References
NIH. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults - The evidence report. Obes Res 1998;6(Suppl 2)(51S–209S).
Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2015–20162017 Oct.
Gottig S, Daskalakis M, Weiner S, et al. Analysis of safety and efficacy of intragastric balloon in extremely obese patients. Obes Surg. Jun 2009;19(6):677–83.
Courcoulas A, Abu Dayyeh BK, Eaton L, et al. Intragastric balloon as an adjunct to lifestyle intervention: a randomized controlled trial. International journal of obesity (2005). Mar. 2017;41(3):427–33.
Abeid M, Kaddah T, Zaitoun N, et al. Efficacy and safety of intragastric balloon placements in 1600 cases, an experience from the Middle East. Obes Surg. 2019;29(7):2087–91.
Herve J, Wahlen CH, Schaeken A, et al. What becomes of patients one year after the intragastric balloon has been removed? Obes Surg. Jun-Jul 2005;15(6):864–70.
Alfredo G, Roberta M, Massimiliano C, et al. Long-term multiple intragastric balloon treatment--a new strategy to treat morbid obese patients refusing surgery: prospective 6-year follow-up study. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2014;10(2):307–11.
Genco A, Bruni T, Doldi S, et al. BioEnterics intragastric balloon: the Italian experience with 2,515 patients. Obes Surg. 2005;15(8):1161–4.
Genco A, Cipriano M, Bacci V, et al. Intragastric balloon followed by diet vs intragastric balloon followed by another balloon: a prospective study on 100 patients. Obes Surg. 2010;20(11):1496–500.
Genco A, Lopez-Nava G, Wahlen C, et al. Multi-centre European experience with intragastric balloon in overweight populations: 13 years of experience. Obes Surg 2013;23(4):515–521.
Crea N, Pata G, Della Casa D, et al. Improvement of metabolic syndrome following intragastric balloon: 1 year follow-up analysis. Obes Surg. 2009;19(8):1084–8.
Genco A, Cipriano M, Materia A, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy versus intragastric balloon: a case-control study. Surg Endosc. 2009;23(8):1849–53.
Mui WL, Ng EK, Tsung BY, et al. Impact on obesity-related illnesses and quality of life following intragastric balloon. Obes Surg. 2010;20(8):1128–32.
Kotzampassi K, Grosomanidis V, Papakostas P, et al. 500 intragastric balloons: what happens 5 years thereafter? Obes Surg. Jun 2012;22(6):896–903.
Kotzampassi K, Shrewsbury AD, Papakostas P, Penna S, Tsaousi GG, Grosomanidis V. Looking into the profile of those who succeed in losing weight with an intragastric balloon. J Laparoendoscopic Adv Surg Tech. Part A 2014;24(5):295–301.
Farina MG, Baratta R, Nigro A, et al. Intragastric balloon in association with lifestyle and/or pharmacotherapy in the long-term management of obesity. Obes Surg. Apr 2012;22(4):565–71.
Fuller NR, Pearson S, Lau NS, et al. An intragastric balloon in the treatment of obese individuals with metabolic syndrome: a randomized controlled study. Obesity (Silver Spring). Aug 2013;21(8):1561–70.
Al-Sabah S, Al-Ghareeb F, Ali DA, et al. Efficacy of intragastric balloon for the management of obesity: experience from Kuwait. Surg Endosc. 2016;30(2):424–9.
da Silva J, Proenca L, Rodrigues A, et al. Intragastric balloon for obesity treatment: safety, tolerance, and efficacy. GE Port J Gastroenterol. 2018;25(5):236–42.
Forlano R, Ippolito AM, Iacobellis A, et al. Effect of the BioEnterics intragastric balloon on weight, insulin resistance, and liver steatosis in obese patients. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71(6):927–33.
Lopez-Nava G, Rubio MA, Prados S, et al. BioEnterics® intragastric balloon (BIB®). Single ambulatory center Spanish experience with 714 consecutive patients treated with one or two consecutive balloons. Obes Surg 2011;21(1):5–9.
Štimac D, Majanović SK, Turk T, et al. Intragastric balloon treatment for obesity: results of a large single-center prospective study. Obes Surg. 2011;21(5):551–5.
Chan AO, Chow WS, Lam KF, et al. The effect of intragastric balloon placement on weight loss and type 2 diabetes control. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;28(1):162–4. author reply 164-165
Mafort TT, Madeira E, Madeira M, et al. Six-month intragastric balloon treatment for obesity improves lung function, body composition, and metabolic syndrome. Obes Surg. 2014;24(2):232–40.
Guedes M, Fittipaldi-Fernandez R, Diestel C, et al. Impact of intragastric balloon treatment on adipokines, cytokines, and metabolic profile in obese individuals. Obes Surg. 2019;29(8):2600–8.
Koc F, Kayaoglu H, Celik A, et al. Effect of weight loss induced by intragastric balloon therapy on cardiac function in morbid obese individuals: a pilot study. Med Princ Pract. 2015;24(5):432–5.
Reimao S, da Silve M, Nunes G, et al. Improvement of body composition and quality of life following intragastric balloon. Obes Surg. 2018;28(6):1806–8.
Apollo. Orbera Managed Weight Loss System. 2018; https://apolloendo.com/orbera/. Accessed 20 Feb 2020.
Dumonceau J. Evidence-based review of the Bioenterics intragastric balloon for weight loss. Obes Surg. 2008 Dec;18(12):1611–7.
Gomez V, Woodman G, Abu Dayyeh BK. Delayed gastric emptying as a proposed mechanism of action during intragastric balloon therapy: results of a prospective study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2016;24(9):1849–53.
Kruizenga HM, Seidell JC, de Vet HCW, et al. Development and validation of a hospital screening tool for malnutrition: the short nutritional assessment questionnaire (SNAQ). Clin Nutr. 200 24(1):75–82. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2004.07.015
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the OPAS-1, ORBERA study investigators, included: Rachel Moore, MD (Metairie, LA); Trace Curry, MD (Cincinnati, OH); Ronald Leo, MD (Baton Rouge, LA); Julie Ellner, MD (San Diego, CA); Angelo Coppola, MD (Little Rock, AR); Barham Abu Dayyeh, MD (Rochester, MN); Carl Pesta, DO (Shelby Township, MI); John Olsofka, MD (Louisville, KY); Tiffany Jesse, DO (South Pasadena, FL); Vivek Kumbhari, MD (Baltimore, MD); Ronnie Keith, DO (Norman, OK); and Shakeel Ahmed, MD (Fairview Heights, IL).
Funding
This study was funded by the research grants provided by Apollo Endosurgery, Austin, TX.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Laura Eaton is a paid clinical research consultant for Apollo Endosurgery. Drs. Ellner and Moore were clinical investigators for this study and received research grants for study participation. Dr. Moore also reports grants from Obalon, Allurion, and Elira, as well as consulting fees from Medtronic outside of the submitted work.
Ethical Approval
This study was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the participating institutions, IRBs, ICH-GCP, and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Data of individual participants and other study documents will not be shared or made available. Data is on file with the US FDA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, R.L., Eaton, L. & Ellner, J. Safety and Effectiveness of an Intragastric Balloon as an Adjunct to Weight Reduction in a Post-Marketing Clinical Setting. OBES SURG 30, 4267–4274 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-020-04798-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-020-04798-5