Abstract
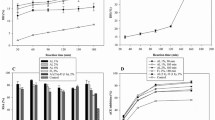
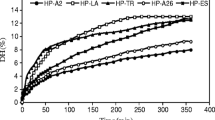
Quinoa protein is increasingly being used a source of plant protein in the food industry because of its high nutrient value, good digestibility, and gluten-free nature. However, its widespread application in the food industry is currently restricted due to its poor water solubility and limited functionality. Controlled enzymatic hydrolysis can improve the functional attributes of plant proteins. Consequently, the objective of this study was to produce bioactive peptides from quinoa protein by enzymatic hydrolysis. The suitability of five commercial proteases were assessed for this purpose: alcalase, compound protease, neutral protease, flavourzyme, and papain. The antioxidant activity and digestion properties of the peptides produced were analyzed. Alcalase was the most efficient enzyme for treating quinoa protein, as it produced the highest degree of hydrolysis, nitrogen recovery rate, and antioxidant activity. Amino acid analysis indicated that quinoa peptides contained all the essential amino acids required for human nutrition, as well as a high level of hydrophobic amino acids, which may provide strong antioxidant activity. In vitro digestion analysis showed that the quinoa peptides exhibited strong resistance to hydrolysis in the stomach but were hydrolyzed in the small intestine. After simulated gastrointestinal digestion, the peptides still exhibited high antioxidant activity. This study therefore suggests that bioactive peptides derived from quinoa protein could be utilized as bioactive ingredients to formulate functional foods.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
R. Abeynayake, S. Zhang, W. Yang, L. Chen, Development of antioxidant peptides from brewers’ spent grain proteins. LWT. 158, 113162 (2022)
M.S. Kumar, Peptides and Peptidomimetics as potential antiobesity agents: overview of current status. Front. Nutr. 6, 11 (2019)
T. Li, X. Zhang, Y. Ren, Y. Zeng, Q. Huang, C. Wang, Antihypertensive effect of soybean bioactive peptides: a review. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 62, 74–81 (2022)
D. Lozano-Ojalvo, R. López-Fandiño, Immunomodulating peptides for food allergy prevention and treatment. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 58(10), 1629–1649 (2018)
B. Mousavi, M.-H. Azizi, S. Abbasi, Antidiabetic bio-peptides of soft and hard wheat glutens. Food Chem. 4, 100104 (2022)
F. Rivero-Pino, M.J. Leon, M.C. Millan-Linares, S. Montserrat-de la Paz, Antimicrobial plant-derived peptides obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation as components to improve current food systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 135, 32–42 (2023)
W. Wongngam, A. Hamzeh, F. Tian, S. Roytrakul, J. Yongsawatdigul, Purification and molecular docking of angiotensin converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides derived from corn gluten meal hydrolysate and from in silico gastrointestinal digestion. Process. Biochem. 129, 113–120 (2023)
S. Lyu, M. Chen, Y. Wang, D. Zhang, S. Zhao, J. Liu, F. Pan, T. Zhang, Foaming properties of egg white proteins improved by enzymatic hydrolysis: the changes in structure and physicochemical properties. Food Hydrocoll. 141, 108681 (2023)
Y. Lv, L. Chen, F. Liu, F. Xu, F. Zhong, Improvement of the encapsulation capacity and emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate through controlled enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Hydrocoll. 138, 108444 (2023)
G. Liang, W. Chen, X. Qie, M. Zeng, F. Qin, Z. He, J. Chen, Modification of soy protein isolates using combined pre-heat treatment and controlled enzymatic hydrolysis for improving foaming properties. Food Hydrocoll. 105, 105764 (2020)
V. Perreault, L. Hénaux, L. Bazinet, A. Doyen, Pretreatment of flaxseed protein isolate by high hydrostatic pressure: impacts on protein structure, enzymatic hydrolysis and final hydrolysate antioxidant capacities. Food Chem. 221, 1805–1812 (2017)
B. Qian, X. Zhao, Y. Yang, C. Tian, Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory peptide fraction from oyster soft tissue by enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Sci. Nutr. 8(7), 3947–3956 (2020)
J.G. d., S. Aguilar, V. Granato Cason, R.J.S. Castro, Improving antioxidant activity of black bean protein by hydrolysis with protease combinations. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 54(1), 34–41 (2019)
M. Galante, R. De Flaviis, V. Boeris, D. Spelzini, Effects of the enzymatic hydrolysis treatment on functional and antioxidant properties of quinoa protein acid-induced gels. LWT. 118, 108845 (2020)
R. Vilcacundo, B. Hernández-Ledesma, Nutritional and biological value of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd). Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 14, 1–6 (2017)
S. Jaikishun, W. Li, Z. Yang, S. Song, Quinoa: In perspective of global challenges (Review). Agronomy. 9(4), 176 (2019)
S. Dakhili, L. Abdolalizadeh, S.M. Hosseini, S. Shojaee-Aliabadi, L. Mirmoghtadaie, Quinoa protein: composition, structure and functional properties. Food Chem. 299, 125161 (2019)
M.J. Kozioł, Chemical composition and nutritional evaluation of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd). J. Food Compost Anal. 5(1), 35–68 (1992)
E.B. Craine, K.M. Murphy, Corrigendum: seed composition and amino acid profiles for Quinoa grown in Washington State. Front. Nutr. 7, 605674 (2020)
S.R. Hertzler, J.C. Lieblein-Boff, M. Weiler, C. Allgeier, Plant proteins: assessing their nutritional quality and effects on health and physical function. Nutrients. 12, 3704 (2020)
Z. Shi, Y. Hao, C. Teng, Y. Yao, G. Ren, Functional properties and adipogenesis inhibitory activity of protein hydrolysates from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd). Food Sci. Nutr. 7(6), 2103–2112 (2019)
S. Abbasi, M. Moslehishad, M. Salami, Antioxidant and alpha-glucosidase enzyme inhibitory properties of hydrolyzed protein and bioactive peptides of quinoa. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 213, 602–609 (2022)
H. Daliri, R. Ahmadi, A. Pezeshki, H. Hamishehkar, M. Mohammadi, H. Beyrami, M. Khakbaz Heshmati, M. Ghorbani, Quinoa bioactive protein hydrolysate produced by pancreatin enzyme- functional and antioxidant properties. LWT. 150, 111853 (2021)
P. Mudgil, B.P. Kilari, H. Kamal, O.A. Olalere, R.J. FitzGerald, C.-Y. Gan, S. Maqsood, Multifunctional bioactive peptides derived from quinoa protein hydrolysates: inhibition of α-glucosidase, dipeptidyl peptidase-IV and angiotensin I converting enzymes. J. Cereal Sci. 96, 103130 (2020)
H. Zhou, B. Safdar, H. Li, L. Yang, Z. Ying, X. Liu, Identification of a novel α-amylase inhibitory activity peptide from quinoa protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 403, 134434 (2023)
H. You, T. Wu, W. Wang, Y. Li, X. Liu, L. Ding, Preparation and identification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides from quinoa protein. Food Res. Int. 156, 111176 (2022)
R. Chirinos, R. Pedreschi, M. Velásquez-Sánchez, A. Aguilar-Galvez, D. Campos, In vitro antioxidant and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory properties of enzymatically hydrolyzed quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) and kiwicha (Amaranthus caudatus) proteins. Cereal Chem. 97(5), 949–957 (2020)
A.M. Nisar, S.R. Charanjit, S. Sukhcharn, Effect of pH and holding time on the characteristics of protein isolates from Chenopodium seeds and study of their amino acid profile and scoring. Food Chem. 272, 165–173 (2019)
P. Mudgil, L.S. Omar, H. Kamal, B.P. Kilari, S. Maqsood, Multi-functional bioactive properties of intact and enzymatically hydrolysed quinoa and amaranth proteins. LWT. 110, 207–213 (2019)
L. Gu, H. Jiao, D.J. McClements, M. Ji, J. Li, C. Chang, S. Dong, Y. Su, Y. Yang, Improvement of egg yolk powder properties through enzymatic hydrolysis and subcritical fluid extraction. LWT. 150, 112075 (2021)
R. Re, N. Pellegrini, A. Proteggente, A. Pannala, M. Yang, C. Rice-Evans, Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 26(9), 1231–1237 (1999)
I.C. Sheih, T.-K. Wu, T.J. Fang, Antioxidant properties of a new antioxidative peptide from algae protein waste hydrolysate in different oxidation systems. Bioresour Technol. 100(13), 3419–3425 (2009)
J. Long, F. Wang, A. Jiao, X. Xu, Z. Xie, Z. Jin, Preparation, characterization and physicochemical properties of novel low-phosphorus egg yolk protein. J. Sci. Food Agr. 99(4), 1740–1747 (2019)
M. Huang, P. Liu, S. Song, X. Zhang, K. Hayat, S. Xia, C. Jia, F. Gu, Contribution of sulfur-containing compounds to the colour-inhibiting effect and improved antioxidant activity of Maillard reaction products of soybean protein hydrolysates. J. Sci. Food Agr. 91(4), 710–720 (2011)
L. Gu, Y. Su, Z. Zhang, B. Zheng, R. Zhang, D.J. McClements, Y. Yang, Modulation of lipid digestion profiles using filled Egg White Protein Microgels. J. Agr Food Chem. 65(32), 6919–6928 (2017)
S. Tang, X. Zhou, M. Gouda, Z. Cai, Y. Jin, Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on the solubility of egg yolk powder from the changes in structure and functional properties. LWT. 110, 214–222 (2019)
T. Kodera, M. Asano, N. Nio, Characteristic property of low bitterness in protein hydrolysates by a novel soybean protease D3. J. Food Sci. 71(9), S609–S614 (2006)
M. Tomita, W. Bellamy, M. Takase, K. Yamauchi, H. Wakabayashi, K. Kawase, Potent antibacterial peptides generated by Pepsin digestion of Bovine Lactoferrin. J. Dairy. Sci. 74(12), 4137–4142 (1991)
J. Zheng, T. Bu, L. Liu, G. He, S. Li, J. Wu, Naturally occurring low molecular peptides identified in egg white show antioxidant activity. Food Res. Int. 138, 109766 (2020)
L. Zhu, J. Chen, X. Tang, Y.L. Xiong, Reducing, radical scavenging, and chelation properties of in vitro digests of alcalase-treated zein hydrolysate. J. Agr Food Chem. 56(8), 2714–2721 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFD2101004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, L., Peng, N., Chen, S. et al. Bioactive peptides derived from quinoa protein: fabrication, antioxidant activities, and in vitro digestion profiles. Food Measure 18, 894–903 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-02212-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-02212-z