Abstract
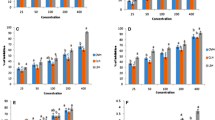
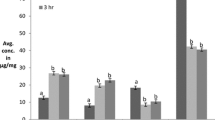
Citrullus lanatus seed is a potential source of edible protein, hence effective extraction of protein components plays a vital role in food application. Therefore, this study aims for optimization and hydrolysis of protein using single factor and Box Behnken design (BBD). Various concentrations of the protein hydrolysates were studied for antioxidant activity using different assays. The one factor test revealed that important parameters such as alkali concentration (0.8%), temperature (40 °C), time (30 min) and solid to alkali ratio (1:30) enhance the protein concentration from C. lanatus (903.1 mg/g). The maximum degree of hydrolysis 39.30% was achieved at pH 2.4, an enzyme to substrate ratio 3% (w/w), and hydrolysis time 180 min by using BBD design. C. lanatus protein hydrolysate showed 15.71 and 61.67% of DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activity at 5 mg/ml. It exhibited reducing power optical density 0.18593 nm and metal chelating activity of 42.69% at the concentration of 25 mg/ml. This implied that C. lanatus could be used as a natural antioxidant agent.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
UNICEF, The state of the world‘s children 2012: children in an urban world. (United Nations Children‘s Fund. UNICEF, New York, 2012)
National Family Health Survey (NFHS), NHFS 3, 2005–06. (Indian Institute of Population Sciences, Mumbai, 2007)
World Bank, Nutrition country profiles: Nutrition at a Glance (India), http://siteresources.worldbank.org/NUTRITION/Resources/2818461271963823772/India.pdf (2010)
R.J. Henry, P. Kettlewell, Cereal Grain Quality. (Chapman and Hall, London, 1996)
M. Duranti, A. Consonni, C. Magni, F. Sessa, A. Scarafoni, The major proteins of lupin seed: characterisation and molecular properties for use as functional and nutraceutical ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 19, 624–633 (2008)
M.S. Teotia, P. Ramakrishna, Chemistry and technology of melon seeds. J. Food Sci. Technol. 21, 332–340 (1984)
S.K. Sonawane, S.S. Arya, Nutritional, functional, thermal and structural characteristics of Citrullus lanatus and Limonia acidissima seed flours. Food Meas. 10(1), 72–79 (2016)
M.M. Bradford, A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72, 248–254 (1976)
N.T. Hoyle, J.O.H.N. Merritt, Quality of fish protein hydrolysates from herring (Clupea harengus). J Food Sci 59(1), 76–79 (1994)
O.H. Lowry, N.J. Rosebrough, A.L. Farr, R.J. Randal, Protein analysis with Folin-phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
G.E.P. Box, N.R. Draper, Empirical Model-Building and Response Surfaces (John Wily and Sons, New York, 1987), p. 249
R. Re, N. Pellegrini, A. Proteggente, A. Pannala, M. Yang, C. Rice-Evans, Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 26, 1231–1237 (1999)
S. Sonawane, S.S. Arya, Antioxidant activity of jambhul, L acidissima, ambadi and ambat chukka: an indigenous lesser known fruits and vegetables of India. Adv. J. Food Sci. Technol. 5(3), 270–275 (2013)
S. Sahreen, M. Khan, R. Khan, Evaluation of antioxidant activities of various solvent extracts of Carissa opaca fruits. Food Chem. 122, 1205–1211 (2010)
I.F.F. Benzie, J.J. Strain, The ferric reducing ability of plasma as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 239, 70–76 (1996)
E.A. Decker, B. Welch, Role of ferritin as a lipid oxidation catalyst in muscle food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 38, 674–677 (1990)
A.A. Wani, D.S. Sogi, L. Grover, D.C. Saxena, Effect of temperature, alkali concentration, mixing time and meal/ solvent ratio on the extraction of watermelon seed proteins—a response surface approach. Biosyst. Eng. 94, 67–73 (2006)
T.Z. Ma, Q. Wang, H.W. Wu, Optimization of extraction conditions for improving solubility of peanut protein concentrates by response surface methodology. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 43, 1450–1455 (2010)
D.F. Hochstrasser, M.G. Harrington, A.C. Hochstrasser, M.J. Miller, C.R. Merril, Methods for increasing the resolution of two-dimensional protein electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 173(2), 424–435 (1988)
J. Adler-Nissen, Enzymic Hydrolysis of Food Proteins (Elsevier Applied Science, London, 1986)
S. Benjakul, M.T. Morrissey, Protein hydrolysates from Pacific whiting solid wastes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 45(9), 3423–3430 (1997)
K. Suetsuna, T. Nakano, Identification of an antihypertensive peptide from peptic digest of wakame. J. Nutr. Biochem. 11, 450–454 (2000)
K.D. Kanbargi, S.K. Sonawane, S.S. Arya, Functional and antioxidant activity of Ziziphus jujube seed protein hydrolysates. Food Meas. 10, 226 (2016)
M. B. Arnao, Some methodological problems in the determination of antioxidant activity using chromogen radicals: a practical case. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 11, 419–421 (2000)
K. Shimada, K. Fujikawa, K. Yahara, T. Nakamura, Antioxidative properties of xanthan on the autioxidation of soybean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 40, 945–948 (1992)
L.J. Zhu, J. Chen, X.Y. Tang, Y.L. Xiong, Reducing, radical scavenging, and chelation properties of in vitro digests of alcalase treated zein hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 2714–2721 (2008)
B.H. Kong, Y.L. Xiong, Antioxidant activity of zein hydrolysate in liposome system and thepossible mode of action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 54, 6059–6068 (2006)
A. Saiga, S. Tanabe, T. Nishimura, Antioxidant activity of peptides obtained from porcine myofibrillar proteins by protease treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 51, 3661–3667 (2003)
R.L. Prior, X. Wu, K. Schaich, Standardized method for the determination of antioxidant capacities and phenolics in foods and dietary supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53, 4290–4302 (2005)
R.J. Elias, S.S. Kellerby, E.A. Decker, Antioxidant activity of proteins and peptides. Crit Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 48(5), 430–441 (2008)
H.M. Chen, K. Muramoto, F. Yamauchi, K. Nokihara, Antioxidant activity of designed peptides based on the antioxidative peptide isolated from digests of a soybean protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 44(9), 2619–2623 (1996)
B.H. Sarmadi, A. Ismail, Antioxidative peptides from food proteins. Peptides 31, 1949–1956 (2010)
Z. Xie, J. Huang, X. Xu, Z. Jin, Antioxidant activity of peptides isolated from alfalfa leaf protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 111, 370–376 (2008)
J.S. Wang, M.M. Zhao, Q.Z. Zhao, M. Y., Jiang,. Antioxidant properties of papain hydrolysates of wheat gluten in different oxidation systems. Food Chem. 101, 1658–1663 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonawane, S.K., Arya, S.S. Citrullus lanatus protein hydrolysate optimization for antioxidant potential. Food Measure 11, 1834–1843 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9565-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9565-7