Abstract
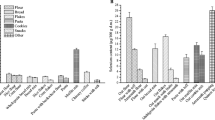
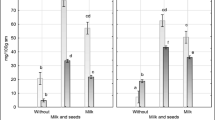
Gluten-free foods are specially designed to be consumed by people who suffer from celiac disease or some type of gluten intolerance. Few studies are currently available about trace element contents in gluten-free foods. This study aimed at analyzing the concentrations of 15 trace elements in commercial gluten-free amaranth bars by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry, after wet digestion by microwave system. The accuracy of the method was determined by the use of a standard reference material (NIST SRM 1570a Spinach Leaves) and recovery experiments, obtaining satisfactory values in all cases. The contents of the investigated trace elements in gluten-free amaranth bars were found to be in the range: Al (3.7–8.1 µg/g), Co (0.02–0.07 µg/g), Cr (0.05–0.25 µg/g), Cu (1.80–6.12 µg/g), Fe (7.0–14.5 µg/g), Mn (6.5–10.6 µg/g), Ni (0.30–0.78 µg/g), Pb (0.25–1.12 µg/g), Sr (1.4–2.7 µg/g), and Zn (4.7–9.8 µg/g). Some of the essential trace elements were found to have good nutritional contribution in accordance to daily nutrient recommendations for adults. The concentrations of non-essential elements such as Al, Ni and Sr, were very low in all samples. The levels of toxic elements such as As, Cd, Sb and Tl were not detected in any of the samples, and do not pose any threat to consumers. However, the Pb concentrations were above the safety limits in 8.9 % of the studied samples. Therefore, regular monitoring of this toxic metal should be conducted in the future, to ensure the quality of the gluten-free products for human health.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Dean, R. Shepherd, A. Arvola, M. Vassallo, M. Winkelmann, E. Claupein, L. Lähteenmäki, M.M. Raats, A. Saba, J. Cereal Sci. (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2007.06.007
W. Marcason, J. Am. Diet. Assoc. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jada.2011.09.030
G.A. Gaesser, S.S. Angadi, J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.jand.2012.06.009
E. Gallagher, T.R. Gormley, E.K. Arendt, Trends Food Sci. Technol. (2004). doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2003.09.012
S. Case, Gastroenterology (2005). doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2005.02.020
C. Ballabio, F. Uberti, C. Di Lorenzo, A. Brandolini, E. Penas, P. Restani, J. Agric. Food Chem. (2011). doi:10.1021/jf2041824
N. Singh, P. Singh, Flour and Breads and their Fortification, in Health and Disease Prevention, ed. by V. Preedy, R. Watson, V. Patel (Academic Press, San Diego, 2011), pp. 101–111
P. Pohl, E. Stelmach, M. Welna, A. Szymczycha-Madeja, Food Anal. Methods (2012). doi:10.1007/s12161-012-9467-6
E.J. Llorent-Martínez, M.L. Fernández-de Córdova, P. Ortega-Barrales, A. Ruiz-Medina, Microchem. J. (2013). doi:10.1016/j.microc.2013.05.016
F.C. Bressy, G.B. Brito, I.S. Barbosa, L.S.G. Teixeira, M.G.A. Korn, Microchem. J. (2013). doi:10.1016/j.microc.2012.03.010
S.S. Mitić, M.V. Obradović, M.N. Mitić, D.A. Kostić, A.N. Pavlović, S.B. Tošić, M.D. Stojković, Food Anal. Methods (2012). doi:10.1007/s12161-011-9232-2
D. Kara, Food Chem. (2009). doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.054
National Research Council, Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements (The National Academies Press, Washington, 2006)
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), EFSA J. (2005). doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2005.146
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), EFSA J. (2005). doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1570
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), EFSA J. (2005). doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2157
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), EFSA J. (2005). doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3595
V. Thomsen, D. Schatzlein, D. Mercuro, Spectroscopy 18(12), 112–114 (2003)
M. Welna, A. Szymczycha-Madeja, P. Pohl, in Wide Spectra of Quality Control, ed. by I. Akyar (Intech, Rijeka, 2011), pp. 53–70
FDA U.S., ORA Laboratory Manual—Volume II—Methods, Method Verification and Validation ORA-LAB.5.4.5 (Food and Drug Administration U.S., 2014), http://www.fda.gov/ScienceResearch/FieldScience/ucm171877.htm. Accessed 6 Apr 2015
E.G. Aguilar, M.A. Cantarelli, E.J. Marchevsky, N.L. Escudero, J.M. Camiña, J. Agric. Food Chem. (2011). doi:10.1021/jf202610t
L. Alvarez-Jubete, E.K. Arendt, E. Gallagher, Trends Food Sci. Technol. (2010). doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2009.10.014
S. Ragaee, E.-S.M. Abdel-Aal, M. Noaman, Food Chem. (2006). doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.04.039
F. Cubadda, F. Aureli, A. Raggi, M. Carcea, J. Cereal Sci. (2009). doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2008.07.008
D. Erba, A. Hidalgo, J. Bresciani, A. Brandolini, J. Cereal Sci. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2011.06.011
A.S. Hager, A. Wolter, F. Jacob, E. Zannini, E.K. Arendt, J. Cereal Sci. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2012.06.005
S. Orecchio, D. Amorello, M. Raso, S. Barreca, C. Lino, F. Di Gaudio, Microchem. J. (2014). doi:10.1016/j.microc.2014.04.011
R.P. Avegliano, V.A. Maihara, F.F. da Silva, J. Food Compos. Anal. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jfca.2011.01.017
P. Ekholm, H. Reinivuo, P. Mattila, H. Pakkala, J. Koponen, A. Happonen, J. Hellström, M.-L. Ovaskainen, J. Food Compos. Anal. (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jfca.2007.02.007
L. Saturni, G. Ferretti, T. Bacchetti, Nutrients (2010). doi:10.3390/nu2010016
R.M. Padovani, D.M. Lima, F.A.B. Colugnati, D.B. Rodriguez-Amaya, J. Food Compos. Anal. (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jfca.2007.03.006
L. Noël, R. Chekri, S. Millour, C. Vastel, A. Kadar, V. Sirot, J.-C. Leblanc, T. Guérin, Food Chem. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.12.009
H. Altundag, M. Tuzen, Food Chem. Toxicol. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.07.064
J.-C. Leblanc, T. Guérin, L. Noël, G. Calamassi-Tran, J.-L. Volatier, P. Verger, Food Addit. Contam. (2005). doi:10.1080/02652030500135367
N. Arnich, V. Sirot, G. Rivière, J. Jean, L. Noël, T. Guérin, J.-C. Leblanc, Food Chem. Toxicol. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.fct.2012.04.016
R. Hernández-Martínez, I. Navarro-Blasco, Food Control (2012). doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.12.024
E.G. Aguilar, M.A. Cantarelli, E.J. Marchevsky, N.L. Escudero, J.M. Camiña, J. Chem. (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/138391
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas and the Universidad Nacional del Nordeste, Argentina. Additionally, we are grateful to the anonymous reviewer for providing important comments that led to significant improvements of this article.
Conflict of interest
Melisa J. Hidalgo, Sonia C. Sgroppo, José M. Camiña, Eduardo J. Marchevsky and Roberto G. Pellerano declare they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
This article does not contain any studies with humans or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hidalgo, M.J., Sgroppo, S.C., Camiña, J.M. et al. Trace element concentrations in commercial gluten-free amaranth bars. Food Measure 9, 426–434 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-015-9250-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-015-9250-7