Abstract
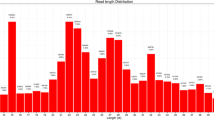
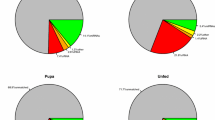
MicroRNAs are a ~22 nucleotide small non-coding RNAs found in animals, plants and viruses. They regulate key cellular processes by enhancing, degrading or silencing protein coding targets. Currently most of the data on miRNA is available from Drosophila . Given their important post-transcriptional role in several organisms, there is a need to understand the miRNA mediated processes in normal and abnormal conditions. Here we report four novel microRNAs ast - mir - 2502, ast - mir - 2559, ast - mir - 3868 and ast - mir - 9891 in Anopheles stephensi identified from a set of 3,052 transcriptome sequences, showing average minimum free energy of −31.8 kcal/mol of duplex formation with mRNA indicating their functional relevance. Phylogenetic study shows conservation of sequence signatures within the Class Insecta. Furthermore, 26 potential targets of these four miRNAs have been predicted that play an important role in the mosquito life-cycle. This work leads to novel leads and experimental possibilities for improved understanding of gene regulatory processes in mosquito.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla H, Wilding CS, Nardini L, Pignatelli P, Koekemoer L, Ranson H, Coetzee M (2014) Insecticide resistance in Anopheles arabiensis in Sudan: temporal trends and underlying mechanisms. Parasit Vectors 7:213. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-7-213
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bartel D (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bartel D (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233
Bennett V, Chen L (2001) Ankyrins and cellular targeting of diverse membrane proteins to physiological sites. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13(1):61–67
Dasso M (1993) RCC1 in the cell cycle: the regulator of chromosome condensation takes on new roles. Trends Biochem Sci 18(3):96–101
Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ (2004) Processing of primary microRNAs by the microprocessor complex. Nature 432:231–235
El-Assaad F, Hempel C et al (2011) Differential microRNA expression in experimental cerebral and non-cerebral malaria. Infect Immun 79(6):2379–2384
Grishok A, Pasquinelli AE, Conte D, Li N, Parrish S, Ha I, Baillie DL, Fire A, Ruvkun G, Mello CC (2001) Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C. elegans developmental timing. Cell 106(1):23–34
Grüring C, Heiber A, Kruse F, Ungefehr J, Gilberger TW, Spielmann T (2011) Development and host cell modifications of Plasmodium falciparum blood stages in four dimensions. Nat Commun 2:165. doi:10.1038/ncomms1169
Guan X, Middlebrooks BW, Alexander S, Wasserman SA (2006) Mutation of TweedleD, a member of an unconventional cuticle protein family, alters body shape in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:16794–16799
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5:522–531
Hittinger CT, Johnston M, Tossberg JT, Rokas A (2010) Leveraging skewed transcript abundance by RNA-Seq to increase the genomic depth of the tree of life. PNAS 107(4):1476–1481. doi:10.1073/pnas.0910449107
Joazeiro CA, Weissman AM (2000) RING finger proteins: mediators of ubiquitin ligase activity. Cell 102(5):549–552
Kariu T, Yuda M, Yano K, Chinzei Y (2002) MAEBL is essential for malarial sporozoite infection of the mosquito salivary gland. J Exp Med 195(10):1317–1323
Khvorova A, Reynolds A, Jayasena SD (2003) Functional siRNAs and miRNAs exhibit strand bias. Cell 115(2):209–216
Kim S, Imoto S, Miyano S (2003) Inferring gene networks from time series microarray data using dynamic Bayesian networks. Brief Bioinform 4(3):228–235
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S (2014) miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acid Research 42:D68–D73
La Monte G, Philip N, Reardon J et al (2012) Translocation of sickle cell erythrocyte microRNAs into Plasmodium falciparum inhibits parasite translation and contributes to malaria resistance. Cell Host Microbe 12(2):187–199
Laity JH, Lee BM, Wright PE (2001) Zinc finger proteins: new insights into structural and functional diversity. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11(1):39–46
Mead EA, Tu Z (2008) Cloning, characterization, and expression of microRNAs from the Asian malaria mosquito, Anopheles stephensi. BMC Genomics 9:244
Megy K et al (2012) VectorBase: improvements to a bioinformatics resource for invertebrate vector genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D729–D734
Miller LH, Baruch DI, Marsh K, Doumbo OK (2002) The pathogenic basis of malaria. Nature 415:673–679. doi:10.1038/415673a
Nwane P, Etang J, ChouaÏbou M, Toto JC, Koffi A, Mimpfoundi R, Simard F (2014) Multiple insecticide resistance mechanisms in Anopheles gambiae s.l. populations from Cameroon, Central Africa. Parasit Vectors 6:41. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-6-41
Ocampo M, Curtidor H, Vera R, Valbuena JJ, Rodríguez LE, Puentes A, López R, García JE, Tovar D, Pacheco P, Navarro MA, Patarroyo ME (2004) MAEBL Plasmodium falciparum protein peptides bind specifically to erythrocytes and inhibit in vitro merozoite invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 315(2):319–329
Rathjen T, Nicol C, Mcconkey G, Dalmay T (2006) Analysis of short RNAs in the malaria parasite and its red blood cell host. FEBS Lett. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2006.08.063
Rubtsov AM, Lopina OD (2000) Ankyrins. FEBS lett 482(1):1–5
Schlöndorff J, Blobel CP (1999) Metalloprotease–disintegrins: modular proteins capable of promoting cell-cell interactions and triggering signals by protein-ectodomain shedding. J Cell Sci 112:3603–3617
Schwarz SD, Hutvágner G, Du T, Xu Z, Aronin N, Zamore PD (2003) Asymmetry in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complex. Cell 115(2):199–208
Sinka ME et al (2011) The dominant Anopheles vectors of human malaria in Asia-Pacific: occurrence data, distribution maps and bionomic précis. Parasit Vectors 4:89. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-4-89
Stefan HIK, Amy RN, Tresa SF, Peter B, John HA (1998) A family of chimeric erythrocyte binding proteins of malaria parasites. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:1230–1235
Sturm A, Amino R, van de Sand C et al (2006) Manipulation of host hepatocytes by the malaria parasite for delivery into liver sinusoids. Science 313(5791):1287–1290. doi:10.1126/science.1129720
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tikar SN, Mendki MJ, Sharma AK, Sukumaran D, Veer V, Prakash S, Parashar BD (2011) Resistance status of the malaria vector mosquitoes, Anopheles stephensi and Anopheles subpictus towards adulticides and larvicides in arid ad semi-arid areas of India. J Insect Sci 11:1–10
Xu T, Zhong D, Tang L, Chang X, Fu F, Yan G, Zheng B (2014) Anopheles sinensis mosquito insecticide resistance: comparison of three mosquito sample collection and preparation methods and mosquito age in resistance measurements. Parasit Vectors 7:54. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-7-54
Xue C, Li F, He T, Liu GP, Li Y, Zhang X (2005) Classification of real and pseudo microRNA precursors using local structure-sequence features and support vector machine. BMC Bioinform 6:310. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-6-310
Zeng Y, Cullen BR (2004) Structural requirements for pre-microRNA binding and nuclear export by Exportin 5. Nucleic Acids Res 32(16):4776–4785
Zhang H, Kolb FA, Jaskiewicz L, Westhof E, Filipowicz W (2004) Single processing center models for human Dicer and bacterial RNase III. Cell 118(1):57–68
Zhao X, Smartt CT, Hillyer JF, Christensen BM (2000) A novel member of the RING-finger gene family associated with reproductive tissues of the mosquito, Aaedes aegypti. Insect Mol Biol 9(3):301–308
Zuker M (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3406–3415
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the State Inter-University Center for Excellence in Bioinformatics, University of Kerala for providing the infrastructure and funds for carrying out the computation involved in the work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnan, R., Kumar, V., Ananth, V. et al. Computational identification of novel microRNAs and their targets in the malarial vector, Anopheles stephensi . Syst Synth Biol 9, 11–17 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11693-014-9159-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11693-014-9159-1