Abstract
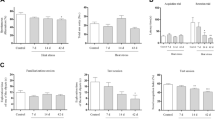
To study the effects of early signal substances induced by heat stress in brains of Kunming mice, six-month-old mice (n = 72) were pretreated with heat stress and subsequent ischemia/reperfusion by clipping of their bilateral cervical common arteries for 7 min. According to different treatments, animals were randomly divided into four groups: (1) normal control group; (2) heat stress pretreatment followed by ischemia and reperfusion group (HS/IR); (3) ischemia and reperfusion group (IR); (4) heat stress group (HS). Animals in the later three groups were subdivided into 3 subgroups (1 day, 4 days, 14 days), respectively. The changes in the expression of cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) were detected by immunohistochemistry and computer image analysis methods. The results showed that compared with the normal group, the expressions of CREB in the hippocampal CA1 region increased significantly in the HS, HS/IR and IR groups (P < 0.05). Compared to the normal group, heat stress could result in CGRP excretion and redistribution in the cerebrum, with the highest level in the 4 d HS/IR group. Following heat stress, CGRP immunoreactivity was observed in varicose fibers and neuronal perikarya within the CA1 region. The results indicate that heat stress can induce CREB expression, which in turn stimulates CGRP secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckmann R P, Mizzen L A, Weich WJ. Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science, 1990, 248(4957): 850–854
Seybold V S, McCarson K E, Mermelstein P G, Groth R D, Abrahams L G. Calcitonin gene-related peptide regulates expression of neurokininl receptors by rat spinal neurons. J Neurosci, 2003, 23(5): 1816–1824
Hata R, Gass P, Mies G, Wiessner C, Hossmann K A. Attenuated c-fos mRNA induction after middle artery occlusion in CREB knockout mice does not modulate focal ischemic injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 1998, 18(12): 1325–1335
Ma W, Zheng W H, Powell K, Jhamandas K, Quirion R. Chronic morphine exposure increases the phosphorylation of MAP kinases and the transcription factor CREB in dorsal root ganglion neurons: an in vitro and in vivo study. Eur J Neurosci, 2001, 14(7): 1091–1104
Paues J, Engblom D, Mackerlova L, Ericsson-Dahlstrand A, Blomqvist A. Feeding-related immune responsive brain stem neurons: association with CGRP. Neuroreport, 2001, 12(11): 2399–2403
Wang S, Yang D, Lippman M E. Targeting Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL with nonpeptidic small-molecule antagonists. Semin Oncol, 2003, 30(5 Suppl 16): 133–142
Schicho R, Donnerer J. Nerve growth factor stimulates synthesis of calcitonin gene-related peptide in dorsal root ganglion cells during sensory regeneration in capsaicin-treated rats. Neurosci Res, 1999, 35(3): 183–187
Bulloch K, Milner T A, Prasad A, Hsu M, Buzsaki G, McEwen B S. Induction of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity in hippocampal neurons following ischemia: a putative regional modulator of the CNS injury/immune response. Exp Neurol, 1998, 150(2): 195–205
Borke R C, Curtis M, Ginsberg C. Choline acetyltransferase and calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in motorneurons after different types of nerve injury. J Neurocytol, 1993, 22(3): 141–153
Tachibana T, Nawa T. Immunohistochemical reactions of receptors to met-enkephalin, VIP, substance P, and CGRP located on Merkel cells in the rat sinus hair follicle. Arch Histol Cytil, 2005, 68(5): 383–391
Liu Z Q, Ma Z J, Li M B. Expression of MAP-2 and NF in CA1 region of hippocampal neurons in rat vascular dementia model. Zhongguo Xiandai Yixue Zazhi, 2004, 6(14): 26–30 (in Chinese)
Peng J, Lu R, Hu C P. The delay-protection of heart induced by heat stress and mechanism. Zhongnan Gongye Daxue Xuebao, 2001, 32: 123–127 (in Chinese)
Freeland K, Liu Y Z, Latchman D S. Distinct signaling pathways mediate the cAMP response element (CRE)-dependent activation of the calcitonin gene-related peptide gene promoter by cAMP and nerve growth factor. Biochem J, 2000, 345: 233–238
Freeland K, Liu Y Z, Latchman D S. Distinct signalling pathways mediate the cAMP response element (CRE)-dependent activation of the calcitonin gene-related peptide gene promoter by cAMP and nerve growth factor. Biochem J, 2000, 345(2): 233–238
Hata R, Gass P, Mies G. Attenuated c-fos mRNA induction after middle artery occlusion in CREB knockout mice does not modulate focal ischemic injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 1998, 18(12): 1325–1335
Ichiki T. Role of cAMP response element binding protein in cardiovascular remodeling: good, bad, or both? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2006, 26(3): 449–455
Wanigasekara Y, Keast J R. Neurturin has multiple neurotrophic effects on adult rat sacral parasympathetic ganglion neurons. Eur J Neurosci, 2005, 22(3): 595–604
Anderson L E, Seybold V S. Calcitonin gene-related peptide regulates gene transcription in primary afferent neurons. J Neurochem, 2004, 91(6): 1417–1429
Haug T, Storm J F. Protenin kinase A mediates the modulation of the slow Ca2+-dependent K+ current, ISAHP, by the neuropeptides CRF, VIP, abd CGRP in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Am Physiol Soc, 2000, 83(4): 2071–2079
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Wang, H. The early signal substances induced by heat stress in brains of mice. Front. Med. China 2, 391–395 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-008-0075-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-008-0075-1