Abstract
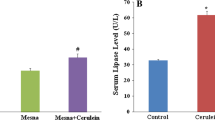
In order to explore the effects of retrograde infusion of chondroitin-sulfate via the pancreatic duct on cytoprotection and attenuation of oxidative damage during acute necrotic pancreatitis (ANP), male Wistar rats were randomly divided into three groups: A, B (experimental groups) and C (sham operation, control group). The rats in group A was subjected to retrograde injection of 5% sodium taurocholate via the pancreatic duct, and those in group B received chondroitin-sulfate therapy after ANP induction. All rats in three groups were killed at 6 h. The levels of malondialdehyde (MAD), total superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH), adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and serum amylase (SAM) were measured. The morphologic changes in pancreatic tissues were observed. It was found that the level of SAM was increased in group A and group B, with corresponding pathological changes of ANP. The levels of ATP, GSH and SOD in group A were decreased markedly and MDN increased significantly as compared with those in group B (P<0.01). In group B, the histopathologic damage was attenuated to a certain extent in comparison to that in group A. It was concluded that endogenous antioxidants were significantly reduced and lipid peroxidation increased during ANP. Retrograde infusion of chondroitin-sulfate via pancreatic duct could alleviate the pancreatic cell damage as a sort of scavengers of oxygen free radicals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho H J, Suonpaa K, Aho la R A, Nevalainen T J. Experimental pancreatitis in the rat-ductal factors in sodium taurocholate-induced acute pancreatitis. Exp Path, 1984, 25(2): 73–79
Hansson K, Lundh G, Stenram U. The toxic effects of bile salts on the pancreas. Acta Chir Scand, 1967, 375(1): 48–64
Aho H J, Koskensalo S M L, Nevalainen T J. Experimental pancreatitis in the rat Sodium taurocholate-induced acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol, 1980, 15(3): 411–416
Gough D B, Boyle B, Joyce W P, Delaney C P, McGeeney K F, Gorey T F, Fitzpatrick J M. Free radical inhibition and serial chemiluminescence in evolving experimental pancreatitis. Br J Surg, 1990, 77(11): 1258–1259
Formela C S, Galloway S W, Kingsnorth A N. Inflammatory mediators in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg, 1995, 82(1): 6–13
Sakorafas G H, Tsiotou A G. Etiology and pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis: current concepts. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2000, 30(2): 343–356
Sweiry J H, Mann G E. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl, 1996, 219(1): 10–15
Albertini R, Deluca G, Passi A, Moratti R, Abuja P M. Chondroitin-4-Sulfate protects high-density lipoprotein against copper-dependent oxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys, 1999, 365(1): 143–149
Albertini R, Passi A, Abuja P M, De Luca G. The effect of glycos-aminoglycans and proteoglycans on lipid peroxidation. Int J Mol Med, 2000, 6(2): 129–136
Campo G M, Avonoso A, Campo S, Ferlazzo A M, Altavilla D, Micali C, Calatroni A. Aromatic trap analysis of free radicals production in experimental collagen-induced arthritis in the rat: protective effect of glycosaminoglycans treatment. Free Radic Res, 2003, 37(3): 257–268
Campo G M, Avonoso A, Campo S, Ferlazzo A M, Altavilla D, Calatroni A. Efficacy of treatment with glycosaminglycans on experimental collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Arthritis Res Ther, 2003, 5(3): 122–131
Niederau C, Ferrell L D, Grendell J H. Caerulein-induced acute necrotizing pancreatitis in mice: protective effects of proglumide, benzotript, and secretin. Gastroenterology, 1985, 88(9): 1192–1204
Ellman G L. Tissue sulphydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys, 1959, 82(1): 70–77
Salzman A L, Menconi M J, Unno N, Ezzell R M, Casey D M, Gonzalez P K, Fink M P. Nitric oxide dilates tight junctions and depletes ATP in cultured Caco-2Bbe intestinal epithelial monolayers. Am J Physiol, 1995, 268(2 Pt 1): G261–G373
Schulz H U, Niedrau C, Klonowski-Stumpe H, Halangk W, Luthen R, Lippert H. Oxidative stress in acute pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999, 46(29): 2736–2750
Grune T, Reinheckel T, Davies K J. Degradation of oxidized proteins in mammalian cells. FASEB J, 1997, 11(5): 526–534
Niederau C, Ude K, Niederau M, Strohmeyer G, Ferrell L D, Grendell J H. Effects of the seleno-organic substance Ebselen in two different models of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas, 1991, 6(3): 282–290
Wang Z, Iguchi H, Ohshio G. Increased pancreatic metallothionein and GSH levels protecting against cerulean-and taurocholate-induced acute pancreatitis in rats.Pancreas, 1996, 13(2): 173–183
Niederau C, Niederau M, Borchard F, Ferrell L D, Grendell J H. Effects of antioxidants and free radical scavengers in three different models of acute pancreatitis.Pancreas, 1992, 7(5): 486–496.
Sugahara K, Kitagawa H. Recent advances in the study of the biosynthesis and function of sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Curr Opin Strct Biol, 2000, 10(5): 518–527
Beren J, Hill SL, Diener-West M, Rose NR. Effect of pre-loading oral glucosamine HCL/Chondroition Sulfate/manganese ascorbate combination on experimental arthritis in rats. Exp Biol Med, 2001, 226(2): 144–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from J Chin Med Univ, 2006, 35(3): 297–298, 301 [译自: 中国医科大学学报]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Z., Guo, R., Xie, C. et al. Alleviation of cell damage in experimental ANP in rats by administration of chondroitin-sulfate reduces. Front. Med. China 1, 36–40 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-007-0007-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-007-0007-5