Abstract
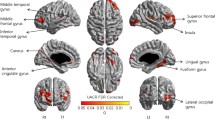
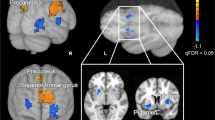
Prior neuroimaging studies of the relationship between the kidney and the brain have been limited to clinical populations and have largely relied on a single modality. We sought to examine the kidney-brain associations in healthy subjects using a combined analysis of multi-modal imaging data. Structural, diffusion, and perfusion magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans were performed to measure cortical thickness, white matter integrity, and cerebral blood flow in 157 healthy young adults. Peripheral venous blood samples were collected to measure serum renal function indexes. Correlation analyses were performed to investigate the relations between brain MRI measures and renal function indexes. Results showed that higher serum uric acid level was associated with increased cortical thickness in the transverse temporal gyrus. We also found that decreased serum creatinine level was linked to lower white matter integrity in the sagittal stratum, anterior corona radiata, superior corona radiata, and external capsule. Furthermore, we observed that increased serum uric acid level was related to hyperperfusion in the opercular and triangular parts of inferior frontal gyrus and supramarginal gyrus, and hypoperfusion in the calcarine sulcus, cuneus and lingual gyrus. More importantly, mediation analysis revealed that the relationship between serum uric acid and working memory performance was mediated by perfusion in the supramarginal gyrus and lingual gyrus. These findings not only may extend current knowledge regarding the relationship between the kidney and the brain, but also may inform real-world clinical practice by identification of potential brain regions vulnerable to renal dysfunction.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Abdul-Kareem, I. A., & Sluming, V. (2008). Heschl gyrus and its included primary auditory cortex: Structural MRI studies in healthy and diseased subjects. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 28(2), 287–299. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.21445
Andrejevic, M., Meshi, D., van den Bos, W., & Heekeren, H. R. (2017). Individual differences in social desirability are associated with white-matter microstructure of the external capsule. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 17(6), 1255–1264. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-017-0548-2
Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage, 38(1), 95–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.007
Aslan, S., & Lu, H. (2010). On the sensitivity of ASL MRI in detecting regional differences in cerebral blood flow. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 28(7), 928–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2010.03.037
Barkhof, F., Haller, S., & Rombouts, S. A. (2014). Resting-state functional MR imaging: A new window to the brain. Radiology, 272(1), 29–49. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14132388
Baxmann, A. C., Ahmed, M. S., Marques, N. C., Menon, V. B., Pereira, A. B., Kirsztajn, G. M., & Heilberg, I. P. (2008). Influence of Muscle Mass and Physical Activity on Serum and Urinary Creatinine and Serum Cystatin C. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 3(2), 348–354. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.02870707
Bjornstad, P., Lanaspa, M. A., Ishimoto, T., Kosugi, T., Kume, S., Jalal, D., & Nakagawa, T. (2015). Fructose and uric acid in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia, 58(9), 1993–2002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-015-3650-4
Bugnicourt, J. M., Godefroy, O., Chillon, J. M., Choukroun, G., & Massy, Z. A. (2013). Cognitive disorders and dementia in CKD: The neglected kidney-brain axis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 24(3), 353–363. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2012050536
Burn, D. J., & Bates, D. (1998). Neurology and the kidney. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 65(6), 810–821. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.65.6.810
Buxton, R. B., Frank, L. R., Wong, E. C., Siewert, B., Warach, S., & Edelman, R. R. (1998). A general kinetic model for quantitative perfusion imaging with arterial spin labeling. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 40(3), 383–396. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.1910400308
Cabeza, R., Ciaramelli, E., & Moscovitch, M. (2012). Cognitive contributions of the ventral parietal cortex: An integrative theoretical account. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 16(6), 338–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2012.04.008
Canovas, R., Cuartero, M., & Crespo, G. A. (2019). Modern creatinine (Bio)sensing: Challenges of point-of-care platforms. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 130, 110–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.01.048
Chan-Seng, E., Moritz-Gasser, S., & Duffau, H. (2014). Awake mapping for low-grade gliomas involving the left sagittal stratum: Anatomofunctional and surgical considerations. Journal of Neurosurgery, 120(5), 1069–1077. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.1.jns132015
Dahnke, R., Yotter, R. A., & Gaser, C. (2013). Cortical thickness and central surface estimation. NeuroImage, 65, 336–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.09.050
Davenport, A. (2008). The brain and the kidney–organ cross talk and interactions. Blood Purification, 26(6), 526–536. https://doi.org/10.1159/000167800
Davis, A. D., Hassel, S., Arnott, S. R., Harris, J., Lam, R. W., Milev, R., & Hall, G. B. (2019). White matter indices of medication response in major depression: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging, 4(10), 913–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2019.05.016
DiBona, G. F. (2001). Peripheral and central interactions between the renin-angiotensin system and the renal sympathetic nerves in control of renal function. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 940, 395–406. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03693.x
El Ridi, R., & Tallima, H. (2017). Physiological functions and pathogenic potential of uric acid: A review. Journal of Advanced Research, 8(5), 487–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2017.03.003
Elias, M. F., Elias, P. K., Seliger, S. L., Narsipur, S. S., Dore, G. A., & Robbins, M. A. (2009). Chronic kidney disease, creatinine and cognitive functioning. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 24(8), 2446–2452. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfp107
Euser, S. M., Hofman, A., Westendorp, R. G., & Breteler, M. M. (2009). Serum uric acid and cognitive function and dementia. Brain, 132(Pt 2), 377–382. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awn316
Granger, J. P., Abram, S., Stec, D., Chandler, D., & LaMarca, B. (2006). Endothelin, the kidney, and hypertension. Current Hypertension Reports, 8(4), 298–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-006-0068-x
Haller, S., Zaharchuk, G., Thomas, D. L., Lovblad, K. O., Barkhof, F., & Golay, X. (2016). Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion of the Brain: Emerging Clinical Applications. Radiology, 281(2), 337–356. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2016150789
Hamm, L. L., Nakhoul, N., & Hering-Smith, K. S. (2015). Acid-Base Homeostasis. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 10(12), 2232–2242. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.07400715
Hannawi, Y., Yanek, L. R., Kral, B. G., Vaidya, D., Becker, L. C., Becker, D. M., & Nyquist, P. A. (2018). Hypertension Is Associated with White Matter Disruption in Apparently Healthy Middle-Aged Individuals. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 39(12), 2243–2248. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5871
Hartung, E. A., Erus, G., Jawad, A. F., Laney, N., Doshi, J. J., Hooper, S. R., & Furth, S. L. (2018). Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Children and Young Adults With CKD. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 72(3), 349–359. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.11.024
Hayes, A. F. (2009). Beyond Baron and Kenny: Statistical Mediation Analysis in the New Millennium. Communication Monographs, 76(4), 408–420. https://doi.org/10.1080/03637750903310360
Hua, K., Zhang, J., Wakana, S., Jiang, H., Li, X., Reich, D. S., & Mori, S. (2008). Tract probability maps in stereotaxic spaces: Analyses of white matter anatomy and tract-specific quantification. NeuroImage, 39(1), 336–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.053
Klein, J. D., Blount, M. A., & Sands, J. M. (2011). Urea transport in the kidney. Comprehensive Physiology, 1(2), 699–729. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c100030
Latourte, A., Bardin, T., & Richette, P. (2018). Uric acid and cognitive decline: A double-edge sword? Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 30(2), 183–187. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0000000000000472
Lawrence, S. J. D., van Mourik, T., Kok, P., Koopmans, P. J., Norris, D. G., & de Lange, F. P. (2018). Laminar organization of working memory signals in human visual cortex. Current Biology, 28(21), 3435-3440.e3434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.08.043
Lerch, J. P., van der Kouwe, A. J., Raznahan, A., Paus, T., Johansen-Berg, H., Miller, K. L., & Sotiropoulos, S. N. (2017). Studying neuroanatomy using MRI. Nature Neuroscience, 20(3), 314–326. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4501
Levey, A. S., & Eckfeldt, J. H. (2017). Estimating glomerular filtration rate using serum creatinine. Clinical Chemistry, 63(6), 1161–1162. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2016.262352
Liu, H. S., Hartung, E. A., Jawad, A. F., Ware, J. B., Laney, N., Port, A. M., & Detre, J. A. (2018). Regional cerebral blood flow in children and young adults with chronic kidney disease. Radiology, 288(3), 849–858. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2018171339
Maiuolo, J., Oppedisano, F., Gratteri, S., Muscoli, C., & Mollace, V. (2016). Regulation of uric acid metabolism and excretion. International Journal of Cardiology, 213, 8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.08.109
Mandal, A. K., & Mount, D. B. (2015). The Molecular physiology of uric acid homeostasis. Annual Review of Physiology, 77(1), 323–345. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-021113-170343
Medler, S., & Harrington, F. (2013). Measuring dynamic kidney function in an undergraduate physiology laboratory. Advances in Physiology Education, 37(4), 384–391. https://doi.org/10.1152/advan.00057.2013
Mitrakou, A. (2011). Kidney: Its impact on glucose homeostasis and hormonal regulation. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 93, S66–S72. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8227(11)70016-x
Morosan, P., Rademacher, J., Schleicher, A., Amunts, K., Schormann, T., & Zilles, K. (2001). Human primary auditory cortex: Cytoarchitectonic subdivisions and mapping into a spatial reference system. NeuroImage, 13(4), 684–701. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2000.0715
Mu, J., Chen, T., Liu, Q., Ding, D., Ma, X., Li, P., & Zhang, M. (2018). Abnormal interaction between cognitive control network and affective network in patients with end-stage renal disease. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 12(4), 1099–1111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9782-z
Muller, F., Dommergues, M., Bussières, L., Lortat-Jacob, S., Loirat, C., Oury, J. F., & Dumez, Y. (1996). Development of human renal function: Reference intervals for 10 biochemical markers in fetal urine. Clinical Chemistry, 42(11), 1855–1860.
Owen, A. M., McMillan, K. M., Laird, A. R., & Bullmore, E. (2005). N-back working memory paradigm: A meta-analysis of normative functional neuroimaging studies. Human Brain Mapping, 25(1), 46–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20131
Papanicolaou, A. C., Rezaie, R., & Simos, P. G. (2019). The auditory and association cortex and language evaluation methods. Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 160, 465–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64032-1.00031-X
Peters, B., Kaiser, J., Rahm, B., & Bledowski, C. (2015). Activity in human visual and parietal cortex reveals object-based attention in working memory. Journal of Neuroscience, 35(8), 3360–3369. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3795-14.2015
Pundir, C. S., Jakhar, S., & Narwal, V. (2019a). Determination of urea with special emphasis on biosensors: A review. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 123, 36–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.09.067
Pundir, C. S., Kumar, P., & Jaiwal, R. (2019b). Biosensing methods for determination of creatinine: A review. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 126, 707–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.11.031
Schwartz, G. J., Munoz, A., Schneider, M. F., Mak, R. H., Kaskel, F., Warady, B. A., & Furth, S. L. (2009). New equations to estimate GFR in children with CKD. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 20(3), 629–637. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2008030287
Seifter, J. L., & Samuels, M. A. (2011). Uremic encephalopathy and other brain disorders associated with renal failure. Seminars in Neurology, 31(2), 139–143. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1277984
Silk, T. J., Bellgrove, M. A., Wrafter, P., Mattingley, J. B., & Cunnington, R. (2010). Spatial working memory and spatial attention rely on common neural processes in the intraparietal sulcus. NeuroImage, 53(2), 718–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.068
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Johansen-Berg, H., Rueckert, D., Nichols, T. E., Mackay, C. E., & Behrens, T. E. (2006). Tract-based spatial statistics: Voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage, 31(4), 1487–1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.02.024
Tana, C., Ticinesi, A., Prati, B., Nouvenne, A., & Meschi, T. (2018). Uric acid and cognitive function in older individuals. Nutrients, 10(8), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10080975
Tanaka, S., & Okusa, M. D. (2020). Crosstalk between the nervous system and the kidney. Kidney International, 97(3), 466–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2019.10.032
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., & Joliot, M. (2002). Automated Anatomical Labeling of Activations in SPM Using a Macroscopic Anatomical Parcellation of the MNI MRI Single-Subject Brain. NeuroImage, 15(1), 273–289. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2001.0978
Vannorsdall, T. D., Kueider, A. M., Carlson, M. C., & Schretlen, D. J. (2014). Higher baseline serum uric acid is associated with poorer cognition but not rates of cognitive decline in women. Experimental Gerontology, 60, 136–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2014.10.013
Wakana, S., Jiang, H., Nagae-Poetscher, L. M., van Zijl, P. C., & Mori, S. (2004). Fiber tract-based atlas of human white matter anatomy. Radiology, 230(1), 77–87. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2301021640
Wenger, R. H., & Kurtz, A. (2011). Erythropoietin. Comprehensive Physiology, 1(4), 1759–1794. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c100075
Xu, G., Rowley, H. A., Wu, G., Alsop, D. C., Shankaranarayanan, A., Dowling, M., & Johnson, S. C. (2010). Reliability and precision of pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI on 30 T and comparison with 15 O-water PET in elderly subjects at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. NMR in Biomedicine, 23(3), 286–293. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1462
Yang, Y., Zhu, D. M., Zhang, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, B., & Yu, Y. (2020). Brain structural and functional alterations specific to low sleep efficiency in major depressive disorder. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 14, 50. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00050
Ye, B. S., Lee, W. W., Ham, J. H., Lee, J. J., Lee, P. H., Sohn, Y. H., & Neuroimaging, A. D. (2016). Does serum uric acid act as a modulator of cerebrospinal fluid Alzheimer’s disease biomarker related cognitive decline? European Journal of Neurology, 23(5), 948–957. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.12969
Yotter, R. A., Dahnke, R., Thompson, P. M., & Gaser, C. (2011). Topological correction of brain surface meshes using spherical harmonics. Human Brain Mapping, 32(7), 1109–1124. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21095
Yousaf, T., Dervenoulas, G., & Politis, M. (2018). Advances in MRI Methodology. International Review of Neurobiology, 141, 31–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.irn.2018.08.008
Zhang, C., Yang, Y., Zhu, D. M., Zhao, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, B., & Yu, Y. (2020). Neural correlates of the association between depression and high density lipoprotein cholesterol change. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 130, 9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.07.012
Zhang, L. J., Wen, J., Liang, X., Qi, R., Schoepf, U. J., Wichmann, J. L., & Lu, G. M. (2016). Brain default mode network changes after renal transplantation: a diffusion-tensor imaging and resting-state functional mr imaging study. Radiology, 278(2), 485–495. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015150004
Zhu, J., Zhuo, C., Qin, W., Xu, Y., Xu, L., Liu, X., & Yu, C. (2015). Altered resting-state cerebral blood flow and its connectivity in schizophrenia. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 63, 28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.03.002
Zhu, J., Zhuo, C., Xu, L., Liu, F., Qin, W., & Yu, C. (2017). Altered coupling between resting-state cerebral blood flow and functional connectivity in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 43(6), 1363–1374. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbx051
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers: 81801679, 82071905 and 81771817).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SL, CW, JZ and YY conceptualized and designed the study. SL was responsible for conducting the analyses, preparing the first draft of the manuscript, and preparing the manuscript for submission. Jiajia Zhu was responsible for obtaining funding for the study, supervising the analyses, and editing drafts of the manuscript. SL, CW, YY, HC, MZ, LS, SZ, YX were responsible for data collection and initial data preprocessing. All authors contributed to and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Wang, C., Yang, Y. et al. Brain structure and perfusion in relation to serum renal function indexes in healthy young adults. Brain Imaging and Behavior 16, 1014–1025 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00565-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00565-x