Abstract
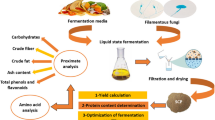
Lignocellulosic substrates are a good carbon source and provide rich growth media for a variety of microorganisms which produce industrially important enzymes. Cellulases are a group of hydrolytic enzymes such as filter paperase (FPase), carboxymethyl cellulase (CMCase) and β-glucosidase—responsible for release of sugars in the bioconversion of the lignocellulosic biomass into a variety of value-added products. This study examined cellulase production by a newly isolated Aspergillus unguis on individual lignocellulosic substrates in solid state fermentation (SSF). The maximum peak production of enzymes varied from one substrate to another, however, based on the next best solid support and local availability of groundnut fodder supported maximum enzyme yields compared with other solid supports used in this study. Groundnut fodder supported significant production of FPase (5.9 FPU/g of substrate), CMCase (1.1 U/g of substrate) and β-glucosidase activity (6.5 U/g of substrate) in SSF. Considerable secretion of protein (27.0 mg/g of substrate) on groundnut fodder was recorded. Constant increment of protein content in groundnut fodder due to cultivation of A. unguis is an interesting observation and it has implications for the improvement of nutritive value of groundnut fodder for cattle.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archana A, Satyanarayana T (1997) Xylanase production by thermophilic Bacillus licheniformis A 99 in solid state fermentation. Enzyme Microb Technol 21:12–17
Bevan MW, Franssen MCR (2006) Investing in green and white biotech. Nat Biotechnol 24:765–767
Chandra MS, Reddy BR (2013) Exoglucanase production by Aspergillus niger grown on wheat bran. Ann Microbiol 63:871–877
Chandra MS, Viswanath B, Reddy BR (2007) Cellulolytic enzymes on lignocellulosic substrates in solid state fermentation by Aspergillus niger. Indian J Microbiol 47:323–328
Chandrakant P, Bisaria VS (1998) Simultaneous bioconversion of cellulose and hemicelluloses to ethanol. Crit Rev Biotechnol 18:295–331
Daroit DJ, Silveir ST, Hertz PF, Brandelli A (2007) Production of extracellular β-glucosidase by Monascus purpureus on different growth substrates. Process Biochem 42(5):904–908
Deschamps F, Giuliano C, Asther M, Huet MC, Roussos S (1985) Cellulase production by Trichoderma harzianum in static and mixed solid state fermentation reactors under nonaseptic conditions. Biotechnol Bioeng 27:869–872
Deswal D, Khasa YP, Kuhad RC (2011) Optimization of cellulase production by a brown rot fungus Fomitopsis sp. RCK2010 under solid state fermentation. Bioresour Technol 102:6065–6072
Dienes D, Egyhazi A, Reczey K (2004) Treatment of recycled fiber with Trichoderma cellulases. Ind Crop Prod 20(1):11–21
Gao JM, Weng HB, Zhu DH, Yuan MX, Guan FX, Xi Y (2008) Production and characterization of cellulolytic enzymes from the thermoacidophilic fungal Aspergillus terreus M11 under solid state cultivation of corn stover. Bioresour Technol 99(16):7623–7629
Gardes MTF, White TJ, Fortin JA, Bruns TD, Taylor JW (1991) Identification of indigenous and introduced symbiotic in ectomycorrhizae by amplification of the nuclear and mitochondrial ribosomal DNA. Can J Bot 69:180–190
Ghosh TK (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59:257–268
Hatti-Kaul R, Ulrika T, Linda GB, Orjesson P (2007) Industrial biotechnology for the production of bio-based chemicals acradle to grave perspective. Trend Biotechnol 25:119–124
Herr D (1979) Secretion of cellulases and β-glucosidase by Trichoderma viride TTCC 1433 in submerged cultures on different substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 21:1361–1363
Kang SW, Park YS, Lee JS, Hong SI, Kim SW (2004) Production of cellulases and hemicellulases by Aspergillus niger KK2 from lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 91(2):153–156
Lonsane BK, Ghildyal NP, Butiatman S, Ramakrishma SV (1985) Engineering aspects of solid state fermentation. Enzyme Microb Technol 7:258–265
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin Phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, Zyl VWH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:506–577
Lynd LR, Vanyl WH, McBride JE, Laser M (2005) Consolidated bioprocessing of cellulosic biomass: an update. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:577–583
Madhavan A, Srivastava A, Kondo A, Bisaria VS (2012) Bioconversion of lignocellulose derived sugars to ethanol by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Crit Rev Biotechnol 32:22–48
Mandels M, Weber J (1969) The production of cellulases. In: George JH (ed) Advances in Chemistry Series, vol 95. American Chemical Society, Washington, pp 391–414
Megharaj M, Kookana K, Singleton S (1999) Activities of fenamiphos on native algal population and some enzyme activities in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1549–1553
Muniswaran PKA, Charyulu NCLN (1994) Solid substrate fermentation of coconut coir pith for cellulase production. Enzym Microb Technol 16:436–440
Ortega N, Busto MD, Perez-Mateos M (2000) Enzymatic saccharification of pretreated wheat straw by T. reesei cellulases and A. niger β-glucosidase. Biocat Biotrans 18:311–330
Pan X, Gilkes N, Kadla J, Pye K, Saka S, Gregg D, Ehara K, Xie D, Lam D, Saddler J (2006) Bioconversion of hybrid poplar to ethanol and co-products using an organosolv fractionation process: optimization of process yields. Biotechnol Bioeng 94(5):851–861
Pandey A, Nigam P, Soccol CR, Soccol VT, Singh D, Mohan R (2000) Advances in microbial amylases. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 31:135–152
Pericin MD, Madarev ZS, Radulovic MLJ, Krinjar MM (2008) Evaluate of pumpkin oil cake as substrate for the cellulase production by Penicillium roqueforti in solid state fermentation. Roum Biotechnol Lett 13:3815–3820
Raghavarao KSMS, Ranganathan TV, Karanth NG (2003) Some engineering aspects of solid state fermentation. Biochem Eng J 13:127–135
Sato K, Sudo S (1990) Small scale solid state fermentation. In: Demain AL, Davies JE (eds) Manual of industrial microbiology and biotechnology. ASM Press, Washington, pp 61–79
St-Germain G, Summerbell R (1996) Identifying filamentous fungi—a clinical laboratory handbook, 1st edn. Star Publishing Co., Belmont
Sticklen M (2006) Plant genetic engineering to improve biomass characteristics for biofuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:315–319
Szetela RW, Winnicki TZ (1981) A novel method for determining the parameters of microbial kinetics. Biotechnol Bioeng 23:1485–1490
Valascova V, Baldrian P (2006) Degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose by the brown-rot fungus Piptoporus betulinus—production of extracellular enzymes and characterization of major cellulases. Microbiol 152:3613–3622
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com
Corresponding editor: Tao Xu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shruthi, K., Yadav, P.S., Prasad, B.V.S. et al. Cellulase production by Aspergillus unguis in solid state fermentation. J. For. Res. 30, 205–212 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0619-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0619-4