Abstract
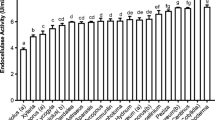
β-Exoglucanase production on the lignocellulosic material, wheat bran, by Aspergillus niger under solid state fermentation (SSF) on a laboratory scale was investigated. Different fermentation parameters, such as moisture content, initial pH, temperature, depth of the substrate, and inoculum size on exoglucanase production were optimized. Moisture content of 40 %, pH of 7.0, substrate depth of 1.0 cm, inoculum size of 2 × 106 spores/g of wheat bran, and temperature at 30 °C were optimal for maximum production of exoglucanase. Maximum yields of exoglucanase with 28.60 FPU/g of wheat bran were obtained within 3 days of incubation under optimal conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikat K, Bhattacharyya BC (2004) Optimization of some parameters of solid state fermentation of wheat bran for protease production by a local strain of Rhizopus oryzae. Acta Biotechnol 20(2):149–159
Badhan AK, Chadha BS, Kaur J, Saini HS, Bhat MK (2007) Production of multiple xylanolytic and cellulolytic enzymes by thermophilic fungus Myceliophthora sp. IMI 387099. Bioresour Technol 98:504–510
Bakri YP, Jacques P, Thonart (2003) Xylanase production by Penicillium canescens 10-10C in solid state fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 108:737–748
Berka R, Coleman N, Ward M (1992) Aspergillus. In: Bennet J and Klich MA (eds) Industrial enzymes from Aspergillus species. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, pp 155–202
Chahal DS (1983) Growth characteristics of microorganisms in solid state fermentation for upgrading of protein value of lignocelluloses and cellulase production. In: Blanch HW, Poputsakis ET, Stephanopoulous G (eds) Foundation of biochemical engineering kinetics and thermodynamics in biological systems. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 207–421, ACS Symp. Series No. 207
Chandra MS, Viswanath B, Reddy BR (2006) Production of cellulolytic enzymes in solid state fermentation by Aspergillus niger. In: Pullaiah T, Venkata Raju RR, Sudhakar C, Ravi Prasad Rao B, Timma Naik S (eds) Recent trends in plant sciences. Regency, New Delhi, pp 34–38
Chandra MS, Viswanath B, Reddy BR (2007) Cellulolytic enzymes on lignocellulosic substrates in solid state fermentation by Aspergillus niger. Indian J Microbiol 47:323–328
Erikson KE, Patterson B (1975) Extra cellular enzyme system produced by the fungus Sporotrichum pulverulentum. Biotechnol Bio eng 20:317–332
Fadel M (1999) Utilization of potato chips industry by products for the production of thermostable alpha-amylase using solid state fermentation system. Egypt J Microbiol 34:1–11
Fadel M (2000) Production physiology of cellulases and β-glucosidase enzymes of Aspergillus niger grown under solid state fermentation conditions. J Biol Sci 1(5):401–411
Harikrishna S, Sekhar Rao KC, Suresh Babu J, Srirami Reddy D (2000) Studies on the production and application of cellulase from Trichoderma reesei QM9414. Bioproc Eng 22:467–470
Ikasari L, Mitchell DA (1994) Protease production by Rhizopus oligosporus in solid state fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 10:320–324
Jha K, Khare SK, Gandhi AP (1995) Solid state fermentation of soyhull for the production of cellulase. Bioresour Technol 54:321–322
Kari A, Flengsrud R, Lindahl V, Tronsmo A (1994) Characterization of production and enzyme properties of an endo-ß-1,4-glucanase from Bacillus subtilis ek-2 isolated from compost soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 66:319–326
Kashyap P, Sabu A, Pandey A, Szakacs G (2002) Extra-cellular L-glutaminase production by Zygosaccharomyces rouxii under solid-state fermentation. Proc Biochem 38:307–312
Krishna C (1999) Production of bacterial cellulases by solid state bioprocessing of banana wastes. Bioresour Technol 69:231–239
Lonsane BK, Ghild NP, Budeatman S, Ramakrishna SV (1985) Engineering aspects of solid state fermentation. Enzyme Microb Technol 7:258–265
Mandels M, Weber J (1969) Cellulases and its application. In: Gould RF (ed) Advances in chemistry series, vol 95. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 391–414
Maurya DP, Singh D, Pratap D, Maurya JP (2012) Optimization of solid state fermentation conditions for production of cellulase by Trichoderma reesei. J Environ Biol 33:5–8
Megharaj M, Kookana K, Singleton S (1999) Activities of fenamiphos on native algal population and some enzyme activities in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1549–1553
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31:426–429
Mullings R (1985) Measurement of sacharification by cellulases. Enzyme Microb Technol 7:586–591
Muniswaran PKA, Charyulu NCLN (1994) Solid substrate fermentation of coconut coir pith for cellulase production. Enzyme Microb Technol 16:436–440
Muthuvelayudham R, Viruthagiri T (2006) Fermentative production and kinetics of cellulase protein on Trichoderma reesei using sugarcane bagasse and rice straw. Afr J Biotechnol 5(20):1873–1881
Narasimha G, Babu GVAK, Reddy BR (1999) Cellulolytic activity of fungal cultures isolated from soil contaminated with effluents of cotton ginning industry. J Environ Biol 20(3):235–239
Nikolay SA, Robson K, Wilson DB (1998) Regulation of biosynthesis of individual cellulases in Thermomonospora fusca. J Bacteriol 180:3529–3532
Ojumu TV, Solomon BO, Betiku E, Layokun SK, Amigun B (2003) Cellulase production by Aspergillus flavus Linn isolate NSPR 101 fermented in sawdust, bagasse and corncob. Afr J Biotechnol 2:150–152
Oxenboll K (1994) Aspergillus enzymes and industrial uses. In: Powell KA (ed) The genus Aspergillus. Plenum, New York, pp 147–158
Panagiotou G, Kekos D, Macris BJ, Christakopoulos P (2003) Production of cellulolytic and xylanolytic enzymes by Fusarium oxysporum grown on corn stover in solid state fermentation. Ind Crops Prod 18:37–45
Raimbault M, Alazard D (1980) Culture method to study fungal growth in solid state fermentation. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 9:199–209
Rajoka MI (2004) Influence of various fermentation variables on exoglucanase production in Cellulomonas flavigena. Electron J Biotechnol 7(3):259–265
Ramana Murthy V, Karanth NG, Raghava KS, Rao MS (1993) Biochemical engineering aspects of solid state fermentation. Adv Appl Microbiol 38:99–147
Ridder ER, Nokes S, Knutson BL (1997) Production of hemicellulolytic enzymes (Xylanases) using solid state fermentation of Trichoderma longibrachiatum. ASAE Annual International Meeting, Minnesota, pp 1–11
Roussos S, Raimbault M, Saucedo-Castaneda G, Viniegra-Gonzalez G, Lonsane BK (1991) Kinetics and ratios of carboxymethyl cellulase and filter paper activities of the cellulolytic enzymes produced by Trichoderma harzianum on different substrates in solid state fermentation. Micol Neotrop Apl 4:19–40
Sandhya X, Lonsane BK (1994) Factors influencing fungal degradation of total soluble carbohydrates in sugarcane – press mud under solid state fermentation. Proc Biochem 29:295–301
Shafique S, Asgher M, Sheikh MA, Asad MJ (2004) Solid state fermentation of banana stalk for exoglucanase production. Int J Agri Biol 6(3):488–491
Sharma DK, Tiwari M, Behere BK (1996) Solid state fermentation of new substrates for production of cellulase and other biopolymer hydrolyzing enzymes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 15:495–500
Singh J, Garg AP (1995) Production of cellulases by Gliocladium virens Miller et al. on Eichhornia under solid state fermentation conditions. J Indian Bot Soc 74:305–309
Singhania RR, Sukumaran RK, Pillai A, Prema P, Szakacs G, Pandey A (2006) Solid state fermentation of lignocellulosic substrates for cellulase production by Trichoderma reesei NRRL 11460. Ind J Biotechnol 5:332–336
Sinnott M (1997) Study of hemicellulolytic enzymes from the fungi Phanerochaete chrsosporium and Trichoderma ressei. J Bacteriol 133:465–471
Sunitha M, Rani E, Devaki K (2006) Production of cellulase from Aspergillus niger and Bacillus subtilis using pine apple peel as substrate by solid state fermentation. Asian J Microbiol Biotechnol Environ Sci 8(3):577–580
Wen ZHY, Liao W, Chen SL (2005) Production of cellulase by Trichoderma reesei from dairy manure. Bioresour Technol 96:91–99
Xavier S, Lonsane BK (1994) Factors influencing fungal degradation of total soluble carbohydrates in sugarcane-press mud under solid state fermentation. Proc Biochem 16:435–440
Yang YH, Wang BC, Wang QH, Xiang LJ, Duan CR (2004) Research on solid-state fermentation on rice chaff with a microbial consortium. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 34:1–6
Zhang YHP, Lynd LR (2004) Toward an aggregated understanding of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose: Noncomplexed cellulase systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 88:797–824
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subhosh Chandra, M., Rajasekhar Reddy, B. Exoglucanase production by Aspergillus niger grown on wheat bran. Ann Microbiol 63, 871–877 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0538-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0538-0