Abstract
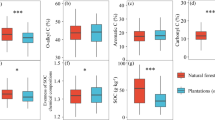
We investigated the effect of forest thinning on soil nitrogen mineralization, nitrification and transformation in a Cryptomeria japonica plantation at high elevation to provide basic data for forest management. We chose four study plots for control, light, medium and heavy thinning treatment, and three sub-plots for buried bag studies at similar elevations in each treatment plot to measure the net N mineralization and nitrification rates in situ. The contents of soil inorganic N (ammonium and nitrate) were similar between treatments, but all varied with season, reaching maxima in September 2003 and 2004. The seasonal maximum net Nmin rates after four treatments were 0.182, 0.246, 0.303 and 0.560 mg·kg−1·d−1 in 2003, and 0.242, 0.258, 0.411 and 0.671 mg·kg−1·d−1in 2004, respectively. These estimates are approximate with the lower annual rates of N mineralization for this region. Forest thinning can enhance net N mineralization and microbial biomass carbon. The percentage of annual rates of Nmin for different levels of forest thinning compared with the control plot were 13.4%, 59.8% and 154.2% in 2003, and 0.1%, 58.8% and 157.7% in 2004 for light, medium, and heavy thinning, respectively. These differences were related to soil moisture, temperature, precipitation, and soil and vegetation types. Well-planned multi-site comparisons, both located within Taiwan and the East-Asia region, could greatly improve our knowledge of regional patterns in nitrogen cycling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams M, Attiwill P. 1986. Nutrient cycling and nitrogen mineralization in eucalypt forests of south-eastern Australia. Plant and Soil, 92(3): 319–339.
APHA. 1998. Cadmium reduction method. In: Franson MAH (ed.), Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association, pp. 117–118.
Baeumler R, Zech W. 1998. Soil solution chemistry and impact of forest thinning in mountain forests in the Bavarian Alps. Forest Ecology and Management, 108(3): 231–238.
Bengtsson G, Bengtson P, Månsson KF. 2003. Gross nitrogen mineralization-, immobilization-, and nitrification rates as a function of soil C/N ratio and microbial activity. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 35(1): 143–154.
Binkley D, Hart SC. 1989. The components of nitrogen availability assessments in forest soils. Advances in Soil Sciences, 10: 57–112.
Blake GR, Hartge KH. 1986. Bulk density. In: Klute A (ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1. Physical and Mineralogical Methods. Madison: American Society of Agronomy, pp. 363–367.
Bonilla D, Rodà F. 1992. Soil nitrogen dynamics in a holm oak forest. Plant Ecology, 99–100(1): 247–257.
Donaldson JM, Henderson GS. 1990. Nitrification Potential of Secondary-Succession Upland Oak Forests: II. Regulation of Ammonium-Oxidizing Bacteria Populations. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 54(3): 898–902.
Dorich RA, Nelson DW. 1983. Direct Colorimetric Measurement of Ammonium in Potassium Chloride Extracts of Soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 47(4): 833–836.
Dyck WJ, Cole DW, Comerford NB. 1994. Impacts of forest harvesting on long-term site productivity. London: Chapman and Hall, pp. 363–368.
Eno CF. 1960. Nitrate Production in the Field by Incubating the Soil in Polyethylene Bags. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 24(4): 277–279.
Entry JA, Stark NM, Loewenstein H. 1986. Effect of timber harvesting on microbial biomass fluxes in a northern Rocky Mountain forest soil. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 16(5): 1076–1081.
Frederick LR. 1956. The formation of nitrate from ammonium nitrogen in soils: I. effect of temperature. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 20(4): 496–500.
Friedland AJ, Miller EK, Battles JJ, Thorne JF. 1991. Nitrogen deposition, distribution and cycling in a subalpine spruce-fir forest in the Adirondacks, New York, USA. Biogeochemistry, 14(1): 31–55.
Gessel SP. 1990. Sustained productivity of forest soils. Vancouver: Forestry Publications, Faculty of Forestry, University of British Columbia, p. 525.
Giardina CP, Ryan MG, Hubbard RM, Binkley D. 2001. Tree Species and Soil Textural Controls on Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization Rates. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65(4): 1272–1279.
Hart SC, Firestone MK. 1989. Evaluation of three in situ soil nitrogen availability assays. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 19(2): 185–191.
Hassink J. 1992. Effects of soil texture and structure on carbon and nitrogen mineralization in grassland soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 14(2): 126–134.
Ho CS. 1988. An introduction to the geology of Taiwan: explanatory text of the geologic map of Taiwan. 2nd Edition. Taipei: Central Geological Survey, Ministry of Economic Affairs, p. 192.
Jackson ML. 1979. Soil chemical analysis: advanced course. 2nd Edition. Madison: University of Wisconsin, p. 452.
Keeney DR. 1980. Prediction of Soil Nitrogen Availability in Forest Ecosystems: A Literature Review. Forest Science, 26(1): 159–171.
Knoepp J, Swank W. 2002. Using soil temperature and moisture to predict forest soil nitrogen mineralization. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 36(3): 177–182.
Knoepp JD, Swank WT. 1998. Rates of nitrogen mineralization across an elevation and vegetation gradient in the southern Appalachians. Plant and Soil, 204(2): 235–241.
Laverman AM, Zoomer HR, van Verseveld HW, Verhoef HA. 2000. Temporal and spatial variation of nitrogen transformations in a coniferous forest soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 32(11–12): 1661–1670.
Lensi R, Mazurier S, GourbiÉre F, and Josserand A. 1986. Rapid determination of the nitrification potential of an acid forest soil and assessment of its variability. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 18(2): 239–240.
Maithani K, Arunachalam A, Tripathi RS, Pandey HN. 1998. Nitrogen mineralization as influenced by climate, soil and vegetation in a subtropical humid forest in northeast India. Forest Ecology and Management, 109(1–3): 91–101.
Matson PA, Boone RD. 1984. Natural Disturbance and Nitrogen Mineralization: Wave-form Dieback of Mountain Hemlock in the Oregon Cascades. Ecology, 65(5): 1511–1516.
Matson PA, Vitousek PM. 1981. Nitrogen mineralization and nitrification potentials following clearcutting in the Hoosier National Forest, Indiana. Forest Science, 27(4): 781–791.
Mladenoff DJ. 1987. Dynamics of nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in hemlock and hardwood treefall gaps. Ecology, 68(5): 1171–1180.
Murakami M, Takeda H, Iwatsubo G. 1990. Seasonal changes in nitrogen mineralization rates in the soils of Chamaecyparis obtuse and Crytomeria japonica Plantations. Bulletin of the Kyoto University Forests, 62: 44–54.
Myrold DD, Huss-Danell K. 2003. Alder and lupine enhance nitrogen cycling in a degraded forest soil in Northern Sweden. Plant and Soil, 254(1): 47–56.
Myrold DD, Matson PA, Peterson DL. 1989. Relationships between soil microbial properties and aboveground stand characteristics of conifer forests in Oregon. Biogeochemistry, 8(3): 265–281.
Nadelhoffer K, Aber J, Melillo J. 1984. Seasonal patterns of ammonium and nitrate uptake in nine temperate forest ecosystems. Plant and Soil, 80(3): 321–335.
Nicolardot B, Fauvet G, Cheneby D. 1994. Carbon and nitrogen cycling through soil microbial biomass at various temperatures. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 26(2): 253–261.
Olson RK, Reiners WA. 1983. Nitrification in subalpine balsam fir soils: Tests for inhibitory factors. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 15(4): 413–418.
Owen JS, Wang MK, Wang CH, King HB, Sun HL. 2003. Net N mineralization and nitrification rates in a forested ecosystem in northeastern Taiwan. Forest Ecology and Management, 176(1–3): 519–530.
Paul EA, Clark FE. 1989. Soil microbiology and biochemistry. New York: Academic Press, p. 341–362.
Piccolo MC, Neill C, Cerri CC. 1994. Net nitrogen mineralization and net nitrification along a tropical forest-to-pasture chronosequence. Plant and Soil, 162(1): 61–70.
Powers RF. 1990. Nitrogen mineralization along an altitudinal gradient: Interactions of soil temperature, moisture, and substrate quality. Forest Ecology and Management, 30(1–4): 19–29.
Raghubanshi AS. 1992. Effect of topography on selected soil properties and nitrogen mineralization in a dry tropical forest. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 24(2): 145–150.
Rhoades CC, Coleman DC. 1999. Nitrogen mineralization and nitrification following land conversion in montane Ecuador. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 31(10): 1347–1354.
Rhoades JD. 1983. Cation exchange capacity. In: Page AL (ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties. Madison: Amer Society of Agronomy, pp. 149–157.
Robertson GP. 1982. Nitrification in Forested Ecosystems. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. B, Biological Sciences, 296(1082): 445–457.
Six J, Elliott ET, Paustian K. 1999. Aggregate and soil organic matter dynamics under conventional and no-tillage systems. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 63(5): 1350–1358.
Soil Survey Staff. 2006. Keys to Soil Taxonomy. 10th Edition. Washington, DC: United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, p. 341.
Standford G, Epstein E. 1974. Nitrogen mineralization-water relations in soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 38(1): 103–107.
Ste-Marie C, Houle D. 2006. Forest floor gross and net nitrogen mineralization in three forest types in Quebec, Canada. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38(8): 2135–2143.
Strader R, Binkley D, Wells C. 1989. Nitrogen mineralization in high elevation forests of the Appalachians. I. Regional patterns in southern spruce-fir forests. Biogeochemistry, 7(2): 131–145.
Sucoff E, Hong SG. 1974. Effects of thinning on needle water potential in red pine. Forest Science, 20(1): 25–29.
Tate RL. 1995. Soil microbiology. New York: Wiley, p. 253–341.
Thibodeau L, Raymond P, Camiré C, Munson AD. 2000. Impact of precommercial thinning in balsam fir stands on soil nitrogen dynamics, microbial biomass, decomposition, and foliar nutrition. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 30(2): 229–238.
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS. 1987. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 19(6): 703–707.
Venkatesh B, Nandagiri L, Purandara BK, Reddy VB. 2011. Modelling soil moisture under different land covers in a sub-humid environment of Western Ghats, India. Journal Earth System Science, 120(3): 387–398.
Vitousek P, Howarth R. 1991. Nitrogen limitation on land and in the sea: How can it occur? Biogeochemistry, 13(2): 87–115.
Wang WJ, Smith CJ, Chen D. 2004. Predicting Soil Nitrogen Mineralization Dynamics with a Modified Double Exponential Model. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 68(4): 1256–1265.
Wu G, Toda H, Haibara K, Aiba Y. 1998. The effects of nitrogen mineralization on water-soluble ions of forests. Journal of the Japanese Forestry Society, 80: 21–26.
Yang SS, Fan HY, Yang CK, Lin IC. 2003. Microbial population of spruce soil in Tatachia mountain of Taiwan. Chemosphere, 52(9): 1489–1498.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project funding: This research was supported by Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA05070303).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, S., Wang, J., Sun, X. et al. Effect of forest thinning on soil net nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in a Cryptomeria japonica plantation in Taiwan. Journal of Forestry Research 25, 571–578 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-014-0496-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-014-0496-4