Abstract
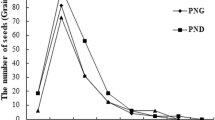
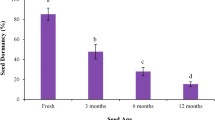
A semi-greenhouse study was conducted to understand the effects of soil burial depth on seed germination and seedling development. The seeds of wild apricot (Prunus armeniaca) were buried at the soil depths of 0-cm, 4-cm, 8-cm, and 12-cm, respectively, to simulate the seed hoarding behavior of rodents in the field. The results revealed that the rates of seed germination and established seedlings from buried seeds were both the highest in 4-cm burial depth group, and then decreased with increasing soil depth. The number of rotten seeds increased in deeper burial depth. It is unfavourable for seed germination at 0-cm burial depth (i.e., seeds were laid on soil surface). There was insignificant effect of burial depth on growth of established seedlings. The results from this study indicated that proper burial depth in soil would be helpful for the seed germination and seedling growth. The seedlings derived from buried seeds at shallower depth (4 cm) in this research have advantage in their early development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong WDM. 2002. Root growth and metabolism under oxygen deficiency. In: Waisel Y, Eshel A, Kafkafi U. (eds.), Plant Roots: the Hidden Half. New York: Marcel Dekker Publishers, pp. 729–761.
Barnett RJ. 1977. The effect of burial by squirrels on germination and survival of oak and hickory nuts. American Midland Naturalist, 98: 319–330.
Borchert MI, Davis FW, Michaelsen J, Oyler LD. 1989. Interactions of factors affecting seedling recruitment of blue oak (Quercus douglasii) in California. Ecology, 70: 389–404.
Chen Hua, Maun MA. 1999. Effects of sand burial depth on seed germination and seedling emergence of Cirsium pitcheri. Plant Ecology, 140: 53–60.
Chen Wei, Gao Wu, Fu Biqian. 2002. Mammalian Fauna of Beijing. Beijing: Beijing Press, pp. 249–254. (in Chinese)
Clarkson K, Eden SF, Sutherland WJ. 1986. Density-dependence and magpie food hoarding. Journal of Animal Ecology, 55: 111–121.
Forget P-M. 1990. Seed-dispersal of Vouacapoua americana (Caesalpiniaceae) by caviomorph rodents in French Guiana. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 6: 459–468.
Griffin JR. 1971. Oak regeneration in the upper Carmel Valley, California. Ecology, 52: 862–868.
Guo Cairu, Lu Jiqi, Yang Dongzhi, Zhao Linping. 2009. Impacts of burial and insect infection on germination and seedling growth of acorns of Quercus variabilis. Forest Ecology and Management, 258: 1497–1502.
Guo Ke, Li Rui, Werger MJA. 2001. Effect of acorn burying depth on germination, seedling emergence and development of Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata. Acta Botanica Sinica, 43: 974–978.
Harper JL. 1977. Population Biology of Plants. London: Academic Press, 1–246.
Jackson M. 1985. Ethylene and the responses of plants to soil waterlogging and submergence. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 36: 145–174.
Jansen PA, Forget PM. 2001. Scatterhoarding rodents and tree regeneration. In: Bongers F, Charles-Dominique P, Forget P-M, Théry M. (Eds.), Nouragues: Dynamics and Plant-animal Interactions in a Neotropical Rainforest. The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. 275–288.
Kevin AE, Brooks JR. 2003. Prolonged flooding decreased stem density, tree seedlings and shifted composition towards clonal species in a central Florida hardwood swamp. Forest Ecology and Management, 173: 261–279.
Kollmann J. Schill HP. 1996. Spatial patterns of dispersal, seed predation and germination during colonization of abandoned grassland by Quercus petraea and Corylus avellana. Vegetatio, 125: 193–205.
Kos M, Poschlod P. 2007. Seeds use temperature cues to ensure germination under nurse-plant shade in Xeric Kalahari Savannah. Annals of Botany, 99: 667–675.
Kos M, Poschlod P. 2008. Correlates of inter-specific variation in germination response to water stress in a semi-arid savannah. Basic and Applied Ecology, 9: 645–652.
Li Hongjun, Zhang Zhibin. 2007. Effects of mast seeding and rodent abundance on seed predation and dispersal by rodents in Prunus armeniaca (Rosaceae). Forest Ecology and Management, 242: 511–517.
Lloret F, Casanovas C, Peñuelas J. 1999. Seedling survival of Mediterranean shrubland species in relation to root: shoot ratio, seed size and water and nitrogen use. Functional Ecology, 13: 210–216.
Lu Jiqi, Zhang Zhibin. 2004a. Seed-hoarding behavior of wild apricot and Liaodong oak by small rodents. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 24: 132–138.
Lu Jiqi, Zhang Zhibin. 2004b. Effects of habitat and season on removal and hoarding of seeds of wild apricot (Prunus armeniaca) by small rodents. Acta Oecologica, 26: 247–254.
Ma Keping, Chen Lingzhi, Yu Shunli, Huang Jianhui, Gao Xianming, Liu Canran. 1997. The major community types in Dongling mountain region. In: Chen Lingzhi, Huang Jianhui. (eds.), The Study on Structure and Function of Forest Ecosystem in Warm Temperate Zone. Beijing: Science Press, pp. 56–75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Michael PD, Paul BC. 2000. Effects of wetting and drying on seed germination and seedling emergence of bull thistle, Cirsium vulgare (Savi) Ten. Canadian Journal of Botany, 78: 1545–1551.
Nicotra AB, Babicka N, Westoby M. 2002. Seedling root anatomy and morphology: an examination of ecological differentiation with rainfall using phylogenetically independent contrast. Oecologia, 130: 136–145.
Pérez-Ramos IM, Marañón T. 2009. Effects of waterlogging on seed germination of three Mediterranean oak species: Ecological implications. Acta Oecologica, 35: 422–428.
Shaw MW. 1968. Factors affection the natural regeneration of sessile oak (Quercus petraea) in North Wales. II. Acorn losses and germination under field conditions. Journal of Ecology, 56: 647–660.
Stapanian MA, Smith CC. 1984. Density-dependent survival of scatter-hoarded nuts: an experimental approach. Ecology, 65: 1387–1396.
Su Yangui., Li Xinrong, Jia Rongliang, Feng Li. 2007. Effects of sand burying on seed germination and seedling emergence of six Psammophytes species. Journal of Desert Research, 27: 968–971. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Vander Wall SB. 1990. Food Hoarding in Animals. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, pp. 1–445.
Vander Wall SB. 1993a. A model of caching depth: implications for scatter hoarders and plant dispersal. American Naturalist, 141: 217–232.
Vander Wall SB. 1993b. Cache site selection by chipmunks (Tamias spp.) and its influence on the effectiveness of seed dispersal in Jeffrey pine (Pinus jeffreyi). Oecologia, 96: 246–252.
Voesenek LACJ, Colmer TD, PIerik R, Millenaar FF, Peeters AJM. 2006. How plant cope with complete submergence. New Phytologist, 170: 213–226.
Willson M, Traveset A. 2000. The Ecology of Seed Dispersal. in: Fenner M (ed.). Seeds: The ecology of regeneration in plant communities. 2nd. Edition. Wallingford: CAB International Publishing, pp. 85–110.
Yang Huiling, Cao Zhiping, Dong Ming, Ye Yongzhong, Huang Zhenying. 2007. Effects of sand burying on caryopsis germination and seedling growth of Bromus inermis Leyss. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 18(11): 2438–2443. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Hongmao, Zhang Zhibin. 2008. Endocarp thickness affects seed removal speed by small rodents in a warm-temperate broad-leafed deciduous forest, China. Acta Oecologica, 34: 285–293.
Zhang Zhibin, Li Hongjun, Xiao Zhishu, Lu Jiqi, Cheng Jinrui. 2007. Effects of animals on the fate of plant seeds. In: Wu Jianguo (ed.) Lectures in Modern Ecology (III): Advances and Key Topics. Beijing: Higher Education Press, pp. 63–91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Zhibin, Wang Fusheng. 2001. Effect of rodents on seed dispersal and survival of wild apricot (Prunus armeniac). Acta Oecologica Sinica, 21: 1762–1768.
Zhang Zhibin, Xiao Zhishu, Li Hongjun. 2005. Impact of small rodents on tree seeds in temperate and subtropical forests, China. In: Forget P-M, Lambert J, Hulme PE, Vander Wall SB. (eds.), Seed Fates: Seed Predation, Seed Dispersal and Seedling Establishment. Wallingford: CAB International Publishing, pp. 269–282.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation project: This study was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2007CB109106), and by the Zoology Key Subject Fund of Henan Province.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Cr., Wang, Zl. & Lu, Jq. Seed germination and seedling development of Prunus armeniaca under different burial depths in soil. Journal of Forestry Research 21, 492–496 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-010-0104-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-010-0104-1