Abstract
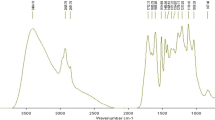
Rice husk high boiling solvent lignin (RHL) was prepared by high boiling solvent method, and its characteristics was analyzed by using chemical composition analysis, infrared spectroscopy, and 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectroscopy. The optimum prepared condition was that the rice husk with 70%–90% aqueous solution of 1, 4-butanediol was mixed with autoclave, under a certain weight ratio of solid raw material and solvent, heated to 200–220°C for 1.0–3.0 h, then water-insoluble RHL was separated from the liquor reaction mixture by water precipitation. Results suggested that the lower digestion temperature and concentration of 1,4-butanediol were both unfavorable for extracting lignin. Chemical weight-average molecular weight of RHL was 1939 g·mol−1, and the residual polysaccharide content was 5.12%. The 1H-NMR spectra of RHL showed the relative intensity ratio, aliphatic over aromatic methoxyl groups, situated at 3.5–3.8 and 3.8–4.0 ppm, respectively. The results from 13C-NMR spectra showed that β-O-4 bond and β-5 carbon-carbon linkage were the major linkages between RHL units. The C9-formula of RHL was calculated by the experiment data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen CL, Robert D. 1988. Characterization of lignin by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. In: Wood, W.A., Kellogg, S.T (eds), Methods in Enzymology Vol 161. San Diego, CA: Academic Press, pp137–174.
Cheng Xiansu, Chen Weijian, Chen Yunping, Chen yuexian, Li Mianjun, Fan Huashu. 2004. Preparation and properties of HBS lignin from masson pine. Chem Res Chinese U, 20(2): 225–228.
Chen Yunping, Cheng Xiansu, Fang Huasu, Chen Yuexian, Li Mianjun, Chen Weijian. 2003. Preparation of HBS lignin and cellulose using mason pine. J Cellul Sci Tecnol, 11(1): 19–23. (in Chinese)
Cheng Xiansu, Shen Feng. 2004. Analysis of the residual sugar containing in HBS lignin. J Minjiang Univ, 25(2): 76–79. (in Chinese)
Faix O. 1991. Classification of lignins from different botanical orignins by FTIR spectroscopy. Holzforschung, 45(suppl): 21–27.
Glasser WG, Barnett CA, Sano Y. 1983. Classification of lignins with different genetic and industrial origins. J Appl Polym Sci, 37: 441
Jiang TD. 2001. Lignin. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, pp 12. (in Chinese)
Glasser WG, Kelley SS. 1987. Lignin. In: Mark HF, Kroschwits JI (eds), Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Engineering, Vol. 8. New York: John Wiley, pp. 795–852.
Kajimoto J, Sano Y, Widodo WE, Kishimoto T, Uraki Y. 2000. HBS pulping (1)-pulping of softwood. Japan Tappi J, 54(9): 88–95.
Nada AMA, El-Sakhawy M, Kamel S. 1998. Infrared spectroscopic studies of different lignins. Polym Degrad Stab, 60(2–3): 247–251.
Nada AMA, El-Saied H, Fadl M, Nassar M. 1994. Spectroscopic studies of bagasse butanol lignin. Polym Degrad Stab, 43(1): 55–59.
Real C, Alcala MD, Criado JM. 1996. Preparation of silica form rice husks. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 79: 2012–2016.
Sun RC, Sun XF, Fowler P, Tomkinson J. 2002. Structural and physico-chemical characterization of lignins solubilized during alkaline peroxide treatment of barley straw. Eur Polym J, 38(7): 1399–1407.
Scholze B, Meier D. 2001. Characterization of the water-insoluble fraction from pyrolysis oil (pyrolytic lignin). Part I. PY-GC/MS, FTIR, and functional groups. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 60(1): 41–54.
Vazquez G, Antorrena G, Gonzalez J, Freire S. 1997. FTIR, 1H and 13C NMR characterization of acetosolv solubilized pine and eucalyptus lignins. Holzforschung, 51: 158–166.
Widodo WE, Kajimoto J, Sano Y. 2000. HBS pulping(2)-pulping of hardwood and annual plants. Japan Tappi J, 54(10): 86–94.
Lundquist K, Von Unge S. 1986. NMR studies of lignins. 8. Examination of pyridine-d5 solutions of acetylated lignins from birch and spruce by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Acta Chem Scand Ser B, 40: 791–797.
Xu Jinxian, Cheng Xiansu, Chen Yunping, Lin Chunying. 2004. Modification of NBR with HBS lignin. Special Purpose Rubber Products, 25(5): 1–4. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation items: This study was sponsored by the Research Funding for Key Laboratory of Cellulose and Ligno cellulosics Chemistry, Guangzhou Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. LCLC-2004-158) and the National Natural Science Foundation of Fujian (No. Z0513015)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Yp., Cheng, Xs. Preparation and characteristic analysis of rice husk high boiling solvent lignin. Journal of Forestry Research 19, 159–163 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-008-0028-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-008-0028-1