Abstract
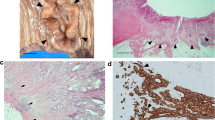
Objective: To determine p16 and cyclin D1 expression in the specimen of gastric carcinoma, atypic hyperplasia, atrophic gastritis, superficial gastritis and normal gastric mucosa. Methods: Using immunohistochemical method (ABC), the samples of 58 adenocarcinomas, 22 atypic hyperplasias, 28 atrophic gastritis, 27 superficial gastritis and 15 gastric epitheliums were analyzed. Results: Positive immunostaining rate for p16 protein was the highest in normal gastric mucosa and decreased with the lesions progressing from superficial gastritis to atrophic gastritis to atypital hyperplasia and to adenocarcinoma (85%, 78.6%, 31.8%, 48.3% respectively); Positive immunostaining of cyclin D1 can observed in atrophic gastritis. With the lesions progressing from atrophic gastritis to atypical hyperplasia to adenocarcinoma, its expression rate increased (17.9%, 36.4%, 53.4% respectively), and there was a significant difference between adenocarcinoma and atrophic gastritis group (P<0.05). An interesting observation was that inverse expression between p16 and cyclin D1, was shown in most of gastric cancer detected. Conclusion: It is indicated that p16 and cyclin D1 play an important role in the gastric carcinogenesis, the inverse expression between p16 and cyclin D1 suggested that there is a suppression trend in them.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu YL, Zhang YC, Wang RN, et al. Multiple genetic expression abnormalities in gastric cancer. Chin J Oncol 1996; 18:199.
Yu J, Zhang JK. Expression of ras oncogene p21 product in human gastric precancerous lesion and carcinoma. Chin J Clin Oncol 1994; 21:901.
Serrano M, Hannon GJ, Beach DA. A new regulatory motif in all cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature 1993; 366:704.
Lü YY, Gao CF, Cui JT, et al. Deletion and doun-regulation of MTS1/p16 gene in human gastric cancer. Chin J Oncol 1996; 18:189.
Hernan JG, Merlo A, Li M, et al. Inactivation of the CDKNZ/p16/MTSI gene is frequently associated with aberrant DNA methylation in all common human cancers. Cancer Res 1995; 55:4525.
Aikou Okamoto, Douglas J Demetriek, Elisa A, et al. Mutations and altered expression of p16 INK4 in human cancer. Proc Natl Acacl Sci USA 1994; 91:10045.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Yl., Xu, F. & Li, Yj. Expression of P16 and cyclin D1 in the course of carcinogenesis of the stomach. Chi J Cancer Res 11, 29–31 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-999-0100-1
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-999-0100-1