Abstract
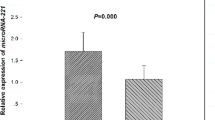
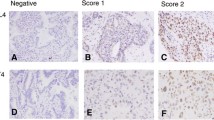
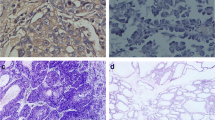
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the MRP-1/CD9mRNA expression in lung cancer and normal lung tissues and the relationship between its expression and pathologic grades, clinical stages, metastasis and prognosis. Methods: To observe MRP-1/C9mRNA expression, tissue microarray (TMA) containing 54 lung cancers and 10 normal lung tissues was prepared and Fluorescence in situ hybridization was used. Results: The positive rate of MRP-1/CD9 expression was 48.1% in lung cancer, lower than that of normal lung tissues. The statistical difference was significant (P<0.05). Its protein expression had no relationship with the patients’ ages, sex and the macroscopic type of tumor, but had relationships with the histological type, clinical stage, differentiated degree and metastasis. The expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) was higher than that in small cell lung cancer (SCLC); in well-moderately differentiated group was higher than that in poorly differentiated group; Earlier period group (I+II) was higher than in later period group (III+IV); and in group without lymphoid metastasis was higher than in patients with lymphoid metastasis. Conclusion: The progression of the lung cancer maybe related with the descended MRP-1/Cd9 expression, which may be useful in evaluating the prognosis of cancer patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A, et al. Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens [J]. Nat Med 1998; 4:844–7.
Ikeyama S, Koyama M, Yamaoko M, et al. Suppression of cell motility and metastasis by transfection with human motility-related protein (MRP-1/CD9) DNA [J]. J Exp Med 1993; 177:1231–7.
Uchida S, Shimada Y, Watanabe G, et al. Motility-related protein (MRP-1/CD9) and KAI1/ CD82 expression inversely correlate with lymph node metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Br J Cancer 1999; 79:1168–73.
Erovic BM, Pammer J, Hollemann D, et al. Motility-related protein-1/CD9 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Head Neck 2003; 25:848–57.
Mhawech P, Dulguerov P, Tschanz E, et al. Motility-related protein-1 (MRP-1/CD9) expression can predict disease-free survival in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck [J]. Br J Cancer 2004; 90:471–5.
Funakoshi T, Tachibana I, Hoshida Y, et al. Expression of tetraspanins in human lung cancer cells: frequent downregulation of CD9 and its contribution to cell motility in small cell lung cancer [J]. Oncogene 2003; 22:674–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: This work was supported by a grant from Tianjin Science and Technology Committee (No. 033804211)
Biography: WANG Xin-yun(1945–), female, professor, Tianjin Medical University, majors in molecular biology of lung cancer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Xy., Liu, T., Li, Y. et al. Detecting expression of MRP-1/CD9 mRNA in lung cancers using tissue microarrays and fluorescence in situ hybridization methods. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 17, 199–202 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-005-0040-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-005-0040-3