Abstract
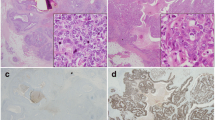
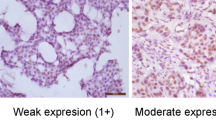
Objective: To study the expression and clinical significance of p73α in breast carcinomas. Methods: The expression of p73α was detected by immunohistochemistry in 41 breast carcinoma tissues, 13 benign breast tumor tissues and 8 normal tissues and 8 normal breast tissues, respectively. Results: The positive expression of p73α was found in 20/41 (48.8%) of breast carcinoma tissues, 1/13 (7.7%) of benign breast tumor tissues. The positive expression rate of p73α in breast carcinoma tissues was significantly higher than that in benign breast tumor tissues and normal breast tissues (P<0.05). The expression intensity of p73α increased significantly in breast carcinoma tissues compared with benign breast tumor tissues and normal breast tissues (P<0.05). Significant association of the expression of p73α with lymph node metastases and TNM stages of the carcinoma was found (P<0.05). The expression of p73α displayed a positive correlation with p53 (P<0.05). Conclusion: These results suggest that there is an up-regulation of p73α expression in breast carcinoma tissues, which may be implicated in the tumorigenesis of breast carcinoma as a molecular alteration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, et al. Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers[J]. Cell 1997; 90:809–19.
Zaika AI, Kovalev S, Marchenko ND, et al. Overexpressed of wild type p73 gene in breast cancer tissues and cell lines [J]. Cancer Res 1999; 59:3257–63.
Tokuchi Y, Hashimoto T, Kobayashi Y, et al. The expression of p73 is increased in lung cancer, independent of p53 gene alteration [J]. Br J Cancer 1999; 80:1623–29.
Sun XF. p73 overexpression is a prognostic factor in patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8:165–70.
Weber A, Bellmann U, Bootz R, et al. Expression of p53 and its homologues in primary and recurrent squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck [J]. Int J Cancer 2002; 99:22–8.
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, et al. p53 mutations in human cancers [J]. Science 1991; 253:49–53.
Tannapfel A, Engeland K, Weinans L, et al. Expression of p73, a novel protein related to the p53 tumor suppressor p53, and apoptosis in cholangiocellular carcinoma of the liver [J]. Br J Cancer 1999; 80:1069–74.
Zwahlen D, Tschan MR, Grob TJ, et al. Differential expression of p73 splice variants and protein in benign and malignant ovarian tumors [J]. Int J Cancer 2000; 88:66–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Biography: ZHOU Xin (1975–), male, master of medicine, Chongqing University of Medical Sciences, majors in treatment of breast carcinoma.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Sun, Zj. Expression and clinical significance of p73A in breast carcinoma tissues. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 17, 75–78 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-005-0016-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-005-0016-3