Abstract
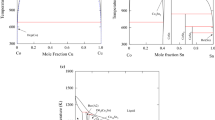
Literature information and authors’ experimental data have been used for the evaluation of optimized polynomial coefficients serving to calculate the cobalt (Co)-zinc (Zn) phase diagram. The programs BINGSS and THERMO-CALC have been used for the optimization. The binary liquid phase, the solid Co-based face-centered-cubic (fcc) and hexagonal close-packed solutions, as well as the intermediate β-, β1-, and γ-compounds have been treated as disordered substitutional phases. The phases with narrow homogeneity ranges (δ, γ1, and γ2) have been modeled as stoichimetric Co2Zn15, CoZn7, and CoZn15, respectively. The calculated phase diagram and thermodynamic quantities are in agreement with the experimental data. For the first time, a eutectoid decomposition (at around 658 K) of the fcc solutions has been predicted. Moreover, the calculations have shown the possibility for a magnetically induced miscibility gap involving both forms (paramagnetic and ferromagnetic) of the fcc solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Lewkonja: “Equilibria Between Liquid and Solid Zn-Rich Cobalt-Zinc Phases,” Z. Anorg. Chem., 1908, 59, pp. 319–22.
W. Pierce and M. Palmerton: “Studies on the Constitution of Binary Zinc-Base Alloys,” Trans. AIME, 1923, 68, pp. 776–95.
W. Ekman: “X-ray Studies of the Cobalt-Zinc Gamma-Phase,” Z. Physikal. Chem., 1931, B12, pp. 57–78.
N. Parravano and V. Caglioti: “On the Structure of the Cobalt-Zinc Gamma-Phase,” Mem. Accad. Italia, Cl. Sci. Fis. Mat. Nat., 1932, 3, pp. 1–21.
U. Hashimoto: Nippon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 1937, 1, pp. 177–90.
W. Köster and E. Wagner: “Effect of the Elements Al, Ti, V, Cu, Zn, Sn and Sb on the Polimorphic Transition of the Cobalt,” Z. Metallkde, 1937, 29, pp. 230–32.
J. Schramm: “The Cobalt-Zinc System,” Z. Metallkde.; 1938, 30, pp. 10–14.
J. Schramm: “The Heats of Formation for the Three-Phase Transformations in the Binary Alloys of Zinc With Iron. Cobalt, Nickel and Manganese,” Z. Metallkde., 1938, 30, pp. 131–35.
J. Schramm: “X-Ray Investigation of Phase and Phase Limits of the Zinc Alloy Systems With Iron. Cobalt and Nickel,” Z. Metallkde., 1938, 30, pp. 122–30.
J. Schramm: “The Magnetic Susceptibility of the Alloys of the Zinc With Nickel, Cobalt and Iron,” Z. Metallkde., 1938, 30, pp. 327–34.
F. Gotzl, F. Halla, and J. Schramm: “δ1 and ξ Phases in the Systems Fe-Zn and Co-Zn,” Z. Metallkde., 1941, 33, p. 375.
J. Schramm: “Co-Zn System,” Z. Metallkde., 1941, 33, pp. 46–48.
F. Pawlek: “Influence of Iron Metals on the Zinc Properties,” Z. Metallkde., 1944, 36, pp. 105–11.
A.J.P. Meyer and P. Taglang: “On the Ferromagnetism of the Beta-1 Phase of the Co-Zn Alloys,” Compt. Rend., 1951, 232, pp. 1914–16.
F. Lihl and E. Weisberg: “Phase Boundaries in the System Co-Zn,” Z. Metallkde., 1955, 46, pp. 579–81.
W. Köster and H. Schmid: “The State of the Beta-Phase in the System Co-Zn.” Z. Metallkde., 1955, 46, pp. 468–69.
M. Hansen and K. Anderko: Constitution of Binary Alloys, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1958, p. 1488.
P. Brown: “The Structure of the ξ-Phase in Transition Metal-Zinc Alloy Systems,” Acta Crystallogr., 1962, 15, pp. 608–12.
V. Melikhov and A. Presnjakov: Structure and Properties of Electron Phases, Nauka, Alma-Ata, Kazakhstan, USSR, 1973 (in Russian).
S. Budurov and G.P. Vassilev: “The Cobalt Side of the Phase Diagram Cobalt-Zinc,” Z. Metallkde., 1976, 67, pp. 170–72.
S. Budurov, G.P. Vassilev, and L. Mandadjieva: “Thermodynamics of Cobalt-Zinc and Nickel-Zinc Austenites,” Z. Metallkde., 1976, 67, pp. 307–10.
S. Budurov and G.P. Vassilev: “Thermodynamics of the β-and γ-Phases in the Nickel-Zinc and Cobalt-Zinc Systems,” Z. Metallkde., 1977, 68, pp. 795–98.
A. Morton: “Inversion Domains in Gamma-brass Type Phases—Stabilization Mechanism—Role of Electron-Concentration,” Phys. Stat. Sol.(a), 1977, 44, pp. 205–14.
A. Mozeva, D. Nenov, and N. Gidicova: “Determination of Activity of Zinc in Liquid Cobalt and Nickel-alloys,” Arch. Eisenhuettenwes., 1977, 48, pp. 533–34.
G.P. Vassilev and S. Budurov: “Kinetics of Intermetallic Phase Layers Growth in the Co-Zn System,” Annual of the University of Sofia, Faculty of Chemistry, 1977/1978, 72, pp. 25–36.
M. Hillert and M. Jarl: “Model for Alloying Effects in Ferromagnetic Metals,” Calphad, 1978, 2, pp. 227–38.
L. Arnberg and S. Westman: “A Discussion of the Ordering in Some Vacancy-Containing Gamma Brasses,” Z. Kristallographie, 1980, 152, pp. 103–08.
S. Ali and V. Geiderich: “Thermodynamic Properties of Solid Co-Zn Alloys,” Zh. Fiz. Khim. 1981, 67, pp. 1248–51. (in Russian).
G. Inden: “The Role of Magnetism in the Calculation of Phase Diagrams,” Physica, 1981, 103B, pp. 82–100.
W.B. Pearson: “Vacancies and Atomic Ordering in Gamma Brasses of Ni, Pd. and Pt With Zn or Cd,” Z. Kristallographie, 1981, 156, pp. 281–94.
H. Comert and J. Pratt: “The Thermodynamic Properties of Solid Cobalt-Zinc Alloys,” Thermoch. Acta, 1982, 59, pp. 267–85.
K.H.J. Buschow, P.G. van Engen. and R. Jongebreur: “Magneto-Optical Properties of Metallic Ferromagnetic Materials,” J. Magnetism Magn. Mater., 1983, 38, pp. 1–22.
A.K. Niessen, A.R. Miedema, F.R. de Boer, and R. Boom: “Model Predictions for the Enthalpy of Formation of Transition Metal Alloys 2,” Calphad, 1983, 7, pp. 51–70.
A.F. Guillermet: “Critical Evaluation of the Thermodynamic Properties of Cobalt,” Intern. J. Thermod., 1987, 8, pp. 481–510.
T. Nishizawa and K. Ishida: “The Cobalt System,” Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr., 1980, 4, pp. 387–90.
A.T. Dinsdale: “SGTE Data for Pure Elements,” CALPHAD, 1991, 15, pp. 317–425.
A. Ray, S. Smith, and J. Scofield: “Study of the Phase Transformation of Cobalt,” J. Phase Equilibria, 1991, 12, pp. 644–47.
M. Kowalski and P.J. Spencer: “Thermodynamic Reevaluation of the Cu-Zn System,” J. Phase Equilibria, 1993, 14, pp. 432–38.
G.P. Vassilev: “Assessment of the Equilibrium between Solid and Liquid Cobalt-Zinc Solutions,” Cryst. Res. Technol., 1993, 28, pp. 57–62.
G.P. Vassilev and S. Budurov: “Growth Kinetics of Cobalt-Zinc Intermediate Phase Layers,” J. Alloys Compounds, 1993, 199, pp. 197–201.
H.L. Lukas, S. Fries, U. Kattner, and J. Weiss: BINGGS, BINFKT, Version 95-1, Max-Planck-Institute of Metall Science, Stuttgart, Germany, 1995.
T. Nishizawa: “Effect of Magnetic Transition on Phase Equilibria in Iron Alloys,” J. Phase Equilibria, 1995, 16, pp. 379–89.
T. Takayama, S. Shinohara, K. Ishida, and T. Nishizawa: “Anomalies in Phase Equilibria due to Magnetic Transition in Fe-Zn, Co-Zn and Fe-Co-Zn Systems,” J. Phase Equilibria, 1995, 16, pp. 390–95.
T. Massalski: Binary Phase Diagrams [CD-ROM], 2nd ed., 1996, ASM International, Materials Park, OH.
Yu.A. Ryabikin, V.D. Melikhov, and O.V. Zashkvara: “Paramagnetic Resonance Studies of the Co-Zn Gamma-Brass Structure,” The Physics of Metals and Metallography, 1996, 81(3), pp. 255–62 (translated from Russian).
G.P. Vassilev, T.G. Acebo, and J.-C. Tedenac: “Thermodynamic Optimization of the Ni-Zn System,” J. Phase Equilibria, 2000, 21, pp. 287–301.
M. Jiang, C.P. Wang, X.J. Liu, I. Ohnuma, R. Kainuma, G.P. Vassilev, and K. Ishida: “Thermodynamic Calculation of Phase Equilibria in Cu-Ni-Zn System,” J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 2003 (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vassiley, G.P., Jiang, M. Thermodynamic optimization of the Co-Zn system. J Phs Eqil and Diff 25, 259–268 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-004-0115-8
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-004-0115-8