Abstract
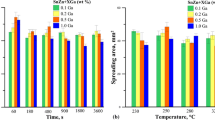
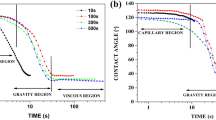
The maximum bubble pressure, dilatometric, and meniscographic methods were used in investigations of the surface tension, density, wetting time, wetting force, contact angles, and interfacial tension of liquid (Sn-Ag)eut and two (Sn-Ag)eut+Cu alloys (Cu at.%=0.46 and 0.74). The density and surface tension measurements were conducted in the temperature range from 230 to 950 °C, and the meniscographic investigations were carried out at 252 °C. The resultant values of surface tension were compared with those calculated from Butler’s model based on optimized thermodynamic parameters and our data from earlier investigations. In an earlier study, experimental data for all investigated compositions (Cu at. %=1.08 to 6.5) exhibit an increase in the surface tension with interesting temperature, while both ternary alloys of this study show a slight lowering tendency in comparison to (Sn-Ag)eut. A more evident decreasing tendency of surface tension and interfacial tension was noted in meniscographic measurements, noting that data of interfacial tension are always lower than surface tension due to the role of the flux. Eight different fluxes were tested to select the lowest interfacial tension for the (Sn-Ag)eut. ROLI (3% solids), which is the alcoholic solution of organic compounds and rosin activated by halogens, was recommended. In (Sn-Ag)eut+Cu Soldering Materials, Part II: Electrical and Mechanical Studies, for the same (Sn-Ag)eut and (Sn-Ag)eut+Cu alloys (Cu at. %=0.46 and 0.74), the electrical resistance and strength measurements will be presented in parallel with printed-circuit boards in wave soldering at 260 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.A.V. Butler: “The Thermodynamic of the Surfaces of Solutions,” Proc. R. Soc., 1932, 135A, p. 375.
J. Glazer: “Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Pb-Free Solder Alloys for Low-Cost Electronic Assambly: A Review,” J. Electron. Mater., 1994, 23, pp. 693–700.
C.M. Miller, I.E. Anderson, and J.F. Smith: “A Viable Tin-Lead Solders Substitute: Sn-Ag-Cu,” J. Electron. Mater., 1994, 23, p. 595.
M. Mizyaki, M. Mizutani, T. Takemoto, and A. Matsunawa: “Conditions for Measurements of Surface Tension of Solders with a Wetting Balance Tester,” Trans. JWRI, 1997, 26, pp. 81–84.
H.M. Lee, S.W. Yoon, and B-J Lee: “Thermodynamic Prediction of Interface at Cu/Solder Joints,” J. Electron. Mater., 1998, 27, pp. 1161–66.
P.T. Vianco and J.A. Rejent: “Properties of Ternary Sn-Ag-Bi Solder Alloys: Part II-Wettability and Mechanical Properties Analyses.” J. Electron. Mater., 1999, 28, pp. 1138–43.
K-W. Moon, W.J. Boettinger, U.R. Kattner, F.S. Biancaniello, and C.A. Handwerker: “Experimental and Thermodynamic Assessment of Sn-Ag-Cu Solder Alloys,” J. Electron. Mater., 2000, 29, pp. 1122–36.
I. Ohnuma, M. Miyashita, A. Anzai, X.J. Liu, H. Ohtani, K. Ishida: “Phase Equilibria and the Related Properties of Sn-Ag-Cu Based Pb-Free Solder Alloys,” J. Electron. Mater., 2000, 29, pp. 1137–47.
T. Takemoto and M. Miyazaki: “Effect of Excess Temperature Above Liquidus of Lead-Free Solders on Wetting Time in a Wetting Balance Test,” Mater. Trans., 2001, 42, p. 745.
I.E. Anderson, J.C. Foley, B.A. Cook, J. Harringa, R.L. Terpstra, and O. Unal: “Alloying Effects in Near-Eutectic Sn-Ag-Cu Solders Alloys for Improved Microstructural Stability,” J. Electron. Mater., 2001, 30, pp. 1050–59.
Z. Moser, W. Gasior, and J. Pstruś: “Density and Surface Tension of the Ag-Sn Liquid Alloys,” J. Phase Equilibria, 2001, 22, pp. 254–58.
Z. Moser, W. Gasior, and J. Pstruś: “Surface Tension Measurements of the Sn-Bi and Sn-Bi-Ag Liquid Alloys,” J. Electron. Mater., 2001, 30, pp. 1104–11.
W. Gasior, Z. Moser, and J. Pstruś: “Surface Tension and Density of the Pb-Sn Liquid Alloys,” J. Phase Equilibria, 2001, 22, pp. 20–25.
X.J. Liu, Y. Inohana, I. Ohnuma, R. Kainuma, K. Ishida, Z. Moser, W. Gasior, and J. Pstruś, “Experimental Determination and Thermodynamic Calculation of the Phase Equilibria and Surface Tension of the Ag-Sn-In System,” Electron, Mater. 2002, 31, pp. 1139–51.
Z. Moser, W. Gasior, J. Pstruś, and S. Ksiezarek: “Surface Tension and Density of the Ag-Sn.eut+Cu Liquid Alloys,” J. Electron. Materials, 2002, 31, pp. 1225–29.
Z. Moser, W. Gasior, and J. Pstruś: “Lead-Free Soldering Materials,” Inżynieria Materiałowa, 2002, 2, pp. 65–68.
W. Gasior, Z. Moser, J. Pstruś, B. Krzyżak, and K. Fitzner: “Surface Tension and Thermodynamic Properties of the Liquid Ag-Bi Solutions,” J. Phase Equilibria, 2003, 2, pp. 21–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gasior, W., Moser, Z., Pstruś, J. et al. (Sn-Ag)eut+Cu soldering materials, part I: Wettability studies. J Phs Eqil and Diff 25, 115–121 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-004-0003-2
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-004-0003-2