Abstract
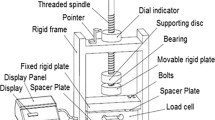
A washer is a thin plate with a hole that is normally used to distribute the load of a threaded fastener, such as a screw or nut. The washer used in automotive engine component is of split or spring lock washer. A ring split at one point and bent into helical shape. The benefit of spring lock washers lies in the trapezoidal shape of the washer. When compressed to loads near proof strength of the bolt, it will twist and flatten. This reduces the spring rate of the bolted joint which allows it to maintain more force under the same vibration levels. This prevents from loosening. The steel washer is one of the critical safety components for automobile engine, and its failure may cause severe safety issue. Before subjecting to manufacturing, the washer undergoes different process lines (wire rod → drawing → annealing → pickling → flattening → spring washer → single spring washer). After manufacturing of washer, toughness test is done to find out the metallurgical soundness and surface quality of the washer. In this toughness test the washer in a vice with the split ends free and straight above the vice jaws, a 90° segment of the free end is gripped with a wrench and bent. Washers should withstand twist test through a 90° angle without signs of fracture. The present paper highlights premature failure of automotive washer which failed during twist test. From the analysis, it has been observed that the distribution of spheroidized carbide is more uniform in good samples than that of rejected samples. Hardness profile variation was observed between good and bad spring samples. Overall investigation does not indicate any problem related to supplied wire rod material quality as no wire breakage problem observed. Inhomogeneous annealed structure in flat wire seems to result into variation in washer performance during twist test.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Das, P. Koli, J. Mathur, A. Dey, T. Bhattacharyya, S. Bhattacharyya, Failure analysis of motor tyre bead wires during torsion test. Eng. Fail. Anal. Prev. 13, 684–688 (2013)
Y. Zhang, L. Chen, Y. Liu, Failure analysis of 65 Mn spring washer fracture. Fail. Anal. Prev. 7(1), 43–45–49 (2012)
S. Das, J. Mathur, T. Bhattacharyya, S. Bhattacharyya, Metallurgical investigation of different causes of centre bursting led to wire breakage during production. Case Study Eng. Fail. Anal. 1, 32–36 (2013)
IS: 6755-1980: Specification of double coil helical spring washers
G. Krauss, Steels Processing, Structure, and Performance (ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2005), pp. 256–259
G.E. Totten, M.A.H. Howes, Steel Heat Treatment Handbook (Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, 1997), p. 540
J.M. O’Brien, W.F. Hosford, Spheroidization of medium-carbon steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 6, 69–72 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, S., Talukder, S., Solanki, V. et al. Breakage of Automotive Spring Washer During Twist Test: A Metallurgical Analysis. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 18, 241–245 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-018-0410-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-018-0410-z