Abstract
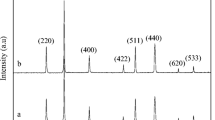
Synthesis and characterization of FexOy nanoparticles were carried out in order to study reaction parameters influence in a spray flame reactor. FexOy powders were prepared with three different precursors aiming to understand how the reactor conditions, dispersion gas flow, and precursor solution flow affect morphology, shape, particle size distribution, crystalline phases, and residue content of the obtained materials. Thermogravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), x-ray diffraction (XRD), and Raman spectroscopy were employed to characterize the materials. In addition, magnetic behavior of the obtained samples was evaluated. It was found that the evaluated parameters influenced the residue contents obtaining weight changes from 10 to 35%. Particle size distribution centers also showed differences between 17 and 24 nm. By XRD, Raman, and TEM, the presence of hematite (a-Fe2O3), maghemite (γ-Fe2O3), and magnetite (Fe3O4) was evidenced and explained based on the gas and liquid content in the flame. Additionally, the saturation magnetization was measured for selected samples, obtaining values between 26 and 32 emu g−1. These magnetic measurements were correlated with the crystalline phase composition and particle size distributions.
Graphic Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Laurent, D. Forge, M. Port, A. Roch, C. Robic, L.V. Elst, and R.N. Muller, Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Vectorization, Physicochemical Characterizations, and Biological Applications, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108(6), p 2064-2110
S. Rajput, L.P. Singh, C.U. Pittman, and D. Mohan, Lead (Pb2+) and Copper (Cu2+) Remediation from Water Using Superparamagnetic Maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) Nanoparticles Synthesized by Flame Spray Pyrolysis (FSP), J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2017, 492, p 176-190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.11.095
A. Afkhami, M. Saber-Tehrani, and H. Bagheri, Modified Maghemite Nanoparticles as an Efficient Adsorbent for Removing Some Cationic Dyes from Aqueous Solution, Desalination, 2010, 263(1-3), p 240-248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.06.065
A.D. Abid, M. Kanematsu, T.M. Young, and I.M. Kennedy, Arsenic Removal from Water Using Flame-Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Variable Oxidation States, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 2013, 47(2), p 169-176
O. Blatt, M. Helmich, B. Steuten, S. Hardt, D. Bathen, and H. Wiggers, Iron Oxide/Polymer-Based Nanocomposite Material for Hydrogen Sulfide Adsorption Applications, Chem. Eng. Technol., 2014, 37(11), p 1938-1944
J. Harra, J.P. Nikkanen, M. Aromaa, H. Suhonen, M. Honkanen, T. Salminen, S. Heinonen, E. Levänen, and J.M. Mäkelä, Gas Phase Synthesis of Encapsulated Iron Oxide-Titanium Dioxide Composite Nanoparticles by Spray Pyrolysis, Powder Technol., 2013, 243, p 46-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2013.03.027
G. Litt and C. Almquist, An Investigation of CuO/Fe2O3 Catalysts for the Gas-Phase Oxidation of Ethanol, Appl. Catal. B Environ., 2009, 90(1-2), p 10-17
N. Zhao, W. Ma, Z. Cui, W. Song, C. Xu, and M. Gao, Polyhedral Maghemite Nanocrystals Prepared by a Flame Synthetic Method: Preparations, Characterizations, and Catalytic Properties, ACS Nano, 2009, 3(7), p 1775-1780
Y. Li, Y. Hu, G. Huang, and C. Li, Metallic Iron Nanoparticles: Flame Synthesis, Characterization and Magnetic Properties, Particuology, Chinese Society of, Particuology, 2013, 11(4), p 460-467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2012.10.008
D. Flak, A. Braun, A. Vollmer, and M. Rekas, Effect of the Titania Substitution on the Electronic Structure and Transport Properties of FSS-Made Fe2O3 Nanoparticles for Hydrogen Sensing, Sensors Actuators, B Chem., 2013, 187, p 347-355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.12.038
T. Kim and B. Guo, Zn-Doped Fe2O3 Sensors for Flammable Gas Detection: Effect of Annealing on Sensitivity and Stability, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2011, 17(1), p 158-164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2010.12.016
S. Inamdar, H.-S. Choi, M.-S. Kim, K. Chaudhari, and J.-S. Yu, Flame Synthesis of 26-Faceted Maghemite Polyhedrons Grown via 14-Faceted Polyhedrons and Their Carbon Composites for Li-Ion Battery Application, CrystEngComm, 2012, 14(20), p 7009. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ce26146d
I. Jönkkäri, M. Sorvali, H. Huhtinen, E. Sarlin, T. Salminen, J. Haapanen, J.M. Mäkelä, and J. Vuorinen, Characterization of Bidisperse Magnetorheological Fluids Utilizing Maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) Nanoparticles Synthetized by Flame Spray Pyrolysis, Smart Mater. Struct., 2017, 26(9), p 095004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665x/aa7f7d
C.F.A. Vogel, J.G. Charrier, D. Wu, A.S. McFall, W. Li, A. Abid, I.M. Kennedy, and C. Anastasio, Physicochemical Properties of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles That Contribute to Cellular ROS-Dependent Signaling and Acellular Production of Hydroxyl Radical, Free Radic. Res., 2016, 50(11), p 1153-1164. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2016.1152360
K. Buyukhatipoglu, T.A. Miller, and A.M. Clyne, Flame Synthesis and In Vitro Biocompatibility Assessment of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Cellular Uptake, Toxicity and Proliferation Studies, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2009, https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2009.1477
B. Guo and I.M. Kennedy, Gas-Phase Flame Synthesis and Characterization of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Use in a Health Effects Study, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 2007, 41(10), p 944-951
D. Li, W.Y. Teoh, C. Selomulya, R.C. Woodward, R. Amal, and B. Rosche, Flame-Sprayed Superparamagnetic Bare and Silica-Coated Maghemite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Protein Adsorption-Desorption, Chem. Mater., 2006, 18(26), p 6403-6413
S. Kluge, L. Deng, O. Feroughi, F. Schneider, M. Poliak, A. Fomin, V. Tsionsky, S. Cheskis, I. Wlokas, I. Rahinov, T. Dreier, A. Kempf, H. Wiggers, and C. Schulz, Initial Reaction Steps during Flame Synthesis of Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles, CrystEngComm, 2015, 17(36), p 6930-6939. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CE00456J
W.Y. Teoh, R. Amal, and L. Mädler, Flame Spray Pyrolysis: An Enabling Technology for Nanoparticles Design and Fabrication, Nanoscale, 2010, 2(8), p 1324-1347
R. Koirala, S.E. Pratsinis, and A. Baiker, Synthesis of Catalytic Materials in Flames: Opportunities and Challenges, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(11), p 3053-3068. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cs00011d
J.D. Judy, J.M. Unrine, W. Rao, S. Wirick, and P.M. Bertsch, Bioavailability of Gold Nanomaterials to Plants: Importance of Particle Size and Surface Coating, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46(15), p 8467-8474
R. Jossen, S.E. Pratsinis, W.J. Stark, and L. Mädler, Criteria for Flame-Spray Synthesis of Hollow, Shell-like, or Inhomogeneous Oxides, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2005, 88(6), p 1388-1393
R. Strobel and S.E. Pratsinis, Flame Aerosol Synthesis of Smart Nanostructured Materials, J. Mater. Chem., 2007, 17(45), p 4743-4756
K. Buyukhatipoglu and A. Morss Clyne, Controlled Flame Synthesis of ΑFe2O3 and Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Effect of Flame Configuration, Flame Temperature, and Additive Loading, J. Nanoparticle Res., 2010, 12(4), p 1495-1508
P.M. Rao and X. Zheng, Rapid Catalyst-Free Flame Synthesis of Dense, Aligned α-Fe 2O 3 Nanoflake and CuO Nanoneedle Arrays, Nano Lett., 2009, 9(8), p 3001-3006
D. Li, W.Y. Teoh, C. Selomulya, R.C. Woodward, P. Munroe, and R. Amal, Insight into Microstructural and Magnetic Properties of Flame-Made γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles, J. Mater. Chem., 2007, 17(46), p 4876. https://doi.org/10.1039/b711705a
R. Strobel and S.E. Pratsinis, Direct Synthesis of Maghemite, Magnetite and Wustite Nanoparticles by Flame Spray Pyrolysis, Adv. Powder Technol., 2009, 20(2), p 190-194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2008.08.002
R. Mueller, L. Mädler, and S.E. Pratsinis, Nanoparticle Synthesis at High Production Rates by Flame Spray Pyrolysis, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2003, 58(10), p 1969-1976
A.K. Gupta and M. Gupta, Synthesis and Surface Engineering of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications, Biomaterials, 2005, 26(18), p 3995-4021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.10.012
G. Cotin, S. Piant, D. Mertz, D. Felder-Flesch, and S. Begin-Colin, Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: Synthesis, Functionalization, and Application, Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-101925-2.00002-4
M. Mahmoudi, S. Sant, B. Wang, S. Laurent, and T. Sen, Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (SPIONs): Development, Surface Modification and Applications in Chemotherapy, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2011, 63(1-2), p 24-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2010.05.006
S. Nizamuddin, M.T.. Siddiqui, N.M. Mubarak, H.A. Baloch, E.C. Abdullah, S.A. Mazari, G.J. Griffin, M.P. Srinivasan, and A. Tanksale, Iron Oxide Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metals and Dyes From Wastewater, Nanoscale Mater. Water Purif., 2018 (November), p 447-472.
L.S. Zhong, J.S. Hu, H.P. Liang, A.M. Cao, W.G. Song, and L.J. Wan, Self-Assembled 3D Flowerlike Iron Oxide Nanostructures and Their Application in Water Treatment, Adv. Mater., 2006, 18(18), p 2426-2431
J. Hu, G. Chen, and I.M.C. Lo, Removal and Recovery of Cr(VI) from Wastewater by Maghemite Nanoparticles, Water Res., 2005, 39(18), p 4528-4536
V. Chandra, J. Park, Y. Chun, J.W. Lee, I.C. Hwang, and K.S. Kim, Water-Dispersible Magnetite-Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites for Arsenic Removal, ACS Nano, 2010, 4(7), p 3979-3986
S. Dixit and J.G. Hering, Comparison of Arsenic(V) and Arsenic(III) Sorption onto Iron Oxide Minerals: Implications for Arsenic Mobility, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2003, 37(18), p 4182-4189
G.L. Chiarello, I. Rossetti, L. Forni, P. Lopinto, and G. Migliavacca, Solvent Nature Effect in Preparation of Perovskites by Flame-Pyrolysis. 1. Carboxylic Acids, Appl. Catal. B Environ., 2007, 72(3-4), p 218-226
G.L. Chiarello, I. Rossetti, L. Forni, P. Lopinto, and G. Migliavacca, Solvent Nature Effect in Preparation of Perovskites by Flame Pyrolysis. 2. Alcohols and Alcohols + Propionic Acid Mixtures, Appl. Catal. B Environ., 2007, 72(3-4), p 227-232
Y.K. Kho, W.Y. Teoh, L. Mädler, and R. Amal, Dopant-Free, Polymorphic Design of TiO2 Nanocrystals by Flame Aerosol Synthesis, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2011, 66(11), p 2409-2416
L. Mädler, H.K. Kammler, R. Mueller, and S.E. Pratsinis, Controlled Synthesis of Nanostructured Particles by Flame Spray Pyrolysis, J. Aerosol Sci., 2002, 33(2), p 369-389. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-8502(01)00159-8
L. Mädler, W.J. Stark, S.E. Pratsinis, and L. Ma, Flame-Made Ceria Nanoparticles, J. Mater. Res., 2002, 17(6), p 1356-1362
L. Mädler and S.E. Pratsinis, Bismuth Oxide Nanoparticles by Flame Spray Pyrolysis, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2004, 85(7), p 1713-1718. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.2002.tb00340.x
O. Waser, R. Büchel, A. Hintennach, P. Novák, and S.E. Pratsinis, Continuous Flame Aerosol Synthesis of Carbon-Coated Nano-LiFePO4 for Li-Ion Batteries, J. Aerosol Sci., 2011, 42(10), p 657-667
S. Li, Y. Ren, P. Biswas, and S.D. Tse, Flame Aerosol Synthesis of Nanostructured Materials and Functional Devices : Processing, Modeling, and Diagnostics, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., 2016, 55, p 1-59
A.J. Gröhn, S.E. Pratsinis, A. Sánchez-Ferrer, R. Mezzenga, and K. Wegner, Scale-up of Nanoparticle Synthesis by Flame Spray Pyrolysis: The High-Temperature Particle Residence Time, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, 53(26), p 10734-10742
T. Kim, A. Sharp, and B. Guo, Effect of Synthesis Condition and Annealing on the Sensitivity and Stability of Gas Sensors Made of Zn-Doped Gamma-Fe2O3 Particles, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 2010, 27(3), p 1003-1009
W. Merchan-Merchan, A.V. Saveliev, and A.M. Taylor, High Rate Flame Synthesis of Highly Crystalline Iron Oxide Nanorods, Nanotechnology, 2008, 19(12), p 125605. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/12/125605
G.H. Evans, W.G. Houf, R. Greif, and C. Crowe, Numerical Modeling of a Solid Particle Solar Central Receiver, SANDIA Rep., 1985, (SAND85-8249 December), https://doi.org/10.2172/6315392.
M. Smith, G. Gregory, F. David, M. Michael; , E. Nigel, and G. Boris, GRI Mech 3.0,” n.d., https://doi.org/http://www.me.berkeley.edu/gri_mech/.
J. Schindelin, I. Arganda-Carreras, E. Frise, V. Kaynig, M. Longair, T. Pietzsch, S. Preibisch, C. Rueden, S. Saalfeld, B. Schmid, J.-Y. Tinevez, D.J. White, V. Hartenstein, K. Eliceiri, P. Tomancak, and A. Cardona, Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis, Nat. Methods, 2012, 9, p 676-682
A. Teleki, M.C. Heine, F. Krumeich, M.K. Akhtar, and S.E. Pratsinis, In Situ Coating of Flame-Made TiO2 Particles with Nanothin SiO2 Films, Langmuir, 2008, 24(21), p 12553-12558
GUW, Polymer Physics, Chapmann & Hall, London, 1995
R.M. Cornell and U. Schwertmann, “The Iron Oxides. Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses,” 2003.
A.M. Jubb and H.C. Allen, Vibrational Spectroscopic Characterization of Hematite, Maghemite, and Magnetite Thin Films Produced by Vapor Deposition, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2010, 2(10), p 2804-2812
O.N. Shebanova and P. Lazor, Raman Study of Magnetite (Fe3O4): Laser-Induced Thermal Effects and Oxidation, J. Raman Spectrosc., 2003, 34(11), p 845-852
D.L.A. de Faria, S. Venâncio Silva, and M.T. Oliveira, Raman Microspectroscopy of Some Iron Oxides and Oxyhydroxides, J. Raman Spectrosc., 1997, 28(11), p 873-878. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4555(199711)28:11<873::AID-JRS177>3.0.CO;2-B
L.S. Darken and R.W. Gurry, The System Iron-Oxygen. II. Equilibrium and Thermodynamics of Liquid Oxide and Other Phases, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1946, 68(5), p 798-816
Y. Li, Y. Hu, H. Jiang, and C. Li, Double-Faced γ-Fe2O3||SiO2 Nanohybrids: Flame Synthesis, in Situ Selective Modification and Highly Interfacial Activity, Nanoscale, 2013, 5(12), p 5360. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr01087b
D. Li, W.Y. Teoh, R.C. Woodward, J.D. Cashion, C. Selomulya, and R. Amal, Evolution of Morphology and Magnetic Properties in Silica/Maghemite Nanocomposites, J. Phys. Chem., 2009, 113, p 12040-12047
J. Frenkel and J. Dorfman, Spontaneous and Induced Magnetisation in Ferromagnetic Bodies, Nature, 1930, 126(3173), p 274-275
F.G. Aliev, M.A. Correa-Duarte, A. Mamedov, J.W. Ostrander, M. Giersig, L.M. Liz-Marzán, and N.A. Kotov, Layer-By-Layer Assembly of Core-Shell Magnetite Nanoparticles: Effect of Silica Coating on Interparticle Interactions and Magnetic Properties, Adv. Mater., 1999, 11(12), p 1006-1010. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-4095(199908)11:12<1006::AID-ADMA1006>3.0.CO;2-2
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge Universidad de Antioquia (CODI) for the founding (Codigo 20157828). Luisa Carvajal acknowledges COLCIENCIAS for the scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carvajal, L., Buitrago-Sierra, R., Santamaría, A. et al. Effect of Spray Parameters in a Spray Flame Reactor During FexOy Nanoparticles Synthesis. J Therm Spray Tech 29, 368–383 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-020-00991-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-020-00991-1