Abstract
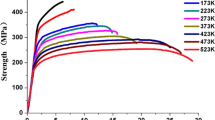
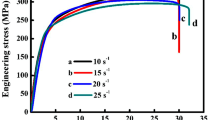
The effect of strain rate on the microstructure and deformation mechanism of a Mg–Y–Nd–Zr alloy was studied. The microstructure and texture were examined by optical microscopy and electron backscatter diffraction, and the dislocation structures were observed by transmission electron microscopy. The results showed that the Mg–Y–Nd–Zr alloy exhibited positive strain rate sensitivity under high-strain-rate compression. At a strain rate of 830 s−1, many grains were re-oriented owing to the formation of a large number of tensile twins in the specimen. With increasing strain rate, the number of extension twins decreased, but those of contraction twins, double twins, and < c + a > dislocations increased. The dominant deformation mechanism of the material changed from extension twin-dominated deformation to extension twin- and < c + a > slip-dominated deformation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Dwain and A. Magers, Global Review of Magnesium Parts in Automobiles, Light Metal Age, 1996, 54(9), p 60–63.
Z. Wu and W.A. Curtin, The Origins of High Hardening and Low Ductility in Magnesium, Nature, 2015, 526(7571), p 62.
K.T. Ramesh and R.S. Coates, Microstructural Influences on the Dynamic Response of Tungsten Heavy Alloys, Med. Clin., 1992, 84(14), p 549–553.
M. Easton, A. Beer, M. Barnett, C. Davies, G. Dunlop, Y. Durandet, S. Blacket, T. Hilditch , and P. Beggs, Magnesium Alloy Applications in Automotive Structures, Jom, 2008, 60(11), p 57–62.
Q. Li, Mechanical Properties and Microscopic Deformation Mechanism of Polycrystalline Magnesium Under High-Strain-Rate Compressive Loadings, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 540(Apr.1), p 130–134.
B. Hutchinson, M.R. Barnett, A. Ghaderi, P. Cizek , and I. Sabirov, Deformation Modes and Anisotropy in Magnesium Alloy AZ31, Int. J. Mater. Res., 2009, 100(4), p 556–563.
S. You, Y. Huang, K.U. Kainer , and N. Hort, Recent Research and Developments on Wrought Magnesium Alloys, J. Magn. Alloy., 2017, 5(3), p 239–253.
E.W. Kelley and J.W.F. Hosford, The Deformation Characteristics of Textured Magnesium, Trans. Metall. Soc. Aime, 1968, 242, p 654–660.
G.Y. Chin and W.L. Mammel, Competition Among Basal, prism, and Pyramidal Slip Modes in HCP Metals, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1970, 1(2), p 357–361.
M.R. Barnett, Z. Keshavarz, A.G. Beer , and D. Atwell, Influence of Grain Size on Compressive Deformation of Wrought Mg-3Al-1Zn, Acta. Mater., Acta. Materialia, 2004, 52(17), p 5093–5103.
T. Xu, Y. Yang, X. Peng, J. Song , and F. Pan, Overview of Advancement and Development Trend on Magnesium Alloy, J. Magn. Alloys, 2019, 7(3), p 536–544.
A. Akhtar and E. Teghtsoonian, Solid Solution Strengthening of Magnesium Single Crystals—ii the Effect of Solute on the Ease of Prismatic Slip, Acta Metall., 1969, 17(11), p 1351–1356.
M.R. Barnett, Twinning and the Ductility of Magnesium Alloys: Part I: “Tension” Twins, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 464(1–2), p 1–7.
M.R. Barnett, Twinning and the Ductility of Magnesium Alloys: Part II “Contraction” Twins, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 464(1–2), p 8–16.
H. Yoshinaga and R. Horiuchi, Deformation Mechanisms in Magnesium Single Crystals Compressed in the Direction Parallel to Hexagonal Axis, Mater. Trans., JIM, 1963, 4(1), p 1–8.
H. Yoshinaga and R. Horiuchi, On the Nonbasal Slip in Magnesium Crystals, Trans. Japan Instit. Metals, 1964, 5(1), p 14–21.
E.W. Kelley and W.F. Hosford, Plane-Strain Compression of Magnesium and Magnesium Alloy Crystals, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME., 1986, 242(1), p 5–13.
S.R. Agnew, J.A. Horton , and M.H. Yoo, Transmission Electron Microscopy Investigation of <c+a> Dislocations in Mg and α-solid Solution Mg-Li Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, 33(3), p 851–858.
O. Muransky, D.G. Carr, M.R. Barnett, E.C. Oliver , and P. Sittner, Investigation of Deformation Mechanisms Involved in the Plasticity of AZ31 Mg alloy: In situ Neutron Diffraction and EPSC Modelling, Mater. Ence Eng. A, 2008, 496(1–2), p 14–24.
A.S. Khan, A. Pandey, T. GnäUpel-Herold , and R.K. Mishra, Mechanical Response and Texture Evolution of AZ31 Alloy at Large Strains for Different Strain Rates and Temperatures, Int. J. Plasticity, 2011, 27(5), p 688–706.
H. Asgari, A.G. Odeshi , and J.A. Szpunar, On Dynamic Deformation Behavior of WE43 Magnesium Alloy Sheet Under Shock Loading Conditions, Mater. Design, 2014, 63(Nov), p 552–564.
K.A. Dannemann, V.B. Chalivendra , and B. Song, Dynamic Behavior of Materials, Exp. Mech., 2012, 52(2), p 117–118.
N. Dixit, K.Y. Xie, K.J. Hemker , and K.T. Ramesh, Microstructural Evolution of Pure Magnesium Under High Strain Rate Loading, Acta Mater., 2015, 87, p 56–67.
N.V. Dudamell, I. Ulacia, F. Gálvez, S. Yi , and M.T. Pérez-Prado, Twinning and Grain Subdivision During Dynamic Deformation of a Mg AZ31 Sheet Alloy at Room Temperature, Acta Mater., 2011, 59(18), p 6949–6962.
L. Li, O. Muránsky, E.A. Flores-Johnson, S. Kabra, L. Shen , and Gl. Proust, Effects of Strain Rate on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Response of Magnesium Alloy AZ31, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.12.015
C. Linbo, L. Wei, S. Yidan , and L. Mei, Effect of Microstructure Evolution on the Mechanical Properties of a Mg–Y–Nd–Zr Alloy with a Gradient Nanostructure Produced via Ultrasonic Surface Rolling Processing, J. Alloy Compd., 2022, 923, p 166495.
W. Tang, Z. Liu, S. Liu, L. Zhou, P. Mao, H. Guo , and X. Sheng, Deformation Mechanism of Fine Grained Mg–7Gd–5Y–1.2Nd–0.5Zr Alloy Under High Temperature and High Strain Rates, J. Magn. Alloys, 2020, 8(4), p 1144–1153.
Y. Tan, W. Li, W. Hu, X. Shi , and L. Tian, The Effect of ECAP Temperature on the Microstructure 18 and Properties of a Rolled Rare Earth Magnesium Alloy, Materials, 2019, 12, p 1554.
L. Aiwen, L. Wei, L. Mei, Y. Hongmin, S. Yidan , and L. Yilong, Effect of Grain Size on the Microstructure and Deformation Mechanism of Mg-2Y-0.6Nd-0.6Zr Alloy at a High Strain Rate, J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 824, p 141774.
W.G. Feather et al., Mechanical Response, twinning, and Texture Evolution of WE43 Magnesium-Rare Earth Alloy as a Function of Strain Rate: Experiments and Multi-level Crystal Plasticity Modeling, Int. J. Plast, 2019, 120, p 180–204.
N. Dixit et al., Microstructural Evolution of Pure Magnesium Under High Strain Rate Loading, Acta Mater., 2015, 87, p 56–67.
J. Koike, Enhanced Deformation Mechanisms by Anisotropic Plasticity in Polycrystalline Mg Alloys at Room Temperature, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36(7), p 1689–1696.
N.S. Barnett, Effect of Composition on the Texture and Deformation Behaviour of Wrought Mg Alloys, Scripta Materialia, 2008, 58(3), p 179–182.
B.Q. Shi, R.S. Chen , and W. Ke, Effects of Yttrium and Zinc on the Texture, Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Hot-Rolled Magnesium Plates, Mater. Sci. Eng: A, 2013, 560(JAN10), p 62–70.
S.G. Hong, S.H. Park , and S.L. Chong, Role of 10–12 Twinning Characteristics in the Deformation Behavior of a Polycrystalline Magnesium Alloy, Acta. Mater., 2010, 58(18), p 5873–5885.
P.R. Okamoto and G. Thomas, On the Four-axis Hexagonal Reciprocal Lattice and its use in the Indexing of Transmission Electron Diffraction Patterns, Phys. Status. Solidi., 2010, 25(1), p 81–91.
S.S. Bes, M. Friák, S. Zaefferer, A. Dick , and D. Raabe, The Relation Between Ductility and Stacking Fault Energies in Mg and Mg-Y Alloys, Acta Mater., 2012, 60, p 3011–3021.
R. Korla and A.H. Chokshi, Strain-Rate Sensitivity and Microstructural Evolution in a Mg–Al–Zn Alloy, Scripta Mater., 2010, 63(9), p 913–916.
M.R. Barnett, Z.K.P.D. Student , and X. Ma, A Semianalytical Sachs Model for the Flow Stress of a Magnesium Alloy, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, 37(7), p 2283–2293.
J. Lan, J.J. Jonas, A.A. Luo, A.K. Sachdev , and S. Godet, Influence of 10–12 Extension Twinning on the Flow Behavior of AZ31 Mg Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 445–446, p 302–309.
Y.N. Wang and J.C. Huang, The Role of Twinning and Untwinning in Yielding Behavior in Hot-Extruded Mg–Al–Zn Alloy, Acta Mater., 2007, 55(3), p 897–905.
B.-Y. Liu, F. Liu, N. Yang, X.-B. Zhai, L. Zhang, Y. Yang, B. Li, J. Li, E. Ma , and J.-F. Nie, Large Plasticity in Magnesium Mediated by Pyramidal Dislocations, Science, 2019, 365(6448), p 73–75.
X. Wang, L. Jiang, A. Luo, J. Song, Z. Liu, F. Yin, Q. Han, S. Yue , and J.J. Jonas, Deformation of Twins in a Magnesium Alloy Under Tension at Room Temperature, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 594, p 44–47.
P. Mao, L. Zheng , and C. Wang, Texture Effect on High Strain Rates Tension and Compression Deformation Behavior of Extruded AM30 Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 539(Mar30), p 13–21.
S. Xu, T. Liu, H. Chen, Z. Miao, Z. Zhang , and W. Zeng, Reducing the Tension–Compression Yield Asymmetry in a Hot-Rolled Mg–3Al–1Zn Alloy via Multidirectional Pre-Compression, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 565, p 96–101.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51661007), Guizhou University cultivation project [2019] 15, central government guide local science and technology development special projects [2019] 4011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GD Writing – original draft. AL Investigation. WL Writing – review & editing, Supervision. GC Software. YL Visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, G., Li, A., Li, W. et al. Deformation Mechanism and Microstructural Evolution of a Mg–Y–Nd–Zr Alloy under High Strain Rate at Room Temperature. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 33, 3101–3114 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08192-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08192-x