Abstract
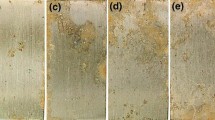
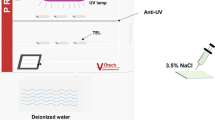
In this study, the influence of different ultraviolet (UV) radiation intensities on the corrosion behavior of 316 stainless steel (316 SS) was investigated using an accelerated test method for simulated salt-lake atmospheric corrosion. The corroded specimens were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM), x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), white light interferometry (WLI), and in situ electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The UV radiation restrained the corrosion rate of 316 SS, wherein the influence of UV inhibition initially increased and then decreased when the intensity of UV radiation was increased from 0.25 to 2 mw/cm2. The strongest inhibition effect was observed for the UV radiation intensity of 0.5 mw/cm2. The inhibition effect on the corrosion rate of 316 SS exposed to UV radiation was related to the protection ability of corrosion products. The protection ability of corrosion products improved with an increase in the ratio of [Cr]/{[Cr] + [Fe]}. The maximum pit depth and pit density formed on 316 SS initially exhibited a gradual decrease and then an increase in the UV radiation intensity in the range 0.25-2 mw/cm2.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.B. Blucher, J.E. Svensson, L.G. Johansson et al., The NaCl-Induced Atmospheric Corrosion of Aluminum - The Influence of Carbon Dioxide and Temperature, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, 150(3), p B93–B98.
C.G. Soares, Y. Garbatov, A. Zayed et al., Influence of Environmental Factors on Corrosion of Ship Structures in Marine Atmosphere, Corros. Sci., 2009, 51(9), p 2014–2026.
C. Qiao, M.N. Wang, L. Hao et al., Temperature and NaCl Deposition Dependent Corrosion of SAC305 Solder Alloy in Simulated Marine Atmosphere, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2021, 75, p 252–264.
F. Mansfeld and J.V. Kenkel, Electrochemical Measurements of Time-of-Wetness and Atmospheric Corrosion Rates, Corrosion, 2013, 33(1), p 13–16.
C.L. Li, Y.T. Ma, Y. Li et al., EIS Monitoring Study of Atmospheric Corrosion Under Variable Relative Humidity, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52(1), p 3677–3686.
A.P. Yadav, A. Nishikata and T. Tsuru, Electrochemical Impedance Study on Galvanized Steel Corrosion Under Cyclic Wet-Dry Conditions-Influence of Time of Wetness, Corros. Sci., 2004, 46(1), p 169–181.
E. Schindelholz, R.G. Kelly, I.S. Cole et al., Comparability and Accuracy of Time of Wetness Sensing Methods Relevant for Atmospheric Corrosion, Corros. Sci., 2013, 67, p 233–241.
M. Mouanga and P. Bercot, Comparison of Corrosion Behaviour of Zinc in NaCl and in NaOH Solutions; Part II: Electrochemical Analyses, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52(12), p 3993–4000.
M. Mouanga, P. Bercot and J.Y. Rauch, Comparison of Corrosion Behaviour of Zinc in NaCl and in NaOH Solutions. Part I: Corrosion Layer Characterization, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52(12), p 3984–3992.
J.B. Zhang, J. Wang and Y.H. Wang, The Deliquescence and Spreading of Sea Salt Particles on Carbon Steel and Atmos Pheric Corrosion, Mar. Sci., 2005, 29(7), p 17–19.
L.Y. Song and Z.Y. Chen, The Role of UV Illumination on the NaCl-Induced Atmospheric Corrosion of Q235 Carbon Steel, Corros. Sci., 2014, 86, p 318–325.
E.A. Thompson and T.D. Burleigh, Accelerated Corrosion of Zinc Alloys Exposed to Ultraviolet Light, Corros. Eng. Sci. Techn., 2007, 42(3), p 237–241.
Y.W. Liu, J. Zhang, Y.H. Wei et al., Effect of Different UV Intensity on Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel Exposed to Simulated Nansha Atmospheric Environment, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2009, 237, p 121855.
C.B. Breslin, D.D. Macdonald, J. Sikora et al., Influence of UV Light on the Passive Behaviour of SS316 - Effect of Prior Illumination, Electrochim. Acta, 1997, 42(1), p 127–136.
S.O. Moussa and M.G. Hocking, The Photo-Inhibition of Localized Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel in Sodium Chloride Environment, Corros. Sci., 2001, 43(11), p 2037–2047.
M.X. Guo, Q. Yin, M.R. Liu et al., Corrosion Behavior of 304 Stainless Steel Exposed to a Simulated Salt Lake Atmosphere, Acta. Metall. (Sin.-Engl.), 2020, 33(6), p 857–870.
T. Shinohara, S. Motoda and W. Oshikawa, Evaluation of Corrosivity in Atmospheric Environment by ACM (Atmospheric Corrosion Monitor) Type Corrosion Sensor, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, 475, p 61–64.
D. To, T. Shinohara, O. Umezawa et al., Experimental Investigation on the Corrosivity of Atmosphere through the Atmospheric Corrosion Monitoring (ACM) Sensors, Electrochem. Soc., 2017, 75(29), p 1–10.
D. Mizuno, S. Suzuki, S. Fujita et al., Corrosion Monitoring and Materials Selection for Automotive Environments by Using Atmospheric Corrosion Monitor (ACM) Sensor, Corros. Sci., 2014, 83, p 217–225.
A.K. Neufeld, I.S. Cole, A.M. Bond et al., The Initiation Mechanism of Corrosion of Zinc by Sodium Chloride Particle Deposition, Corros. Sci., 2002, 44(3), p 555–572.
C. Pan, W.Y. Ly, Z.Y. Wang et al., Atmospheric Corrosion of Copper Exposed in a Simulated Coastal-Industrial Atmosphere, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2017, 33(6), p 587–595.
A. Nishikata, Y. Ichihara and T. Tsuru, An Application of Electorchemical Impedance Spectroscopy to Atmospheric Corrosion Study, Corros. Sci., 1995, 37(6), p 897–911.
X.N. Liao, F.H. Cao, A.N. Chen et al., In-Situ Investigation of Atmospheric Corrosion Behavior of Bronze Under Thin Electrolyte Layers Using Electrochemical Technique, T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 2012, 22(5), p 1239–1249.
C. Qiao, X. Sun, Y.Z. Wang et al., A Perspective on Effect by Ag Addition to Corrosion Evolution of Pb-Free Sn Solder, Mater. Lett., 2021, 297, p 129935.
W. Lv, C. Pan, W. Su, Z. Wang et al., Atmospheric Corrosion Mechanism of 316 Stainless Steel in Simulated Marine Atmosphere, Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol., 2016, 51(3), p 155–162.
D. Kong, X. Ni, C. Dong et al., Bio-Functional and Anti-Corrosive 3D Printing 316L Stainless Steel Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting, Mater. Des., 2018, 152, p 88–101.
R.-H. Jung, H. Tsuchiya and S. Fujimoto, Growth Process of Passive Films on Austenitic Stainless Steels under Wet-dry Cyclic Condition, ISIJ Int., 2012, 52(7), p 1356–1361.
T. Ishitsuka and K. Nose, Stability of Protective Oxide Films in Waste Incineration Environment - Solubility Measurement of Oxides in Molten Chlorides, Corros. Sci., 2002, 44(2), p 247–263.
K. Asami and K. Hashimoto, Importance of Initial Surface Film in the Degradation of Stainless Steels by Atmospheric Exposure, Corros. Sci., 2003, 45(10), p 2263–2283.
Z.X. Li, L.M. Zhang, A.L. Ma et al., Comparative Study on the Cavitation Erosion Behavior of Two Different Rolling Surfaces on 304 Stainless Steel, Tribol. Int., 2021, 159, p 106994.
S. Fujimoto, T. Yamada and T. Shibata, Improvement of Pitting Corrosion Resistance of Type 304 Stainless Steel by Modification of Passive Film with Ultraviolet Light Irradiation, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1998, 145(5), p L79–L81.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Prof. Zhuoyuan Chen of Foshan University for his scientific comments on this paper. The investigation is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51671197) and Liaoning Shenyang Soil and Atmosphere Corrosion of Material National Observation and Research Station.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, M., Feng, H., Tariq, N.u.H. et al. Influence of Different Ultraviolet Radiation Intensities on the Corrosion Behavior of Type 316 Stainless Steel in a Simulated Salt-Lake Atmospheric Environment. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 4375–4384 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06527-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06527-0