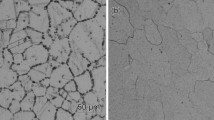
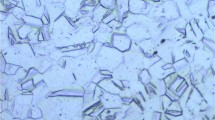
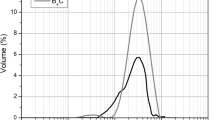
Abstract
It’s well known that wear can accelerate degeneration of materials in corrosive media. Less attention has been paid to effects of different cathodic reactions on tribocorrosion behaviors. In this study, linear reciprocating sliding wear test of AISI 430 was carried out in distilled water and 0.5 mol/L sulfuric acid media, respectively. The results revealed that oxygen reduction reaction is in favor of oxide films forming on the surface, which increased subsurface hardness of the wear track. However, hydrogen evolution reaction restrained the formation of oxide films and induced hydrogen embrittlement, thus worsened the tribocorrosion properties and increased material removal. Interaction between wear and corrosion contributed most mass loss in the material deterioration, which was related to the reciprocating frequency.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Kajdas, E. Wilusz and S. Harvey, Encyclopedia of Tribology, Elsevier, 1990.
B. Hou, X. Li, X. Ma, C. Du, D. Zhang, M. Zheng, W. Xu, D. Lu and F. Ma, The Cost of Corrosion in China, npj Mater. Degrad., 2017, 1(1), p 1–10.
K. Holmberg, P. Andersson and A. Erdemir, Global Energy Consumption Due to Friction in Passenger Cars, Tribol. Int., 2012, 47, p 221–234. (in English)
Y. Sun and V. Rana, Tribocorrosion Behaviour of AISI 304 Stainless Steel in 0.5 M NaCl Solution, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 129(1–2), p 138–147. (in English)
A.C. Vieira, L.A. Rocha, N. Papageorgiou and S. Mischler, Mechanical and Electrochemical Deterioration Mechanisms in the Tribocorrosion of Al Alloys in NaCl and in NaNO3 Solutions, Corros. Sci., 2012, 54, p 26–35. (in English)
M. Azzi and J.A. Szpunar, Tribo-Electrochemical Technique for Studying Tribocorrosion Behavior of Biomaterials, Biomol. Eng., 2007, 24(5), p 443–446. (in English)
X. Jiang, S. Li and S. Li, Corrosive Wear of Metals, Chemistry Industry Press, Beijing, 2003.
R.A. Lula, Stainless Steel, American Society for Metals, 1986.
G. Tammann, The Chemical and Galvanic Characteristics of Compound Crystals and their Atomic Distribution: An Article on the Understanding of Alloying, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 1919, 107(1/3), p 1–239. (in German)
H. Fischmeister and U. Roll, Passive Layers on Stainless-Steels: A Survey of Surface-Analysis Results, Fresenius Zeitschrift Fur Analytische Chemie, 1984, 319(6–7), p 639–645. (in German)
J. Beddoes and J.G. Parr, Introduction to Stainless Steels, ASM International, 1999.
T. Hong, T. Ogushi and M. Nagumo, Effect of Chromium Enrichment in the Film Formed By Surface Treatments on the Corrosion Resistance of Type 430 Stainless Steel, Corros. Sci., 1996, 38(6), p 881–888. (in English)
I. Sekine, S. Hatakeyama and Y. Nakazawa, Corrosion Behavior of Type-430 Stainless-Steel in Formic and Acetic-Acids, Corros. Sci., 1987, 27(3), p 275–288. (in English)
R. Nishimura, D. Shiraishi and Y. Maeda, Hydrogen Permeation and Corrosion Behavior of High Strength Steel MCM 430 in Cyclic Wet-Dry SO2 Environment, Corros. Sci., 2004, 46(1), p 225–243. (in English)
S. Hastuty, A. Nishikata and T. Tsuru, Pitting Corrosion of Type 430 Stainless Steel under Chloride Solution Droplet, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52(6), p 2035–2043. (in English)
R.M. Fisher, E.J. Dulis and K.G. Carroll, Identification of the Precipitate Accompanying 885-Degrees-F Embrittlement in Chromium Steels, Trans. Am. Inst. Mining Metall. Eng., 1953, 197(5), p 690–695. (in English)
M.J. Blackburn and J. Nutting, Metallography of Iron-21 Per Cent Chromium Alloy Subjected to 457 Degrees C Embrittlement, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1964, 202(7), p 610–613. (in English)
M. Liu, D.L. Duan, S.L. Jiang, M.Y. Li and S. Li, Tribocorrosion Behavior of 304 Stainless Steel in 0.5 mol/L Sulfuric Acid, Acta Metall, Sin.-Engl. Lett., 2018, 31(10), p 1049–1058. (in English)
C. Wagner and W.E. Traud, The Analysis of Corrosion Procedures through the Interaction of Electrochemical Partial Procedures and on the Potential Difference of Mixed Electrodes, Z. Elektrochem. Angew. Phys. Chem., 1938, 44, p 391–402. (in German)
Y.X. Qiao, Y.G. Zheng, P.C. Okafor and W. Ke, Electrochemical Behaviour of High nitrogen Bearing stainless Steel in Acidic Chloride Solution: Effects of Oxygen, Acid Concentration and Surface Roughness, Electrochim. Acta, 2009, 54(8), p 2298–2304. (in English)
L. Bjornkvist and I. Olefjord, The Electrochemistry of Chromium in Acidic Chloride Solutions: Anodic-Dissolution and Passivation, Corros. Sci., 1991, 32(2), p 231–242.
R. Iler, The Chemistry of Silica, Wiley, New York, 1979.
N. Liu, J.Z. Wang, B.B. Chen and F.Y. Yan, Tribochemical Aspects of Silicon Nitride Ceramic Sliding Against Stainless Steel under the Lubrication of Seawater, Tribol. Int., 2013, 61, p 205–213. (in English)
J.R. Jiang and M.M. Stack, Modelling Sliding Wear: From Dry to Wet Environments, Wear, 2006, 261(9), p 954–965. (in English)
J. Jiang, M.M. Stack and A. Neville, Modelling the Tribo-Corrosion Interaction in Aqueous Sliding Conditions, Tribol. Int., 2002, 35(10), p 669–679. (in English)
S. Zor, M. Soncu and L. Capana, Corrosion Behavior of G-X CrNiMoNb 18–10 Austenitic Stainless Steel in Acidic Solutions, J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, 480(2), p 885–888. (in English)
J. Perret, E. Boehm-Courjault, M. Cantoni, S. Mischler, A. Beaudouin, W. Chitty and J.P. Vernot, EBSD, SEM and FIB Characterisation of Subsurface Deformation During Tribocorrosion of Stainless Steel in Sulphuric Acid, Wear, 2010, 269(5–6), p 383–393. (in English)
W. Schumacher, Corrosive Wear Synergy of Alloy and Stainless Steel, Wear Mater., 1985, 1985, p 558–566.
T.C. Zhang, X.X. Jiang, S.Z. Li and X.C. Lu, A Quantitative Estimation of the Synergy Between Corrosion and Abrasion, Corros. Sci., 1994, 36(12), p 1953–1962. (in English)
H. Abdelkader and S.M. Elraghy, Wear-Corrosion Mechanism of Stainless-Steel in Chloride Media, Corros. Sci., 1986, 26(8), p 647–653. (in English)
S.M. Elraghy, H. Abdelkader and M.E. Abouelhassan, Electrochemistry of Abrasion Corrosion of Low-Alloy Steel in 1-Percent Nacl Solution, Corrosion, 1984, 40(2), p 60–61. (in English)
W.J. Tomlinson and M.G. Talks, Erosion and Corrosion of Cast-Iron under Cavitation Conditions, Tribol. Int., 1991, 24(2), p 67–75. (in English)
U.K. Viswanathan, G.K. Dey and M.K. Asundi, Precipitation Hardening in 350-Grade Maraging-Steel, Metall. Trans. Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 1993, 24(11), p 2429–2442. (in English)
S.W. Ooi, P. Hill, M. Rawson and H. Bhadeshia, Effect of Retained Austenite and High Temperature Laves Phase on the Work Hardening of an Experimental Maraging Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process., 2013, 564, p 485–492. (in English)
V. Olden, C. Thaulow and R. Johnsen, Modelling of Hydrogen Diffusion and Hydrogen Induced Cracking in Supermartensitic and Duplex Stainless Steels, Mater. Des., 2008, 29(10), p 1934–1948. (in English)
R.G. Davies, Hydrogen Embrittlement of Dual-Phase Steels, Metall. Trans. Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 1981, 12(9), p 1667–1672. (in English)
A.W. Thompson and J.A. Brooks, Hydrogen Performance of Precipitation-Strengthened Stainless-Steels Based on a-286, Metall. Trans. Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 1975, 6(7), p 1431–1442. (in English)
T. Neeraj, R. Srinivasan and J. Li, Hydrogen Embrittlement of Ferritic Steels: Observations On Deformation Microstructure, Nanoscale Dimples and Failure by Nanovoiding, Acta Mater., 2012, 60(13–14), p 5160–5171. (in English)
M.L. Holzworth, Hydrogen Embrittlement of Type 304L Stainless Steel, Corrosion, 1969, 25(3), p 107–115. (in English)
A.J. Ardell, Precipitation Hardening, Metall. Trans. Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 1985, 16(12), p 2131–2165. (in English)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Z., Liu, M., Jiang, S. et al. Effects of Different Cathodic Reactions on Tribocorrosion Behavior of AISI 430 in 0.5 mol/L Sulfuric Acid. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 2708–2714 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06342-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06342-7